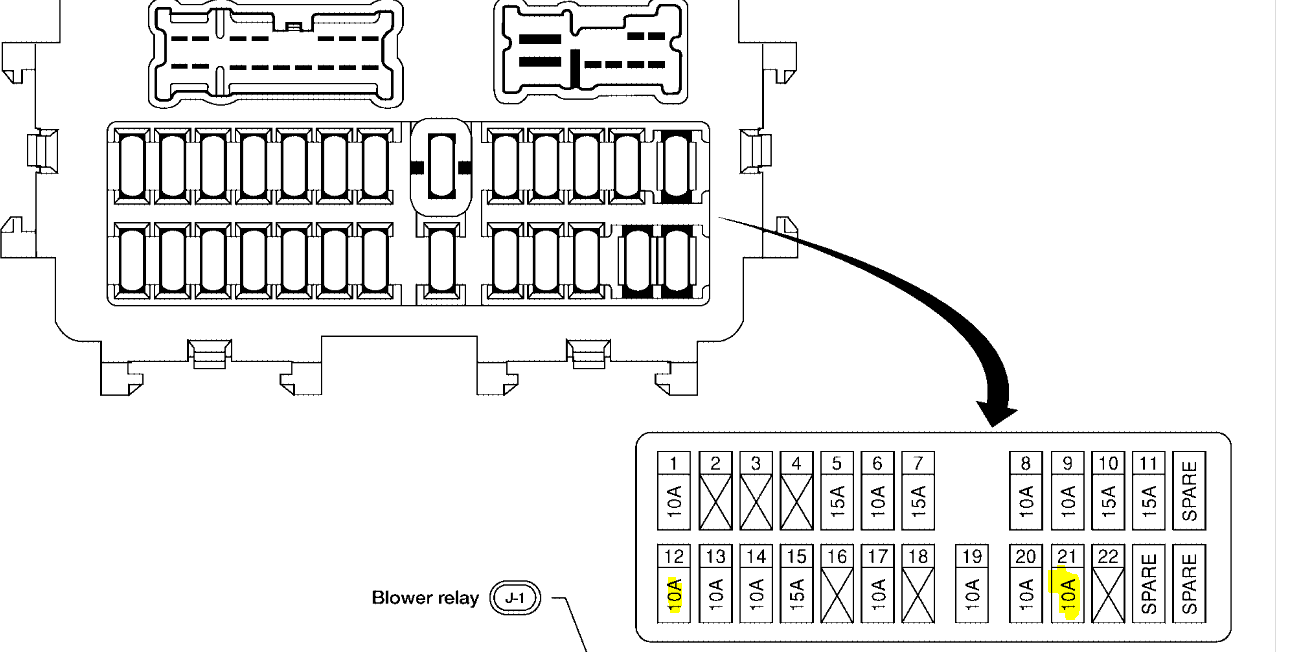
2010 Nissan Titan Fuse Box Diagram
For the seasoned DIY enthusiast or shade-tree mechanic, understanding your vehicle's electrical system is paramount. The fuse box, acting as the central nervous system's circuit breaker, is a critical point for troubleshooting electrical issues and performing modifications. This article delves into the 2010 Nissan Titan fuse box diagram, offering a comprehensive guide to its layout, function, and safe usage. We'll equip you with the knowledge to diagnose electrical problems effectively and perform maintenance tasks with confidence.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
Why bother with a fuse box diagram? Several compelling reasons exist:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: A blown fuse is often the culprit behind a malfunctioning component, like a radio, headlights, or power windows. The diagram allows you to quickly identify the correct fuse for the affected circuit and replace it.
- Identifying Circuits for Modifications: Planning to install aftermarket accessories like a new sound system, auxiliary lights, or a trailer brake controller? The diagram is crucial for identifying suitable power sources and tapping into existing circuits safely. Incorrect wiring can damage your vehicle's electrical system.
- Preventative Maintenance: Periodically inspecting the fuses can help identify potential problems before they escalate. Look for signs of corrosion, loose connections, or melting, all of which can indicate an overloaded or failing circuit.
- Understanding Vehicle Systems: The diagram provides a visual representation of how different electrical components are connected, improving your overall understanding of the vehicle's electrical system.
- Emergency Repairs: When stranded with an electrical issue, knowledge of the fuse box can be invaluable for temporary fixes or identifying the root cause of the problem.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2010 Nissan Titan typically has two fuse box locations:
- Interior Fuse Box: Usually located under the dashboard on the driver's side, near the steering column. This box primarily houses fuses for interior components like the radio, lights, power windows, and climate control.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box (IPDM E/R - Intelligent Power Distribution Module Engine Room): Located under the hood, typically near the battery. This box contains fuses and relays for critical engine components such as the fuel pump, ignition system, and cooling fans. It also integrates some computer functions.
Main Parts:
- Fuses: These are sacrificial devices designed to protect circuits from overcurrent. They contain a thin wire that melts and breaks the circuit when the current exceeds a safe level. Fuses are rated in amperes (amps), indicating the maximum current they can handle. Common ratings include 5A, 7.5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, and 30A.
- Relays: These are electrically operated switches that control high-current circuits using a low-current signal. They are used for components like headlights, starter motors, and electric fans. Relays help protect the switch gear in the cab, allowing a small switch to control a large electrical load.
- Fuse Box Housing: The plastic enclosure that houses the fuses and relays, protecting them from environmental factors and providing a organized layout.
- Diagram Label: A sticker or printed diagram, usually located on the inside of the fuse box cover, indicating the location and function of each fuse and relay. This is what we're focusing on dissecting.
Understanding Fuse Box Symbols
The fuse box diagram uses symbols and abbreviations to represent different components and functions. Deciphering these symbols is crucial for understanding the diagram.
- Lines: Solid lines represent electrical wires connecting different components. Thicker lines generally indicate higher-current circuits.
- Colors: Wire colors are often indicated next to the lines, using abbreviations like "BLU" for blue, "RED" for red, "BLK" for black, "WHT" for white, and "GRN" for green. These color codes are helpful when tracing wires.
- Fuse Symbols: Fuses are typically represented by a rectangle with a squiggly line inside, symbolizing the fusible link.
- Relay Symbols: Relays are usually shown as a square with internal components representing the coil and contacts.
- Component Icons: Icons represent various components, such as headlights (a lightbulb symbol), horns (a trumpet symbol), and windshield wipers (a stylized wiper blade symbol).
- Ampere Ratings: Numbers next to the fuse symbols indicate the fuse's amperage rating (e.g., "15A").
- Abbreviations: The diagram utilizes abbreviations for component names. Common examples include:
- ACC: Accessory
- IGN: Ignition
- ECU: Engine Control Unit
- BCM: Body Control Module
- ECM: Engine Control Module
- HTR: Heater
- P/W: Power Window
- P/L: Power Locks
How It Works: The Electrical Flow
The 2010 Nissan Titan's electrical system operates on a 12-volt direct current (DC) system. The battery provides the initial power source. When you turn the ignition key, the system activates, allowing electricity to flow through various circuits. Fuses are strategically placed in these circuits to protect components from damage due to overloads or short circuits. For example, if a short circuit occurs in the headlight wiring, the headlight fuse will blow, preventing damage to the wiring and the headlight switch.
Relays, controlled by the vehicle's computer or switches, activate high-current devices. For example, the starter relay allows a low-current signal from the ignition switch to activate the high-current starter motor. This prevents the ignition switch from being overloaded and damaged.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting
Here's a simple troubleshooting scenario using the fuse box diagram:
- Symptom: The radio is not working.
- Check the Diagram: Consult the interior fuse box diagram to locate the fuse labeled "Radio" or "Audio."
- Inspect the Fuse: Remove the fuse using a fuse puller (usually located in one of the fuse boxes). Examine the fuse. If the thin wire inside is broken or blackened, the fuse is blown.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Never use a fuse with a higher amperage rating, as this could overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- Test the Radio: Turn on the radio to see if it works. If the new fuse blows immediately, there is a short circuit in the radio wiring or the radio itself. Further diagnosis is required.
Safety Considerations
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous. Always take the following precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical component, disconnect the negative battery terminal. This prevents accidental short circuits and electrical shocks.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools designed for automotive electrical work.
- Never Bypass a Fuse: Bypassing a fuse with a wire or a higher-amperage fuse is extremely dangerous and can cause a fire.
- Identify High-Risk Components: Be particularly cautious when working with components like the airbag system, fuel pump, and ignition system. These components can be dangerous if mishandled.
- Consult a Professional: If you are unsure about any aspect of electrical system troubleshooting or repair, consult a qualified mechanic. Especially with hybrid vehicles, high-voltage areas exist and can be lethal.
Understanding the 2010 Nissan Titan fuse box diagram empowers you to effectively diagnose and resolve electrical issues. By using the diagram in conjunction with a multimeter and basic electrical knowledge, you can save time and money on repairs and modifications. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult a professional when needed.
We have a detailed, downloadable PDF of the 2010 Nissan Titan fuse box diagram available. This diagram includes specific locations for both interior and engine compartment fuse boxes. It also includes a comprehensive listing of fuse functions and amperages. Contact us for access to the file.
