2010 Nissan Maxima Fuse Box Diagram
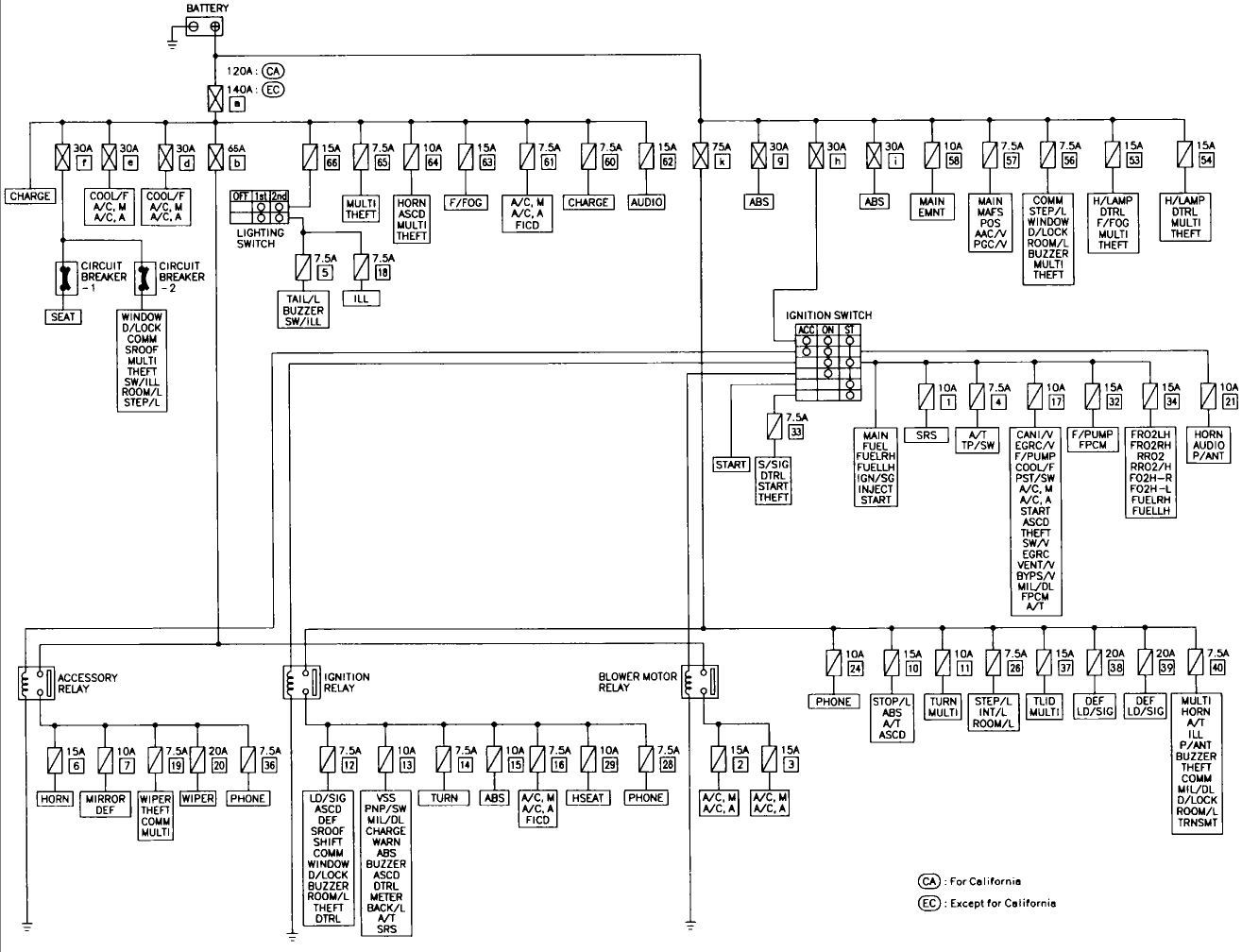
For the experienced DIYer tackling electrical work on a 2010 Nissan Maxima, a reliable fuse box diagram is absolutely essential. It's the roadmap to your car's electrical system, enabling efficient troubleshooting, safe modifications, and preventing costly repairs. Whether you're tracing a short, adding aftermarket accessories, or simply replacing a blown fuse, understanding your Maxima's fuse box layout is a powerful skill. Let's dive into the specifics of the 2010 Maxima's fuse box.
Purpose and Importance of the Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram serves multiple critical purposes. Firstly, it's your primary resource for identifying the correct fuse for a specific circuit. Incorrect fuse replacement can lead to serious electrical damage, so knowing the right amperage and circuit protection is paramount. Secondly, the diagram aids in troubleshooting electrical issues. By referencing the diagram, you can isolate potential problem areas within the wiring harness. Thirdly, if you're planning any aftermarket modifications, such as installing new lights, a sound system, or a remote starter, the diagram helps you tap into the appropriate circuits safely and without causing interference to other systems. Ignoring the fuse diagram and guessing can cause serious harm to yourself or your car.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2010 Nissan Maxima typically features two main fuse box locations: one inside the cabin, usually located under the dashboard on the driver's side, and another in the engine compartment, close to the battery. The engine compartment fuse box tends to house fuses and relays related to critical engine functions, lighting, and other high-current devices. The interior fuse box generally handles accessories, comfort features, and other lower-current circuits.
Key components within the fuse boxes include:
- Fuses: These are sacrificial devices designed to protect circuits from overcurrents. They come in various amperage ratings, indicated by a number printed on the fuse and a color-coded body.
- Relays: These are electromagnetic switches that control high-current circuits using a low-current signal. They are used to manage things like headlights, the starter motor, and other high-power components.
- Fusible Links: These are heavy-duty fuses designed to protect major circuits and components, such as the alternator and the battery. They're typically located near the battery and are designed to handle very high currents.
- Connector Blocks: The fuse box also incorporates connector blocks for wire harnesses.
- Grounding Points: Some of the wires run to grounding points nearby to the fuse box.
It's important to note that the exact layout and fuse assignments can sometimes vary slightly based on the specific trim level and options installed on your Maxima. Therefore, always refer to the diagram specific to your vehicle. Don't assume one model is similar to another.
Understanding the Symbols
A fuse box diagram isn't just a random collection of lines and numbers. It's a standardized representation of the electrical system, using specific symbols to convey information concisely. Here's a breakdown of common symbols you'll encounter:
- Lines: Lines represent wires connecting components. Thicker lines may indicate higher-gauge wires capable of carrying more current.
- Colors: Wire colors are often indicated on the diagram (e.g., BLK for black, RED for red, BLU for blue). This is crucial for identifying the correct wire when troubleshooting. The wiring color code is an industry-wide standard.
- Fuse Symbols: Fuses are typically represented by a rectangle with a line or a squiggle through it. The amperage rating is usually noted next to the symbol.
- Relay Symbols: Relays are usually represented by a coil symbol and a switch symbol, indicating the control circuit and the switched circuit.
- Component Icons: The diagram often includes icons representing the components the fuses protect, such as a headlight, a windshield wiper, or a radio.
Pay close attention to the legends and notes accompanying the diagram. These sections often provide critical information about specific circuits, fuse ratings, and component locations. Ignoring the legend can lead to misinterpretations and incorrect repairs.
How It Works
The fuse box acts as a central distribution point for electrical power throughout the vehicle. Power from the battery flows to the fuse box, and from there, it's distributed to various circuits, each protected by a fuse or relay. When an overcurrent occurs in a circuit (e.g., due to a short circuit), the fuse blows, interrupting the flow of electricity and preventing damage to the components and wiring in that circuit. The fuse melts open a wire inside the fuse's glass or plastic housing.
Relays, on the other hand, allow low-current circuits to control high-current circuits. For example, the headlight switch only needs to handle a small current to activate a relay. The relay then closes a high-current circuit that powers the headlights. This prevents the headlight switch from being overloaded and potentially damaged.
Real-World Use and Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting tips using the fuse box diagram:
- Identify the Symptom: What's not working? Is it a headlight, the radio, or something else?
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse or relay associated with the malfunctioning component.
- Inspect the Fuse: Remove the fuse and visually inspect it. A blown fuse will have a broken filament inside. You can also use a multimeter set to continuity mode to test the fuse.
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a fuse of the exact same amperage rating. Never use a higher amperage fuse, as this could damage the circuit.
- Test the Circuit: After replacing the fuse, test the circuit to see if the problem is resolved. If the fuse blows again immediately, there's likely a short circuit in the wiring.
- Check the Relay: If the fuse is good, the relay might be the problem. You can test the relay using a multimeter or swap it with a known good relay to see if the issue is resolved.
If you suspect a short circuit, you'll need to trace the wiring associated with that circuit, looking for damaged insulation or exposed wires that may be grounding out. A wiring diagram, which shows the complete layout of the electrical system, will be very helpful in this scenario.
Safety Precautions
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Always take the following precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical circuits, disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent accidental shocks or short circuits.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use tools with insulated handles to protect yourself from electric shock.
- Avoid Water: Never work on electrical systems in wet or damp conditions.
- Identify High-Risk Components: Be especially careful around high-current components like the battery, alternator, and starter motor. These components can deliver a dangerous shock.
- Consult a Professional: If you're not comfortable working on electrical systems, consult a qualified mechanic. Electrical problems can be complex and dangerous to diagnose and repair.
- Do not alter the wire harnesses.
Important: Modifying or tampering with the vehicle's electrical system can void your warranty and potentially damage the vehicle. Proceed with caution and always follow the manufacturer's recommendations.
Remember, a little preparation and a good understanding of the fuse box diagram can save you time, money, and frustration when dealing with electrical issues on your 2010 Nissan Maxima. We have the complete fuse box diagram available as a downloadable file. This resource will be an invaluable asset for any DIY project or repair you undertake.
