2008 Chevy Colorado Fuse Box Diagram
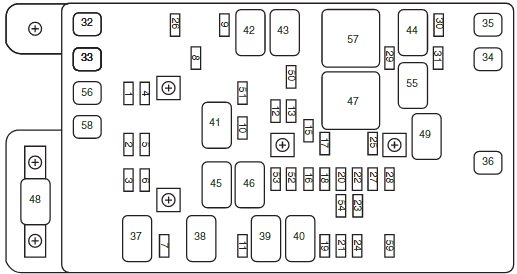
The 2008 Chevy Colorado, a popular mid-size pickup, relies on a complex electrical system to function. Understanding the fuse box diagram is crucial for anyone looking to perform repairs, diagnose electrical issues, or even add aftermarket accessories. This article provides an in-depth look at the 2008 Colorado fuse box, offering a guide to its components, symbols, and practical applications.
Purpose: Why Understand the Fuse Box Diagram?
Why bother diving into the intricacies of a fuse box? The answer is simple: it empowers you to diagnose and fix electrical problems yourself, saving time and money. Here's a breakdown of the key reasons:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Issues: When a component like a headlight, power window, or radio stops working, the first place to check is often the fuse box. A blown fuse is a common culprit. The diagram helps you locate the correct fuse for that component.
- Performing Repairs: Replacing a faulty fuse is a straightforward repair, but only if you know which one to replace. The diagram removes the guesswork.
- Adding Aftermarket Accessories: Installing new accessories like fog lights, a stereo system, or a trailer brake controller often requires tapping into the electrical system. The fuse box diagram helps you find suitable power sources and ensures you're adding fuses with the correct amperage to protect the circuit.
- Understanding Your Vehicle's Electrical System: Even if you don't plan on doing any repairs yourself, understanding the fuse box diagram gives you a better understanding of how your vehicle's electrical system is organized and protected.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2008 Chevy Colorado actually has *two* fuse box locations:
- Underhood Fuse Box: Located in the engine compartment, typically on the driver's side. This box houses fuses and relays for high-current components like the starter, alternator, headlights, and power windows.
- Instrument Panel Fuse Box: Located inside the cab, usually on the driver's side, often behind a small access panel. This box contains fuses for lower-current components like the radio, interior lights, and the cigarette lighter/accessory power outlets.
Key Components:
- Fuses: Fuses are safety devices designed to protect electrical circuits from overcurrent. They contain a thin wire or strip that melts and breaks the circuit if the current exceeds a certain level. Fuses are rated in amperes (amps or A), which indicates the amount of current they can handle.
- Relays: Relays are electromechanical switches that control high-current circuits using a low-current control signal. They allow components like headlights and the starter motor to be controlled by the vehicle's computer or switches without overloading the switches themselves.
- Circuit Breakers: Similar to fuses, circuit breakers protect circuits from overcurrent. However, instead of melting, they trip and interrupt the circuit. They can be reset manually, unlike fuses, which must be replaced. While less common in the 2008 Colorado, some high-current circuits might use them.
- Fuse Puller: A small plastic tool, often found in the fuse box, used to safely remove fuses. Using pliers or other tools can damage the fuse box or the fuses themselves.
Symbols: Lines, Colors, and Icons
Fuse box diagrams use a variety of symbols to represent different components and circuits. Understanding these symbols is essential for interpreting the diagram correctly.
- Lines: Lines represent electrical wires or circuits. Thicker lines generally indicate wires carrying higher currents.
- Colors: Wire colors are often indicated on the diagram. This is extremely helpful when tracing wires in the vehicle. Common colors include red (power), black (ground), and various other colors for specific circuits.
- Icons: Icons represent specific components. Common icons include:
- Headlight: A stylized representation of a headlight.
- Horn: A drawing of a horn.
- Radio: A depiction of a radio or stereo system.
- Power Window: A drawing of a window with an arrow indicating up or down movement.
- Cigar Lighter: An icon of a cigar lighter.
The diagram will also list the amperage rating for each fuse. This is typically displayed as a number followed by "A" (e.g., 10A, 20A, 30A). It's crucial to replace a blown fuse with one of the same amperage rating. Using a higher amperage fuse can overload the circuit and cause damage or even a fire.
How It Works: Understanding the Circuit
The electrical system in your Colorado works as a series of circuits. Each circuit provides power to a specific component or group of components. The fuse box acts as a central distribution point and protection mechanism for these circuits.
When a circuit experiences an overcurrent condition (e.g., due to a short circuit or a faulty component), the fuse in that circuit blows. This breaks the circuit and prevents further damage. The fuse is the weak link in the chain, designed to fail before more expensive components are damaged.
Relays, on the other hand, allow low-current circuits to control high-current circuits. For example, the headlight switch only carries a small amount of current to activate the headlight relay. The relay then closes a circuit that allows a much larger current to flow to the headlights themselves.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's a step-by-step guide to troubleshooting common electrical problems using the fuse box diagram:
- Identify the Problem: What component isn't working?
- Consult the Fuse Box Diagram: Locate the fuse or relay associated with the non-functional component in the relevant fuse box (underhood or instrument panel).
- Inspect the Fuse: Visually inspect the fuse. A blown fuse will typically have a broken filament inside. You can also use a multimeter to test the fuse for continuity. Set the multimeter to the continuity setting (often indicated by a diode symbol or a sound wave symbol) and touch the probes to the two terminals of the fuse. If the multimeter shows continuity (e.g., a beep or a reading of 0 ohms), the fuse is good. If there's no continuity, the fuse is blown.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Never use a fuse with a higher amperage rating.
- Test the Component: After replacing the fuse, test the component to see if it's working again.
- If the Fuse Blows Again: If the new fuse blows immediately or shortly after being replaced, there's likely a short circuit in the wiring or a faulty component. This requires further investigation and may require professional help.
Safety: Highlight Risky Components
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous. Always take the following precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative (black) terminal of the battery. This will prevent accidental short circuits and shocks.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools to avoid shocks.
- Never Bypass a Fuse: Never bypass a fuse by using a wire or other conductive material. This can overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- Be Careful Around High-Current Components: Components like the starter, alternator, and battery cables carry very high currents. Avoid touching these components while the engine is running or the ignition is on.
- If in Doubt, Seek Professional Help: If you're not comfortable working on electrical systems, seek help from a qualified mechanic.
The high-current circuits, particularly those controlled by relays in the underhood fuse box, present the greatest risk. Exercise extreme caution when working around these components.
We have a high-resolution file of the 2008 Chevy Colorado fuse box diagram available for download. This diagram will provide you with a detailed visual reference for all the fuses and relays in your vehicle. Having access to this diagram can greatly simplify troubleshooting and repair tasks. Look for the download link below.
