2011 Nissan Armada Fuse Box Diagram
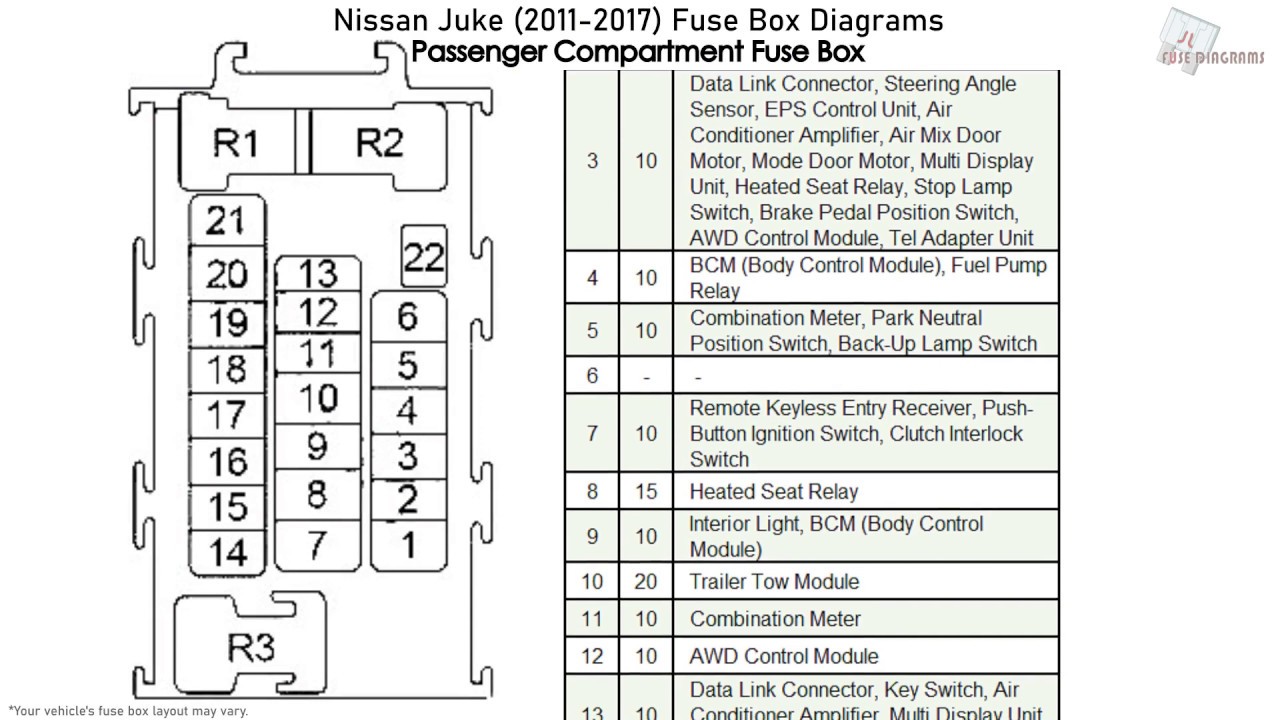
For the experienced DIYer or modder tackling electrical work on a 2011 Nissan Armada, understanding the fuse box diagram is absolutely critical. Whether you're diagnosing a malfunctioning tail light, adding an aftermarket accessory, or simply trying to learn more about your vehicle's electrical system, a clear and accurate fuse box diagram is your best friend. This article will break down the intricacies of the 2011 Armada's fuse boxes, empowering you to confidently troubleshoot and perform electrical repairs.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram serves several vital purposes:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Issues: Quickly identify which fuse corresponds to a particular circuit, saving time and effort in locating the source of a problem.
- Locating the Correct Fuse: Fuses are designed to protect specific circuits. The diagram shows exactly which fuse controls which component.
- Performing Electrical Modifications: When adding accessories like lights, sound systems, or auxiliary power outlets, you need to know which circuits can handle the extra load and where to safely tap into the vehicle's power system.
- Understanding the Vehicle's Electrical System: Studying the fuse box diagram offers a deeper understanding of how the different electrical components in your Armada are interconnected.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2011 Nissan Armada typically has two primary fuse boxes:
- Interior Fuse Box: Usually located under the dashboard, often on the driver's side, but sometimes on the passenger side. This fuse box primarily controls interior components like the radio, power windows, interior lighting, and various control modules.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Located in the engine bay, near the battery. This fuse box handles high-current components such as the headlights, starter motor, ABS (Anti-lock Braking System), and other engine-related systems.
Each fuse box consists of the following:
- Fuse Panel: The physical housing that holds the fuses and relays.
- Fuses: Overcurrent protection devices designed to blow (open the circuit) when the current exceeds a specified limit, preventing damage to the circuit and components. Fuses are rated in Amperes (Amps), indicating the maximum current they can handle.
- Relays: Electrically operated switches used to control high-current circuits with a low-current signal. They allow the car's computer to control devices that require more power.
- Diagram Label: A sticker or label attached to the fuse box cover, providing a map of fuse and relay locations and their corresponding circuits. This is what we refer to as the fuse box diagram.
Symbols, Lines, Colors, and Icons
Understanding the symbols and conventions used in the fuse box diagram is crucial for accurate interpretation. Here's a breakdown:
- Fuse Symbols: Fuses are typically represented by a simple line or a zigzag line. The Amp rating is usually indicated next to the symbol (e.g., 10A, 15A).
- Relay Symbols: Relays are often depicted as a square or rectangle with internal symbols representing the coil and switch contacts.
- Lines: Lines connect the fuse or relay symbol to the corresponding component or circuit it protects.
- Colors: Fuse bodies are color-coded to indicate their Amp rating. This is an industry standard and helps quickly identify the correct fuse. Common colors include:
- Yellow: 20 Amps
- Blue: 15 Amps
- Red: 10 Amps
- Brown: 7.5 Amps
- Orange: 5 Amps
- Icons: Diagrams often use icons to represent the components being protected. Examples include a light bulb for headlights, a steering wheel for power steering, a windshield wiper for the wiper system, and a speaker for the audio system.
How It Works
The fuse box serves as a central distribution point for electrical power in the vehicle. Power from the battery is routed through the fuse box, and each circuit is protected by a fuse of the appropriate rating. If a short circuit or overload occurs in a particular circuit, the fuse blows, interrupting the flow of current and preventing damage to the wiring and components. Relays act as switches, allowing low-current signals from control modules to activate high-current circuits like headlights or the starter motor. The fuse box diagram provides a roadmap to understand how these fuses and relays are connected and what circuits they protect.
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's a step-by-step guide to using the fuse box diagram for troubleshooting:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which component is malfunctioning (e.g., a non-functioning tail light).
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse box diagram (usually on the inside of the fuse box cover).
- Find the Corresponding Fuse: Using the diagram, identify the fuse associated with the malfunctioning component. Look for the icon or label that matches the component's function (e.g., "Tail Light" or "T/L").
- Inspect the Fuse: Visually inspect the fuse. A blown fuse will have a broken filament inside.
- Test the Fuse: Use a multimeter to test the fuse for continuity. If the multimeter shows no continuity, the fuse is blown.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the same Amp rating. Never use a fuse with a higher Amp rating, as this can damage the circuit.
- Test the Component: After replacing the fuse, test the component to see if it is now functioning correctly.
- If the Fuse Blows Again: If the new fuse blows immediately or shortly after being replaced, there is likely a short circuit in the wiring or component. Further investigation is required to locate and repair the short. This might involve checking wiring harnesses, connectors, and the component itself.
Safety – Highlight Risky Components
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some important safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical system, disconnect the negative (-) terminal of the battery to prevent accidental shorts and electrical shock.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools designed for automotive electrical work.
- Never Bypass Fuses: Never bypass a fuse by using a wire or other conductive material. This can cause a fire and serious damage to the vehicle.
- High-Current Circuits: Be especially cautious when working with high-current circuits like the starter motor, alternator, and ABS. These circuits can deliver a significant electrical shock.
- Airbag Systems: Some fuses are related to the airbag system. Improper handling of these systems can cause accidental deployment, which can be dangerous. Refer to the vehicle's service manual for specific instructions on working with airbag systems. It's often best to leave these to professionals.
Disclaimer: While this article provides guidance, automotive electrical systems can be complex. If you are not comfortable working on electrical systems, it is best to consult a qualified mechanic.
We have a detailed and downloadable 2011 Nissan Armada fuse box diagram available. This comprehensive resource provides all the information you need to effectively troubleshoot and repair your vehicle's electrical system. With this diagram in hand, you'll be well-equipped to tackle a wide range of electrical tasks with confidence.
