2009 Nissan Altima 2.5 Belt Diagram
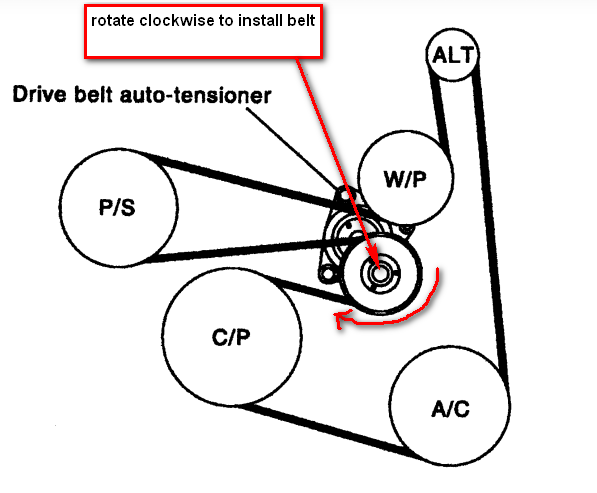
Understanding the serpentine belt routing in your 2009 Nissan Altima 2.5L is crucial for various maintenance tasks, from simple belt replacements to diagnosing more complex engine issues. A clear belt diagram provides a visual roadmap of the belt's path, ensuring you can correctly reinstall it after removing it for component service or if it happens to break. This article aims to provide you with a detailed guide to interpreting the 2009 Altima 2.5L belt diagram, empowering you to confidently tackle your automotive projects. We've got the complete file and the reader can download the diagram at the end of the article.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
The serpentine belt diagram serves several critical purposes:
- Repair Reference: The primary use is as a reference guide during belt replacement. Incorrect routing can lead to component malfunction, damage, and even engine failure.
- Component Identification: The diagram helps identify the various engine components driven by the belt, such as the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump.
- Troubleshooting Aid: Understanding the belt's path can aid in diagnosing issues like belt slippage, unusual noises, or component failure. By visually inspecting the belt and its components, you can identify potential problems.
- Preventative Maintenance: The diagram is also beneficial during routine inspections, helping you assess the belt's condition and the alignment of pulleys.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 2009 Altima 2.5L Serpentine Belt System
The 2009 Nissan Altima 2.5L engine typically utilizes a single serpentine belt to drive multiple engine accessories. Key components within the system include:
- Serpentine Belt: This is the main component, a long, winding belt made of reinforced rubber. It's designed to withstand high temperatures and constant flexing.
- Crankshaft Pulley (Harmonic Balancer): This pulley is attached to the crankshaft and is the driving force for the entire system. It absorbs engine vibrations, hence the name "harmonic balancer."
- Alternator Pulley: The alternator converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy to power the car's electrical system and charge the battery.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: The power steering pump provides hydraulic pressure to assist steering.
- Air Conditioning Compressor Pulley: The A/C compressor circulates refrigerant to cool the cabin.
- Water Pump Pulley: The water pump circulates coolant through the engine to maintain optimal operating temperature.
- Tensioner Pulley: The tensioner pulley maintains proper tension on the serpentine belt. This is crucial for preventing slippage and ensuring proper component operation. The 2009 Altima 2.5L uses a spring loaded auto tensioner.
- Idler Pulley(s): Idler pulleys provide support and guidance for the belt, helping it maintain its path and prevent excessive wear. The 2009 Altima 2.5L usually has one or more idler pulleys.
Understanding Symbols on the Diagram
Serpentine belt diagrams often use standardized symbols to represent different components and belt routing features. Here's a breakdown:
- Solid Lines: Represent the main path of the serpentine belt. The direction of the line indicates the belt's movement.
- Dashed Lines: Sometimes used to indicate the back side of the belt or a less prominent section of the routing.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of belt travel around each pulley. This is critical for ensuring proper routing.
- Component Icons: Each component is typically represented by a simplified icon. These icons are often labeled with abbreviations, such as "ALT" for alternator, "P/S" for power steering, "A/C" for air conditioning, and "W/P" for water pump.
- Tensioner Symbol: The tensioner pulley is usually depicted with a spring or a stylized representation of the tensioning mechanism. The direction of the arrow on the tensioner indicates the direction the tensioner arm moves to relieve tension on the belt.
- Pulley Grooves: Diagrams might indicate whether a pulley has grooves (for the grooved side of the belt) or is smooth (for the back side of the belt).
How It Works: The Serpentine Belt's Operation
The serpentine belt system is ingeniously simple yet essential for engine operation. The crankshaft pulley, driven directly by the engine, transfers rotational force to the serpentine belt. The belt, in turn, wraps around the pulleys of various engine accessories, transferring power to them. The tensioner pulley maintains optimal belt tension, ensuring adequate grip and preventing slippage. Slippage causes the components to not work properly and in the case of the water pump can lead to overheating and serious engine damage.
The routing of the belt is carefully designed to maximize efficiency and minimize stress on the belt and components. The belt's path often involves a combination of grooved and smooth pulleys, using the grooved side of the belt to drive grooved pulleys and the smooth side to drive smooth pulleys. The idler pulleys ensure the belt maintains its proper path, even around tight corners or between components with different pulley sizes.
Real-World Use and Basic Troubleshooting
Knowing the belt diagram is very helpful when diagnosing a problem. Here are some tips:
- Belt Replacement: Always consult the diagram before removing the old belt and follow it carefully when installing the new one. Take a picture of the old belt on your phone before removing it, as this can save you a lot of time if you get confused later.
- Squealing Noise: A squealing noise, especially when the engine is cold or under load (e.g., turning the steering wheel), often indicates a slipping belt. Check the belt tension and condition. The tensioner could be bad and require replacement.
- Component Failure: If an accessory, like the alternator or power steering pump, stops working, inspect the belt for damage or breakage. If the belt is intact, the problem may lie within the component itself.
- Belt Wear: Regularly inspect the belt for cracks, fraying, or glazing. Replace the belt if you notice any of these signs of wear.
- Pulley Alignment: Use a straight edge to check the alignment of the pulleys. Misalignment can cause premature belt wear and component failure.
Example: Imagine your alternator is not charging the battery. The first step is to visually inspect the serpentine belt. Using the belt diagram, confirm that the belt is correctly routed around the alternator pulley and that the belt is in good condition. If the belt is loose or damaged, it might not be transferring enough power to the alternator, leading to charging issues. If the belt appears fine, the problem may lie within the alternator itself.
Safety Precautions
Working on the serpentine belt system involves potential hazards. Always observe the following safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative battery terminal before starting any work to prevent electrical shock.
- Engine Coolant: Do not work on the engine if it is hot. Let it cool down completely to avoid burns from hot components or coolant.
- Rotating Parts: Keep hands, hair, and clothing away from the serpentine belt and pulleys while the engine is running. These are extremely dangerous.
- Tensioner Spring: The tensioner pulley uses a strong spring. Use the proper tool to relieve tension on the belt. Incorrectly releasing the tension can cause injury or damage to the tensioner.
- Proper Tools: Use the correct tools for the job. Avoid using makeshift tools, as they can damage components or cause injury.
The crankshaft pulley and the harmonic balancer are very close to the frame of the vehicle. Exercise extreme caution when working in this area.
By carefully following the serpentine belt diagram and adhering to safety precautions, you can confidently perform various maintenance tasks on your 2009 Nissan Altima 2.5L. This knowledge will save you time and money while ensuring the proper operation of your vehicle. You can download the 2009 Nissan Altima 2.5L serpentine belt diagram from [Download Link Placeholder].
