2011 Dodge Ram 1500 5.7 Hemi Serpentine Belt Diagram
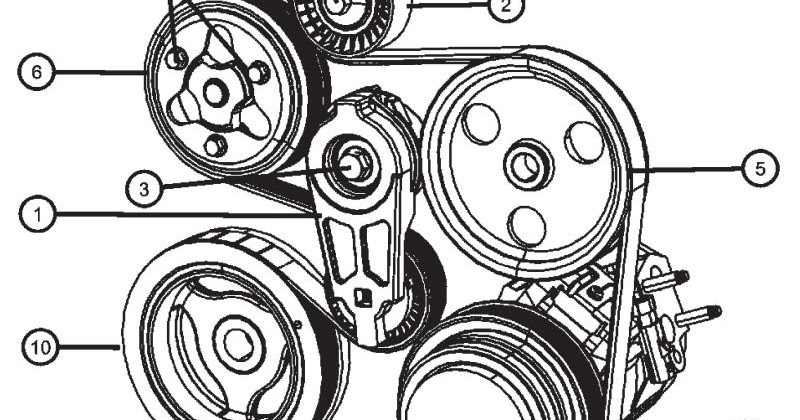
Alright folks, let's talk about the serpentine belt on a 2011 Dodge Ram 1500 with the 5.7L Hemi. This engine's a workhorse, but that serpentine belt is crucial for keeping everything spinning. Understanding its routing and how it works is vital for maintenance, troubleshooting, and even some performance upgrades. Having a reliable diagram at your fingertips can save you a lot of time, frustration, and money. We've got that diagram available for download, which we'll mention again at the end. For now, let's dive into the details.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
Why bother with a diagram in the first place? Well, the serpentine belt drives several critical engine components. A broken or improperly routed belt can lead to serious problems. The diagram serves several key purposes:
- Repair and Replacement: If your belt snaps or needs replacing, the diagram is your roadmap for correct installation. Incorrect routing can cause component failure and even engine damage.
- Troubleshooting: Squealing belts, overheating, or a dead battery can often be traced back to issues with the serpentine belt system. The diagram helps you identify potential problems like misaligned pulleys or seized components.
- Maintenance: Regular inspections are key. The diagram allows you to easily locate and inspect each component driven by the belt for signs of wear or damage.
- Learning and Understanding: Even if you're not actively working on the engine, understanding how the serpentine belt system functions provides a deeper appreciation for automotive mechanics.
- Modifications: Planning an underdrive pulley kit, or upgrading to a higher-output alternator? The diagram is essential for ensuring compatibility and proper belt length.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Before we get into the diagram itself, let's identify the major components driven by the serpentine belt on the 2011 Ram 1500 5.7L Hemi. Knowing what these parts *do* helps you understand the belt's function.
Components:
- Crankshaft Pulley: This is the heart of the system. Connected directly to the crankshaft, it provides the rotational force that drives the entire serpentine belt.
- Alternator: The alternator generates electricity to power the vehicle's electrical system and charge the battery. A failing alternator due to a slipping belt can cause a dead battery.
- Water Pump: The water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine, preventing overheating. Belt slippage or failure can lead to rapid overheating and potential engine damage.
- Power Steering Pump: The power steering pump provides hydraulic pressure to assist with steering. If the belt slips, you'll notice stiff steering.
- Air Conditioning Compressor: The A/C compressor is responsible for cooling the air in the cabin. A failing compressor due to a faulty belt can cause the AC to stop blowing cold air.
- Idler Pulley(s): These pulleys provide tension and guide the belt along its optimal path.
- Tensioner Pulley: This spring-loaded pulley maintains the correct tension on the belt. A failing tensioner can cause belt slippage, noise, and premature wear. The tensioner is a critical component, and its proper function is essential for the entire system.
Belt Specifications: While you should always verify with your vehicle's specific VIN and parts catalog, the typical belt length for the 2011 Ram 1500 5.7L Hemi is around 91-92 inches. It's a multi-ribbed belt, meaning it has several V-shaped grooves that engage with the pulleys. Always use a high-quality replacement belt designed for your specific application. Using the wrong belt size or quality can lead to premature failure and damage to other components.
Symbols and Diagram Conventions
Serpentine belt diagrams are usually straightforward, but let's clarify common symbols you might encounter:
Line Styles:
- Solid Line: Represents the belt itself, showing its path around the pulleys.
- Dashed Line: Often indicates the *rear* of a pulley, showing that the belt passes behind it.
- Arrow(s): Show the direction of belt travel. Follow these arrows closely when installing a new belt.
Iconography:
- Pulleys: Typically represented as circles. The diagram will often label each pulley with its corresponding component (e.g., "ALT" for Alternator, "P/S" for Power Steering).
- Tensioner: Usually depicted with a spring symbol, indicating its spring-loaded mechanism.
Additional Notes:
- Some diagrams use different colors to highlight specific sections of the belt path or to indicate the "smooth" vs. "ribbed" side of the belt. In general, the ribbed side makes contact with most pulleys, while the smooth side makes contact with the idler pulley and the tensioner.
How It Works
The serpentine belt system is elegantly simple: the crankshaft pulley spins, transferring rotational force to all the other components connected by the belt. The tensioner pulley keeps the belt taut, ensuring optimal grip and preventing slippage. The idler pulleys simply guide the belt along its intended path.
Imagine it like this: the crankshaft pulley is the engine's driving force, while the serpentine belt is the transmission system for that power to the different components. If there's slack in the belt, components might not spin at the speed they require, leading to performance problems or even complete failure.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting
Here are some common serpentine belt-related issues and how the diagram can help:
- Squealing Belt: Often caused by a loose belt, worn pulley, or misaligned components. Use the diagram to visually inspect the belt path, tensioner, and pulleys for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. A glazing on the belt would also indicate the belt is slipping.
- Overheating: If the water pump isn't spinning correctly due to a slipping or broken belt, the engine will overheat quickly. Verify that the belt is properly routed around the water pump pulley and that the tensioner is functioning correctly.
- Dead Battery: A slipping alternator belt won't allow the alternator to charge the battery properly. Use the diagram to confirm the belt is correctly routed and tensioned around the alternator pulley.
- Stiff Steering: If the power steering pump isn't receiving adequate power due to a belt issue, you'll experience stiff steering. Check the belt's routing and tension around the power steering pump pulley.
- A/C Not Working: Similar to the other components, the AC compressor relies on the serpentine belt. Double-check belt placement and condition.
- Belt Shredding/Breaking: Misalignment is a common cause of belts shredding prematurely. Use a straight edge to check that all the pulleys are in alignment.
Safety Precautions
Working on the serpentine belt system can be dangerous. Here are some essential safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on any electrical components. This prevents accidental shorts or electrical shocks.
- Engine Must Be Cool: Never work on the serpentine belt system while the engine is hot. The components can be extremely hot and cause severe burns.
- Keep Fingers Clear: The serpentine belt system contains moving parts that can cause serious injury. Keep your fingers and clothing clear of the belt and pulleys while the engine is running (if you *must* run it for diagnostic purposes).
- Beware of Spring Tension: The tensioner pulley is spring-loaded and can snap back with considerable force. Use the appropriate tools to relieve the tension before removing the belt.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
The Crankshaft Pulley rotates at a high rate of speed, making it one of the most dangerous parts of the system.
By understanding the diagram and following these safety precautions, you can confidently maintain and troubleshoot your 2011 Dodge Ram 1500's serpentine belt system. Remember, if you're not comfortable performing these tasks yourself, it's always best to consult a qualified mechanic.
As promised, we have a detailed serpentine belt diagram for the 2011 Dodge Ram 1500 5.7L Hemi available for you to download. This diagram includes clear labeling and routing information to help you with your repairs and maintenance. Good luck, and stay safe out there!
