2009 Nissan Maxima Fuse Box Diagram
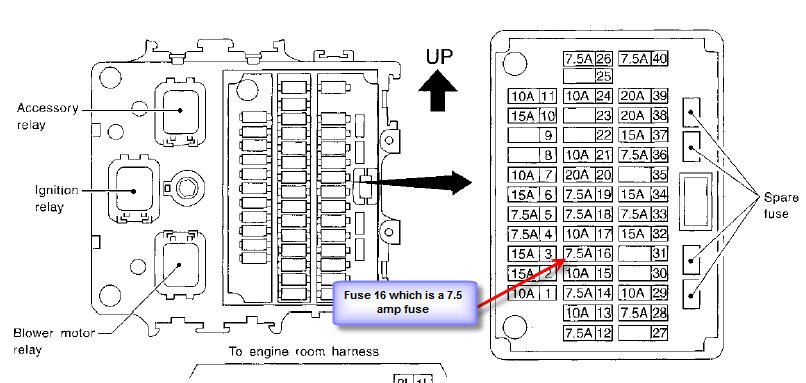
For the experienced DIY mechanic or car enthusiast tackling electrical work on a 2009 Nissan Maxima, understanding the fuse box diagram is absolutely crucial. It's the roadmap to your car's electrical system, guiding you through troubleshooting, repairs, and even modifications. Without it, you're essentially working in the dark, risking further damage or, worse, personal injury. This guide provides a detailed breakdown of the 2009 Maxima's fuse box, empowering you to confidently diagnose and resolve electrical issues.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram serves several vital purposes:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: When an electrical component malfunctions – headlights, power windows, radio – the first step is often checking the corresponding fuse. The diagram tells you exactly which fuse to inspect.
- Identifying Circuit Locations: Want to tap into a specific circuit for a modification, like adding aftermarket lighting? The diagram pinpoints the correct fuse and, by extension, the circuit.
- Understanding Electrical System Layout: The diagram provides a visual representation of how different components are connected and protected within the electrical system. This is crucial for deeper understanding and more complex repairs.
- Preventing Further Damage: Attempting to diagnose electrical faults without a diagram can lead to short circuits and damage to other components. Proper identification is paramount.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2009 Nissan Maxima typically has two main fuse box locations:
- Interior Fuse Box: Located inside the cabin, often under the dashboard on the driver's side. This box generally houses fuses for interior components like the radio, power windows, interior lights, and instrument panel.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Located in the engine bay, typically near the battery. This box houses fuses and relays for critical engine and vehicle functions, such as the fuel pump, ignition system, headlights, and ABS (Anti-lock Braking System).
Each fuse box contains several key components:
- Fuses: These are the sacrificial elements designed to protect the circuit from overcurrent. They are typically color-coded based on their amperage rating (e.g., red for 10A, blue for 15A, yellow for 20A).
- Relays: Electrically operated switches that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. Relays are often used for high-power components like headlights and the fuel pump.
- Connectors: Provide a secure and reliable electrical connection between the fuse box and the vehicle's wiring harness.
- Cover/Diagram: A protective cover that also houses the fuse box diagram, usually printed on the inside. While convenient, these diagrams can sometimes be faded or missing.
Understanding Fuse Box Diagram Symbols
The fuse box diagram uses a combination of lines, colors, and icons to represent different components and their functions. Deciphering these symbols is essential for proper interpretation:
- Lines: Solid lines indicate direct electrical connections. Dashed lines may indicate a ground connection or a connection to a specific module.
- Colors: Colors on the diagram often correspond to the color of the wiring in the vehicle's harness. Knowing the wire color can help trace circuits.
- Icons: Specific icons represent different electrical components:
- Headlight Symbol: Indicates the fuse for the headlights.
- Radio Symbol: Indicates the fuse for the radio.
- Window Symbol: Indicates the fuse for the power windows.
- Horn Symbol: Indicates the fuse for the horn.
- ECU (Engine Control Unit) Symbol: Indicates the fuse for the engine control unit.
- Amperage Rating: Each fuse is labeled with its amperage rating (e.g., 10A, 15A, 20A). This indicates the maximum current the fuse can handle before blowing. Never replace a fuse with a higher amperage rating than specified, as this can damage the circuit.
- Relay Symbols: Relays are typically represented by a square or rectangle with specific symbols indicating the coil and contact connections.
How It Works: The Electrical Protection System
The fuse box is the heart of the vehicle's electrical protection system. Each circuit in the vehicle is protected by a fuse that is designed to blow (open) if the current flow exceeds its amperage rating. This prevents damage to the wiring and components in the circuit. When an electrical component malfunctions, it can sometimes draw excessive current, causing the fuse to blow. The fuse box diagram allows you to quickly identify the fuse protecting that specific circuit and determine if it has blown.
Relays act as intermediaries. For instance, the headlight switch in your car might only handle a small current, but the headlights themselves require a much higher current. The headlight switch activates a relay, which then allows the higher current to flow to the headlights.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's a basic troubleshooting process using the fuse box diagram:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which electrical component is malfunctioning.
- Locate the Fuse Box Diagram: Consult the owner's manual or search online for a 2009 Nissan Maxima fuse box diagram.
- Identify the Corresponding Fuse: Use the diagram to locate the fuse that corresponds to the malfunctioning component.
- Inspect the Fuse: Visually inspect the fuse for a broken filament. A blown fuse will have a noticeable break in the wire inside.
- Test the Fuse (Recommended): Use a multimeter to test the fuse for continuity. A good fuse will have continuity (a reading of 0 ohms or close to it).
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a fuse of the same amperage rating. Never use a higher amperage fuse.
- Test the Component: After replacing the fuse, test the component to see if it is working correctly.
- If the Fuse Blows Again: If the new fuse blows immediately, there is likely a short circuit in the wiring or component. Further diagnosis is required. This might involve checking the wiring harness for damaged insulation or testing the component itself.
Important: If you are unsure about any aspect of electrical troubleshooting, consult a qualified mechanic.
Safety Precautions
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous. Observe the following safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical system, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent accidental short circuits.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools to prevent electrical shock.
- Avoid Water: Never work on electrical systems in wet conditions.
- High-Current Components: Be extremely careful when working with high-current components like the starter motor, alternator, and ABS system. These components can deliver a powerful electrical shock. Consider these components to be risky.
- Airbag System: The airbag system is extremely sensitive and can be triggered by electrical interference. If you are working near the airbag system, disconnect the battery and wait at least 30 minutes before proceeding.
Finally, remember that even with a diagram, electrical troubleshooting can be complex. If you are not comfortable working with electrical systems, it is always best to consult a qualified mechanic.
We have the complete 2009 Nissan Maxima fuse box diagram available for download. This detailed file includes both interior and engine compartment fuse box layouts, along with fuse amperage ratings and component designations. This resource will be invaluable for your troubleshooting and repair efforts.
