2011 Nissan Versa Fuse Box Diagram
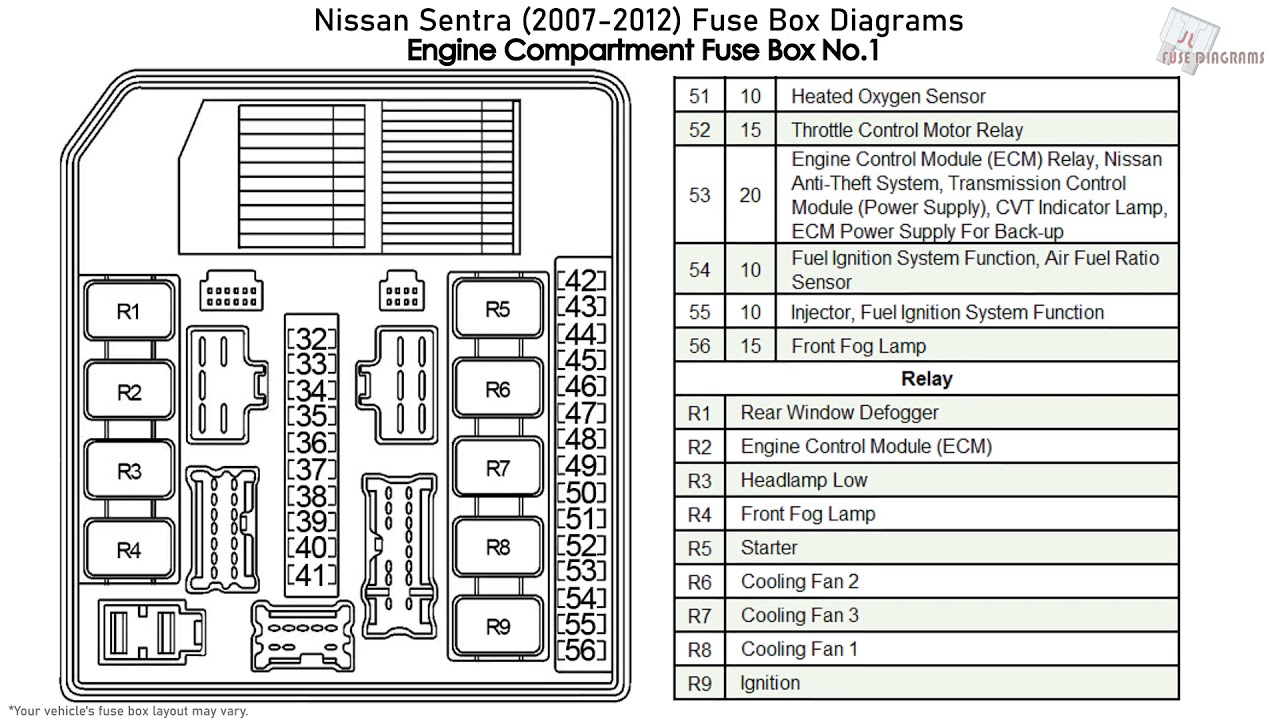
Alright, let's dive into the fuse box diagram for the 2011 Nissan Versa. Understanding this diagram is crucial for various reasons, from simple troubleshooting to more complex electrical modifications. Think of it as the roadmap to your car's electrical system. Whether you're dealing with a blown fuse, installing aftermarket accessories, or just trying to understand how a specific circuit works, this diagram is your best friend. This article will break down the key aspects, symbols, and practical uses of the 2011 Versa's fuse box diagram, so you can confidently tackle your automotive electrical projects.
Why You Need This Diagram
The 2011 Nissan Versa fuse box diagram serves several important purposes:
- Troubleshooting: Quickly identify and locate the fuse responsible for a malfunctioning component. Instead of blindly checking every fuse, you can pinpoint the exact one based on the affected system (e.g., headlights, radio, power windows).
- Repairing: Replacing a blown fuse is a simple repair, but only if you know which one to replace and the correct amperage. The diagram provides this crucial information.
- Modifications: When adding aftermarket accessories like amplifiers, lights, or remote starters, you need to tap into the car's electrical system safely. The diagram helps you find suitable power sources and protect new circuits with appropriate fuses.
- Learning: Understanding the fuse box layout provides valuable insight into how the vehicle's electrical system is designed and how different components are interconnected. This knowledge empowers you to perform more advanced diagnostics and repairs.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2011 Nissan Versa typically has two main fuse box locations:
- Interior Fuse Box: Usually located under the dashboard, often on the driver's side. This box primarily houses fuses for interior components like the radio, lights, power windows, and climate control system.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Found in the engine bay, this box contains fuses for critical engine components such as the fuel pump, ignition system, engine control unit (ECU), and headlights. It also may contain relays.
Each fuse box contains a variety of fuses and relays, each protecting a specific electrical circuit. The amperage rating of each fuse is crucial. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating than specified can damage the circuit it's intended to protect.
Essential Components:
- Fuses: These are sacrificial devices designed to break the circuit if the current exceeds a safe level. They protect the wiring and components from overheating and potential fire. Common fuse types include blade fuses (ATO/ATC), mini blade fuses, and occasionally cartridge fuses.
- Relays: Electrically operated switches that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. Relays are used to control components like headlights, starter motors, and fuel pumps. A relay consists of a coil and contacts. When the coil is energized, it closes the contacts, allowing current to flow through the circuit.
- Fuse Puller: A small plastic tool used to safely remove fuses from the fuse box. Avoid using metal tools, as they can cause short circuits.
Understanding the Diagram's Symbols
Fuse box diagrams use standardized symbols to represent various components and connections. Here's a breakdown of common symbols:
- Lines: Represent electrical wires or circuits. Thicker lines may indicate higher current carrying capacity. Dashed lines can indicate a ground connection or a signal wire.
- Rectangles: Typically represent fuses. The number inside the rectangle indicates the amperage rating of the fuse (e.g., 10A, 15A, 20A).
- Squares or Circles with Internal Markings: Usually represent relays. The internal markings may indicate the type of relay or its function (e.g., fuel pump relay, headlight relay).
- Ground Symbol (Typically three lines descending to a point): Indicates a connection to the vehicle's chassis, providing a return path for the electrical current.
- Component Icons: Small icons may represent specific components like headlights, turn signals, or the horn. These icons help you quickly identify the fuse or relay associated with that component.
Color coding can sometimes be used in fuse box diagrams. For example, different colors may represent different voltage levels or circuit types. However, color coding is not always standardized and may vary between diagrams. Always refer to the legend or key that accompanies the diagram to understand the meaning of any color codes used.
How It Works: Circuit Protection
The 2011 Nissan Versa's electrical system is designed with multiple circuits, each protected by a fuse. When an electrical overload occurs (e.g., a short circuit), the excessive current flowing through the circuit causes the fuse's internal element to melt, breaking the circuit and preventing damage to the wiring and components.
Relays, on the other hand, act as intermediaries. They allow a low-current signal from a switch or sensor to control a high-current component. For example, the headlight switch activates a relay that then supplies power to the headlights. This arrangement prevents the headlight switch from having to handle the high current required by the headlights, which could damage the switch.
The fuse box diagram illustrates how these fuses and relays are connected to various circuits and components. By tracing the lines on the diagram, you can follow the flow of electricity through the system and identify potential points of failure.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how to use the fuse box diagram for basic troubleshooting:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which component or system is malfunctioning (e.g., the radio isn't working, the headlights are dim).
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse or relay associated with the malfunctioning component in the fuse box diagram. Always consult the owner's manual alongside the diagram for clarification.
- Locate the Fuse/Relay: Find the corresponding fuse or relay in the physical fuse box. Use the diagram as a guide to locate the correct position.
- Inspect the Fuse: Visually inspect the fuse. If the element inside the fuse is broken or blackened, the fuse is blown and needs to be replaced.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating. Using a higher amperage fuse can be extremely dangerous.
- Test the System: After replacing the fuse, test the component to see if it's working again. If the fuse blows again immediately, there's likely a more serious problem in the circuit that needs further investigation. This may involve a short circuit or a faulty component.
Safety First: Risky Components
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous if proper precautions are not taken. Here are some important safety considerations:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical component, always disconnect the negative battery cable. This will prevent accidental short circuits and electrical shocks.
- Avoid Working on Live Circuits: Never work on live circuits unless absolutely necessary for testing purposes. Use a multimeter to verify that a circuit is de-energized before touching any wires or components.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools designed for automotive electrical work. Avoid using metal tools that could cause short circuits.
- Identify High-Current Components: Be extra cautious when working near high-current components like the starter motor, alternator, and battery. These components can deliver a powerful electrical shock.
- Do Not Bypass Fuses: Never bypass a fuse with a wire or other conductive material. This eliminates the circuit protection and can lead to overheating, fire, and damage to the vehicle's electrical system.
- ECU and Airbag systems: Handle with extreme care. Interference or accidental shorting of certain circuits related to the ECU (Engine Control Unit) or Airbag systems can cause malfunctions or even deployment, which can be dangerous and costly to repair.
Always consult a qualified mechanic if you are unsure about any aspect of the electrical system or if you encounter a problem that you cannot resolve yourself.
Remember that electrical systems can be complex. If you are not comfortable working on your car's electrical system, it is best to leave it to a professional.
We have a downloadable version of the 2011 Nissan Versa Fuse Box Diagram file available. This will allow you to zoom in on specific areas and print it out for easy reference while you're working on your car.
