2008 Nissan Armada Fuse Box Diagram
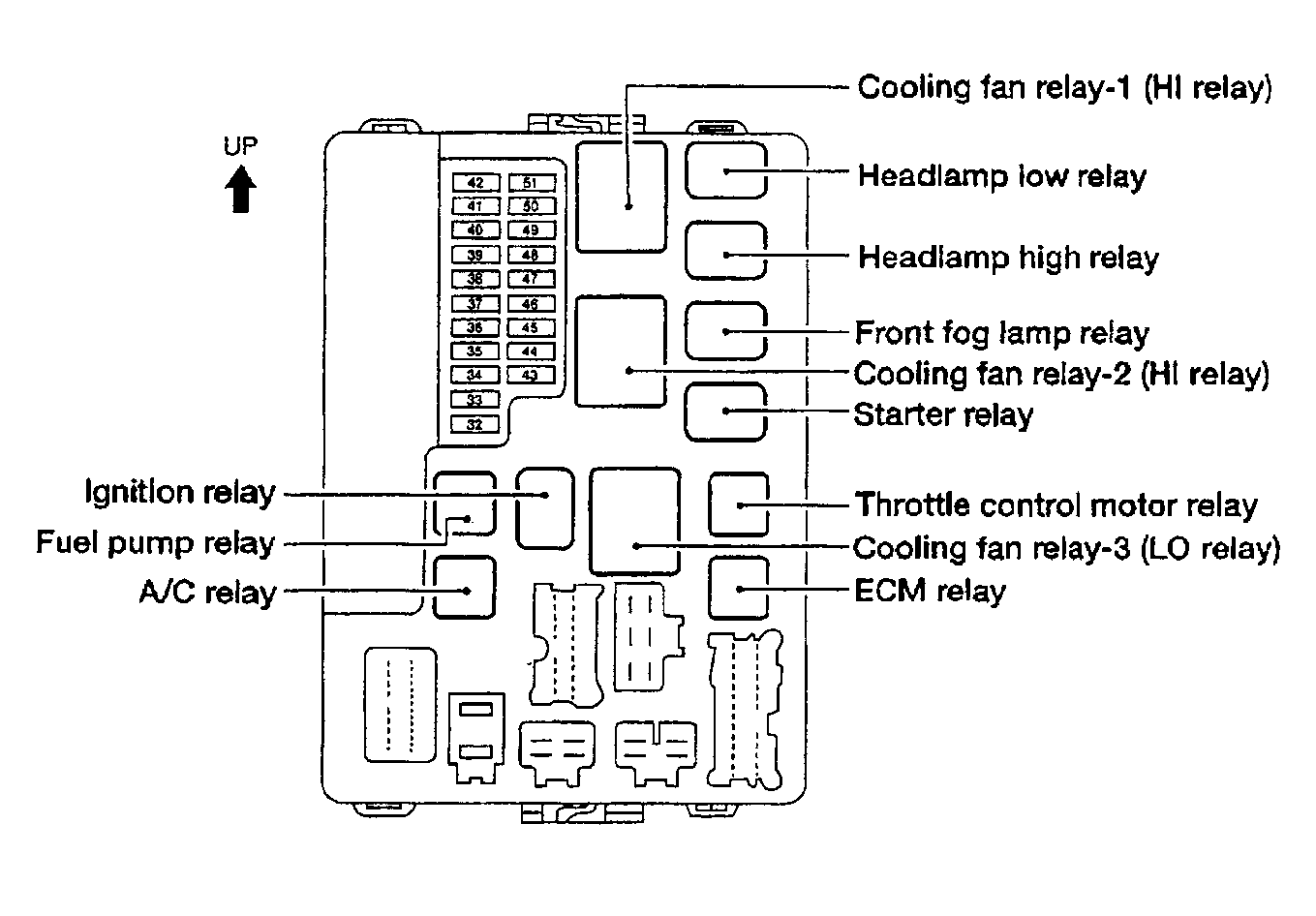
Alright, let's dive into the often-overlooked but absolutely crucial component of your 2008 Nissan Armada: the fuse box. Understanding its diagram isn't just about replacing a blown fuse; it's about empowering yourself to diagnose electrical issues, perform modifications safely, and truly understand your vehicle's intricate systems. This guide will break down the 2008 Armada's fuse box diagram in a way that's both technically accurate and easy to grasp, even if you're not a seasoned mechanic.
Purpose of Understanding the Fuse Box Diagram
Why bother learning about the fuse box diagram? Simple. It's your roadmap to the Armada's electrical system. Without it, you're troubleshooting in the dark. Specifically, having a clear understanding allows you to:
- Identify Blown Fuses Quickly: The most common reason. A malfunctioning component often blows a fuse, and the diagram tells you which one to check.
- Diagnose Electrical Problems: Understanding which circuit a fuse protects helps narrow down the source of an electrical fault.
- Perform Safe Modifications: Adding aftermarket accessories (lights, sound systems, etc.) requires tapping into the electrical system. Knowing the fuse ratings and circuit functions prevents overloading and potential fires.
- Gain a Deeper Understanding of Your Vehicle: Learning the purpose of each fuse reveals how the various systems of your Armada are interconnected.
- Save Money on Repairs: Simple fuse replacements can often be done yourself, avoiding costly trips to the mechanic.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2008 Nissan Armada typically has two main fuse box locations:
- Interior Fuse Box: Located inside the cabin, often under the dashboard on the driver's side or behind a small access panel. This fuse box generally handles circuits for interior lighting, power windows, the radio, climate control, and other cabin-related functions.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Situated in the engine bay, this box contains fuses and relays protecting engine management systems, headlights, horn, ABS, and other critical components.
Each fuse box consists of several key parts:
- Fuse Block: The physical housing that holds the fuses and relays.
- Fuses: Overcurrent protection devices that melt and break the circuit when excessive current flows through them. They are rated in amperes (amps), which indicates the maximum current they can safely handle. Common ratings include 5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, 30A, and higher.
- Relays: Electromagnetic switches that control high-current circuits using a low-current signal. They are used to switch on things like headlights, the starter motor, and other power-hungry components.
- Fuse Puller: A small plastic tool often included in the fuse box for safely removing fuses. Using pliers can damage the fuse box.
- Diagram Label: A sticker or printed card, usually inside the fuse box cover, that identifies each fuse and relay. This is what we're deciphering in this guide!
Understanding the Symbols and Layout of the Diagram
The fuse box diagram is a symbolic representation of the electrical circuits. Understanding these symbols is key to proper interpretation. Here's a breakdown of common elements:
- Lines: Represent wires or electrical conductors.
- Boxes: Usually indicate fuses or relays.
- Numbers: Correspond to the fuse or relay number in the fuse box.
- Abbreviations: Represent the protected circuit or component. For example:
- ECU: Engine Control Unit (the engine's computer)
- ABS: Anti-lock Braking System
- HTR: Heater
- ACC: Accessory
- IG: Ignition
- STOP: Brake Lights
- Amperage Rating: The number followed by "A" indicates the fuse's amperage rating (e.g., 10A, 20A). Always replace a blown fuse with one of the same amperage rating. Using a higher amperage fuse can overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- Colors (Often Implied): While the diagram itself may be black and white, the actual fuses are color-coded to indicate their amperage. This helps you quickly identify the correct fuse. For example, a red fuse is typically 10A.
The layout of the diagram usually mirrors the physical arrangement of the fuses and relays in the fuse box. This makes it easier to locate the correct fuse once you've identified it on the diagram.
How It Works: Circuit Protection
The fuse box acts as a central distribution and protection point for the Armada's electrical system. Each circuit is designed to handle a specific amount of current. When that current is exceeded – due to a short circuit, a faulty component, or an overload – the fuse blows, interrupting the circuit and preventing damage to other components or a fire. This is the fundamental principle of overcurrent protection.
Think of it like a weak link in a chain. The fuse is designed to be the weakest point, sacrificing itself to protect the rest of the circuit.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how to use the fuse box diagram for basic troubleshooting:
- Identify the Problem: What's not working? For example, the radio isn't turning on.
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse associated with the radio (it might be labeled "Radio," "Audio," or "ACC").
- Locate the Fuse: Find the fuse in the corresponding fuse box (interior or engine compartment).
- Inspect the Fuse: Visually inspect the fuse. A blown fuse will have a broken filament inside. You can also use a multimeter set to continuity to test the fuse. A good fuse will show continuity (a beep or a reading close to zero ohms).
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating.
- Test the System: Turn on the radio to see if it now works.
- If the Fuse Blows Again: This indicates a more serious problem in the circuit, such as a short circuit or a faulty component. Further diagnosis is required, and you may need to consult a professional mechanic.
Safety Considerations
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some essential safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery. This prevents accidental short circuits.
- Use the Correct Fuse: Never replace a fuse with one of a higher amperage rating. This can overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- Avoid Wet Conditions: Do not work on the electrical system in wet or damp conditions.
- Be Aware of Airbag Circuits: Some fuses protect the airbag system. Improper handling of these circuits can cause the airbags to deploy, which can be dangerous. If you're unsure, consult a professional.
Warning: The fuel injection system, ignition system, and ABS system are all high-risk components. It is highly recommended to have a professional technician handle the troubleshooting for these systems.
We have a copy of the 2008 Nissan Armada Fuse Box Diagram available for download. Having this resource readily accessible will greatly aid you in troubleshooting and maintaining your vehicle's electrical system.
