2009 Nissan Titan Fuse Box Diagram
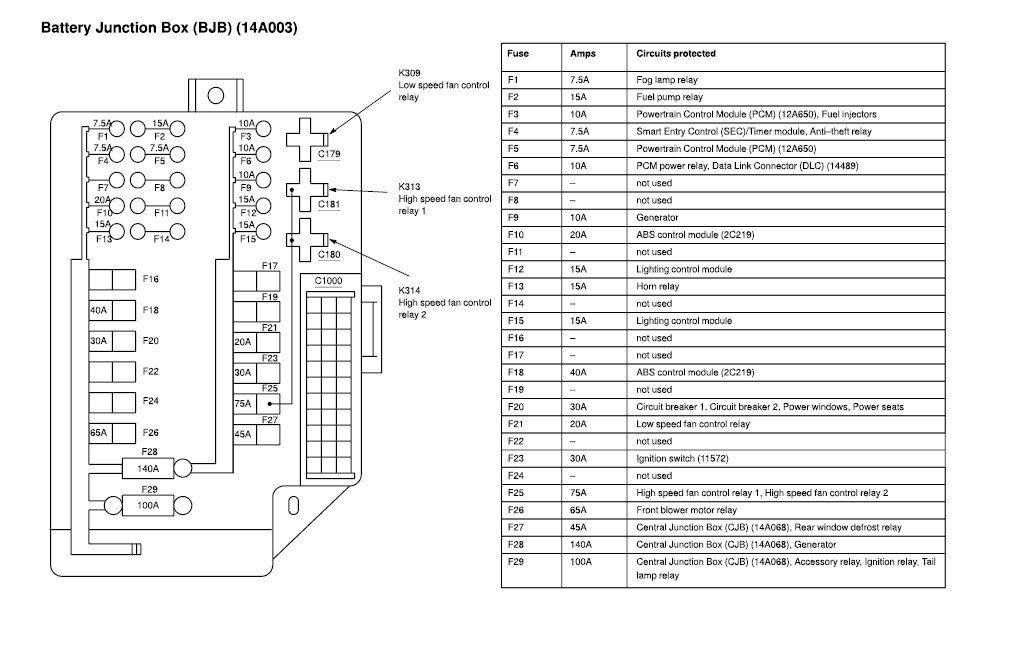
Working on your 2009 Nissan Titan? Knowing your way around the fuse boxes is crucial for everything from basic maintenance to installing aftermarket accessories. This article provides a detailed look at the 2009 Nissan Titan fuse box diagrams, equipping you with the knowledge to diagnose electrical issues, perform repairs, and confidently tackle DIY projects. We'll break down the components, symbols, and troubleshooting techniques, ensuring you understand how your Titan's electrical system is protected.
Purpose of Understanding the Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram is your roadmap to the electrical heart of your Titan. It’s more than just a piece of paper; it’s your key to:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: When a circuit malfunctions – your headlights go out, the radio dies, or the power windows stop working – the first thing you should check is the fuse. The diagram tells you which fuse corresponds to which component.
- Performing Repairs: Replacing a blown fuse is a simple task, but you need to know which one to replace! The diagram eliminates guesswork.
- Installing Aftermarket Accessories: Planning to install a new sound system, auxiliary lights, or a trailer brake controller? You'll need to tap into the electrical system, and the fuse box diagram shows you where you can safely draw power.
- Preventive Maintenance: Regularly inspecting your fuses can help you identify potential problems before they become major headaches. A blown fuse is a sign of a circuit overload, which could indicate a wiring issue.
- Understanding Your Vehicle: Even if you’re not actively working on your Titan, familiarizing yourself with the fuse box diagram gives you a better understanding of how its electrical systems are organized and protected.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2009 Nissan Titan typically has two main fuse box locations:
- Interior Fuse Box (Integrated Power Distribution Module - IPDM E/R): Located inside the cabin, often under the dashboard on the driver's side. This fuse box primarily protects circuits related to interior components like the radio, lights, power windows, and climate control system.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box (IPDM E/R): Situated in the engine bay, usually near the battery. This box handles circuits for critical engine components like the fuel pump, ignition system, and engine control unit (ECU, also sometimes referred to as the Powertrain Control Module - PCM).
Key Components:
- Fuses: These are the sacrificial links in the circuit. They're designed to melt and break the circuit when the current exceeds a safe level, preventing damage to the components downstream. Fuses are rated in amperes (amps), indicating the maximum current they can handle.
- Relays: These are electrically operated switches that control high-current circuits using a low-current control signal. They're often used to switch power to components like headlights, starter motors, and electric cooling fans.
- Fusible Links: These are larger, heavier-gauge wires designed to protect entire wiring harnesses from major overloads. They're typically found in the engine compartment fuse box and are more difficult to replace than standard fuses.
Understanding the Fuse Box Diagram Symbols
Fuse box diagrams aren't just random layouts of boxes; they use a system of symbols to represent different components and circuits. Understanding these symbols is key to interpreting the diagram accurately.
- Lines: Solid lines typically represent wires, indicating the path of the electrical current. Dashed lines may indicate grounding points or shielding.
- Colors: Wire colors are often indicated on the diagram (e.g., "BLU" for blue, "RED" for red, "BLK" for black). These colors can help you trace wires in the vehicle.
- Icons:
- Headlight Symbol: Indicates the fuse or relay for the headlights.
- Radio Symbol: Represents the fuse for the radio or audio system.
- Window Symbol: Shows the fuse for the power windows.
- Fan Symbol: Indicates the fuse or relay for the cooling fan or climate control system.
- Engine Symbol: Represents the fuse or relay for critical engine components.
- Ampere Ratings: Each fuse location on the diagram is labeled with a number, which indicates the ampere rating of the fuse that should be installed in that position.
It's important to consult the specific diagram for your 2009 Nissan Titan, as variations may exist between trim levels and model years. Look for a legend or key on the diagram that explains all the symbols used.
How It Works
The fuse box serves as a central distribution point for electrical power throughout your Titan. Power from the battery flows through the fuse box, where it's divided into individual circuits, each protected by a fuse. When a circuit experiences an overload – typically caused by a short circuit or a faulty component – the fuse blows, interrupting the flow of current and preventing damage to the wiring and components.
Relays act as remotely controlled switches. The ECU or another control module sends a low-current signal to the relay, which then closes the high-current circuit, allowing power to flow to the intended component. This allows the control module to manage high-power devices without having to handle the full current load directly.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting tips using the fuse box diagram:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which component isn't working (e.g., the cigarette lighter, the power windows, a headlight).
- Locate the Fuse: Consult the fuse box diagram to find the fuse that corresponds to the malfunctioning component. Remember to check both the interior and engine compartment fuse boxes.
- Inspect the Fuse: Remove the fuse and visually inspect it. A blown fuse will have a broken filament.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the same ampere rating. Never use a fuse with a higher rating, as this could damage the wiring and components.
- Test the Circuit: After replacing the fuse, test the circuit to see if the problem is resolved. If the fuse blows again immediately, there's a short circuit in the wiring or a faulty component. You'll need to investigate further to find the cause of the short.
Example: Your headlights aren't working. You consult the fuse box diagram, find the fuse labeled "Headlights," remove it, and see that the filament is broken. You replace it with a new fuse of the same ampere rating, and the headlights now work. Problem solved!
Safety Considerations
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some safety precautions to keep in mind:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on the fuse box, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent accidental shorts.
- Use the Right Tools: Use insulated tools to avoid electrical shock.
- Replace Fuses Correctly: Always replace a blown fuse with a fuse of the same ampere rating. Using a higher-rated fuse can damage the wiring and components, and could even cause a fire.
- Be Careful Around High-Voltage Components: Be extremely careful around the ignition system, as it generates high voltage that can be lethal.
- Do Not Work in Wet Conditions: Avoid working on the electrical system in wet conditions, as water can conduct electricity.
- Fusible Links: Exercise caution when working with fusible links. They are designed to handle significant current, and a failure or improper handling can be dangerous.
If you're not comfortable working on the electrical system yourself, it's best to consult a qualified mechanic.
We have a downloadable PDF of the 2009 Nissan Titan fuse box diagram for your convenience. This file contains detailed diagrams for both the interior and engine compartment fuse boxes, along with a legend explaining the symbols and ampere ratings. Download it now and keep it handy for all your future Titan projects!
