2010 Dodge Ram 1500 5.7 Belt Diagram
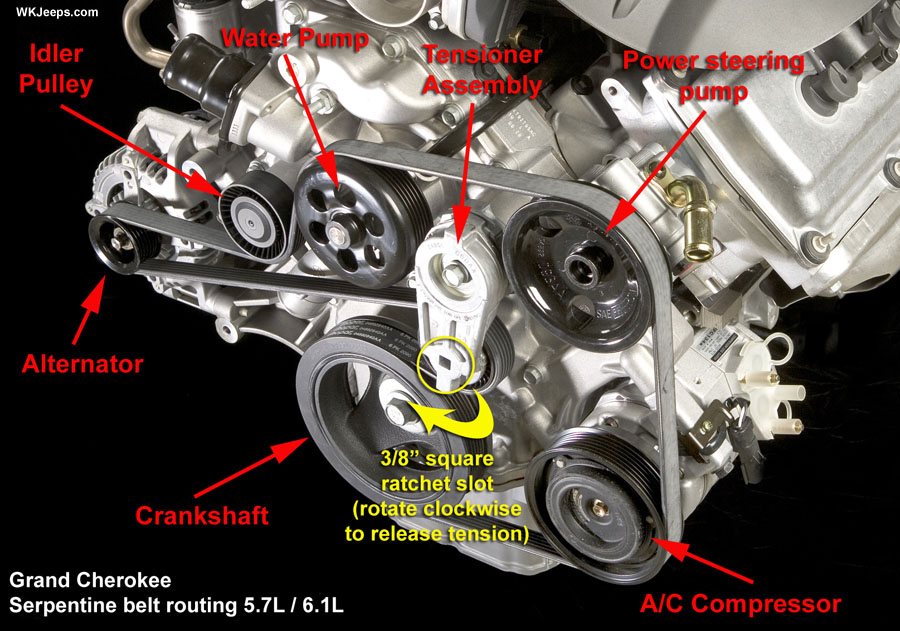
Let's dive into the serpentine belt system of a 2010 Dodge Ram 1500 equipped with the 5.7L Hemi engine. Understanding this system is crucial for various reasons, from routine maintenance to diagnosing and repairing potential problems. Whether you're replacing a worn belt, troubleshooting a squealing noise, or simply want to understand how your truck works, this guide will provide the knowledge you need. We'll cover the key components, the belt routing diagram, and practical troubleshooting tips.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
The serpentine belt diagram is your roadmap to understanding how the belt is routed around various engine accessories. Why is this important? Well, imagine you're replacing a worn belt and forget the exact routing. Without the diagram, you're left guessing, potentially causing serious engine damage. The diagram is essential for:
- Belt Replacement: Ensuring the new belt is installed correctly.
- Troubleshooting: Identifying misaligned or worn pulleys.
- Learning: Understanding the function and location of engine accessories.
- Maintenance: Properly tensioning the belt after installation.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Before we dissect the diagram, let's familiarize ourselves with the key components of the serpentine belt system in the 2010 Dodge Ram 1500 5.7L Hemi:
- Crankshaft Pulley: This is the driving force of the entire system, powered directly by the engine's crankshaft.
- Alternator: The alternator generates electricity to power the vehicle's electrical system and charge the battery.
- Power Steering Pump: This pump provides hydraulic pressure to assist with steering.
- Air Conditioning (A/C) Compressor: The A/C compressor circulates refrigerant to cool the cabin.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant through the engine to prevent overheating. Critically important.
- Idler Pulley(s): Smooth, non-driven pulleys that guide the belt and maintain proper tension and routing.
- Tensioner Pulley: A spring-loaded pulley that automatically adjusts to maintain the correct belt tension. This is crucial for the belt's lifespan and the proper functioning of the accessories.
- Serpentine Belt: A single, continuous belt that drives all of the above accessories.
The specific belt length for the 2010 Dodge Ram 1500 5.7L Hemi can vary slightly depending on whether your truck is equipped with or without certain options (like air conditioning). It is always best to verify the correct part number using your VIN at a reputable auto parts store.
Symbols and Diagram Interpretation
Understanding the symbols used in the serpentine belt diagram is key to deciphering its information. Here's a breakdown:
- Solid Lines: Represent the belt itself. The direction of the line indicates the belt's path.
- Circles: Represent pulleys. Sometimes, they may be labeled with abbreviations (e.g., ALT for alternator, P/S for power steering).
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of rotation for each pulley. Pay close attention to these!
- Tensioner Symbol: The tensioner pulley is often represented with a spring symbol indicating its spring-loaded function. You'll usually see an arrow indicating which direction to move the tensioner to release the belt tension.
- Ribbed/Grooved vs. Smooth Pulleys: The diagram often shows which side of the belt (ribbed or smooth) contacts the pulley. Ribbed pulleys drive the belt, while smooth pulleys are typically idler pulleys or the back side of a driving pulley.
Colors are rarely used in these diagrams, but if present, they might differentiate between the front and back sides of the belt in complex routing scenarios.
How It Works: The Serpentine Belt System
The serpentine belt system is elegantly simple: the crankshaft pulley, driven by the engine, spins, and this rotational energy is transferred to all the other accessories via the serpentine belt. The tensioner pulley ensures that the belt remains taut, preventing slippage and ensuring efficient power transfer. The belt snakes around each pulley in a specific route, ensuring that each accessory receives the necessary power. A properly tensioned and routed belt is crucial for the reliable operation of all the accessories.
Think of it like a well-choreographed dance. Each pulley has a specific role, and the belt is the dancer, moving seamlessly between them. If the belt is too loose (poor tension) or misrouted, the dance falls apart, and the accessories won't function correctly.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how your understanding of the serpentine belt system and diagram can help you troubleshoot common problems:
- Squealing Noise: A squealing noise, especially when the engine is first started or under heavy load, is often a sign of a loose or worn belt. Check the belt tension and inspect the belt for cracks, glazing, or missing ribs.
- Accessory Malfunction: If your alternator isn't charging, power steering isn't working, or A/C isn't cooling, the serpentine belt could be the culprit. Check if the belt is broken, slipping, or misrouted.
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the belt for wear and tear. Look for cracks, fraying, missing chunks, or glazing (a shiny, smooth surface). Replace the belt if you see any of these signs.
- Tensioner Check: Ensure the tensioner pulley is moving freely and applying adequate tension to the belt. A weak or seized tensioner can cause belt slippage and damage.
- Pulley Alignment: A misaligned pulley can cause premature belt wear and squealing. Use a straightedge to check that all the pulleys are in alignment.
Safety Considerations
Working on the serpentine belt system can be dangerous if you're not careful. Here are some important safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on any part of the electrical system. This prevents accidental electrical shocks.
- Hot Engine: Never work on the serpentine belt system when the engine is hot. Allow the engine to cool down completely before starting any work.
- Moving Parts: Keep your hands, hair, and clothing away from the serpentine belt and pulleys when the engine is running.
- Tensioner Release: When releasing the tension on the belt, use the correct tool and follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully. The tensioner spring is strong and can cause injury if released improperly.
- Proper Tools: Use the correct tools for the job. Using the wrong tools can damage the components and increase the risk of injury.
The serpentine belt tensioner is a risky component due to the high spring pressure. Always use the correct tool to relieve the tension, and wear eye protection. A slip can cause serious injury.
Additionally, ensure the vehicle is stable and properly supported if you need to get underneath it to access any part of the system.
With this detailed guide and the diagram in hand, you're well-equipped to tackle serpentine belt-related tasks on your 2010 Dodge Ram 1500 5.7L Hemi. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult a professional mechanic if you're unsure about any aspect of the repair.
For your convenience, we have a high-resolution, downloadable version of the 2010 Dodge Ram 1500 5.7L Hemi serpentine belt diagram. It includes clear routing and component labels to assist you in your repairs and maintenance.
