2011 Jeep Grand Cherokee 5.7 Serpentine Belt Diagram
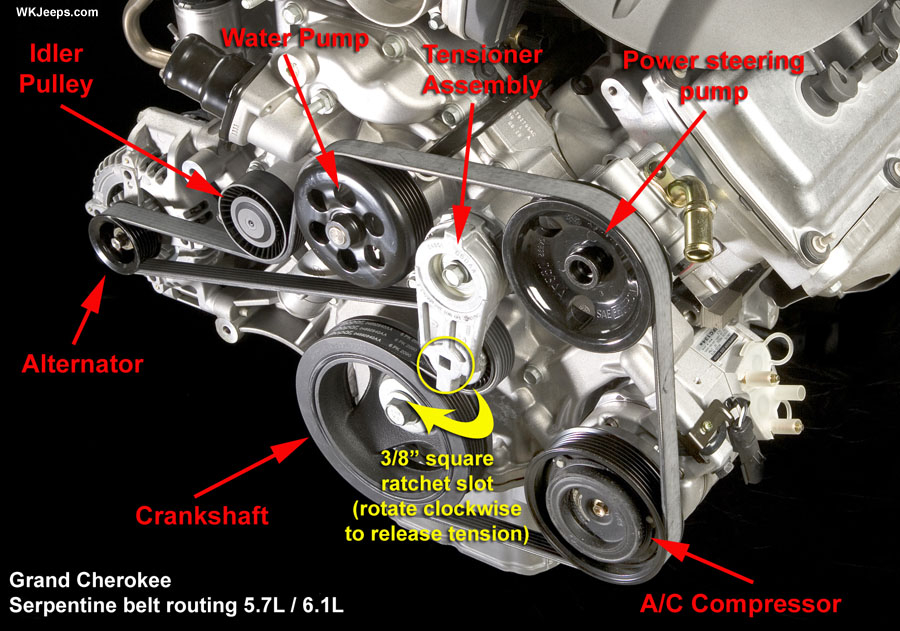
Alright, let's dive into the serpentine belt system of your 2011 Jeep Grand Cherokee with the 5.7L HEMI engine. Understanding this system and having the right diagram is crucial for everything from routine maintenance to diagnosing and fixing driveability issues. This isn't just about knowing where the belt goes; it's about understanding the system's function, potential problems, and how to safely work on it. We'll break down the diagram, the components, and some real-world troubleshooting tips.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
The serpentine belt diagram is your roadmap to the accessory drive system. It serves several crucial purposes:
- Repair Reference: When replacing a worn or damaged serpentine belt, the diagram ensures you route the new belt correctly. An incorrectly routed belt can damage components, reduce performance, or even snap.
- Component Identification: The diagram identifies each component driven by the belt, allowing you to trace problems back to a specific pulley or accessory.
- Troubleshooting: By observing the belt's path and condition, you can often diagnose issues like misaligned pulleys or failing bearings in accessories.
- Learning the System: For the DIY enthusiast, the diagram is an invaluable tool for understanding the overall layout and function of the engine's accessory drive.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 2011 Jeep Grand Cherokee 5.7L Serpentine Belt System
The 2011 Jeep Grand Cherokee 5.7L uses a single, long serpentine belt to drive multiple engine accessories. Here's a rundown of the key components:
- Crankshaft Pulley (Crank Pulley): This is the driving force of the entire system. Bolted to the crankshaft, it transmits the engine's rotational energy to the belt.
- Alternator Pulley: The alternator generates electrical power for the vehicle. The belt spins the alternator pulley, causing it to produce electricity.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: The power steering pump provides hydraulic assistance to the steering system, making it easier to turn the wheel.
- Air Conditioning Compressor Pulley: The A/C compressor circulates refrigerant to cool the cabin air.
- Water Pump Pulley: The water pump circulates coolant through the engine to regulate temperature.
- Idler Pulley(s): These smooth, unpowered pulleys are strategically placed to guide the belt and maintain proper tension.
- Tensioner Pulley: This is the most crucial pulley. The tensioner maintains the correct amount of tension on the belt, preventing slippage and ensuring efficient operation. It typically uses a spring-loaded arm to apply force. The tensioner assembly also includes a pivot point and a dampener to keep the tension smooth.
- Serpentine Belt: The heart of the system, this reinforced rubber belt transmits power from the crankshaft to all the accessories.
Regarding specs, the specific belt length is critical. Consult the parts catalog for your 2011 Grand Cherokee with the 5.7L HEMI to get the exact belt length specification. Using the wrong length belt will either be too tight, stressing the components, or too loose, leading to slippage.
Serpentine Belt Diagram Symbols Explained
Understanding the symbols on the diagram is key to interpreting it correctly. Here's a breakdown of common symbols you might encounter:
- Solid Lines: These typically represent the belt's path. The diagram will illustrate how the belt weaves around each pulley.
- Arrows: Arrows indicate the direction of belt travel around each pulley. Pay close attention to these; they're vital for proper routing.
- Component Icons: Each component (alternator, power steering pump, etc.) is usually represented by a simplified icon. The diagram should include a legend to identify each icon.
- Tensioner Indicator: The tensioner may be depicted with a spring symbol or a curved arrow indicating the direction in which to rotate the tensioner for belt removal and installation.
Typically, diagrams don't use color, but if they do, it might be to distinguish between different belt paths or to highlight specific components. Always refer to the diagram's legend for clarification.
How the Serpentine Belt System Works
The serpentine belt system is relatively straightforward in its operation. The crankshaft pulley, driven by the engine's rotation, spins the serpentine belt. The belt then transfers this rotational energy to each accessory pulley. The tensioner pulley maintains optimal belt tension to prevent slippage and ensure efficient power transfer. The idler pulleys simply guide the belt along the correct path.
Think of it as a chain reaction: the crankshaft starts it, and the belt is the chain that links all the accessories together. Any failure in this chain, such as a worn belt, a seized pulley bearing, or a malfunctioning tensioner, will disrupt the entire system.
Real-World Use and Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common problems you might encounter and how the diagram can help:
- Squealing Belt: This is often caused by a loose belt. Check the tensioner. If it's functioning properly, the belt may be worn or glazed. The diagram helps you visually inspect the belt's path and ensure it's properly seated on all pulleys.
- Belt Slippage: Slippage can be caused by a loose belt, worn pulleys, or contamination (oil, coolant). The diagram allows you to check the alignment of the pulleys. Misaligned pulleys can cause premature belt wear and slippage.
Use a straight edge or laser alignment tool to confirm proper alignment.
- Accessory Failure: If an accessory like the alternator or power steering pump fails, the diagram helps you isolate the problem. You can visually inspect the pulley for damage or seizure. A seized pulley will cause the belt to squeal or even break.
- Belt Breakage: A broken belt is usually the result of age, wear, or a seized accessory. Replace the belt and thoroughly inspect all pulleys for damage and proper rotation before installing a new belt. Consult the diagram to ensure correct routing of the replacement belt.
When troubleshooting, always start by visually inspecting the belt and pulleys. Look for cracks, wear, glazing, or any signs of damage. Check the tensioner for proper movement and tension.
Safety Considerations
Working on the serpentine belt system can be dangerous if proper precautions are not taken.
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any part of the engine, disconnect the negative battery cable to prevent accidental starting.
- Hot Engine: Never work on the engine when it's hot. Allow it to cool down completely before attempting any repairs.
- Moving Parts: Be extremely cautious around the serpentine belt when the engine is running. Loose clothing or tools can get caught in the belt, causing serious injury. Never put your hands near the belt while the engine is running.
- Tensioner Spring: The tensioner spring is under significant tension. Use the correct tools to relieve the tension when removing or installing the belt. Never attempt to release the tensioner with makeshift tools. A slip can cause serious injury.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
Remember, if you are not comfortable performing these repairs yourself, it's always best to consult a qualified mechanic. The serpentine belt system is crucial to your vehicle's operation, and improper repairs can lead to further damage.
With this knowledge and the proper diagram, you're well-equipped to understand, maintain, and troubleshoot the serpentine belt system on your 2011 Jeep Grand Cherokee 5.7L. Happy wrenching!
We have a high-resolution, printable version of the 2011 Jeep Grand Cherokee 5.7L Serpentine Belt Diagram available for download. This will provide you with a clear and detailed reference for your repairs and maintenance.
