2012 Chevy Impala 3.6 Serpentine Belt Diagram
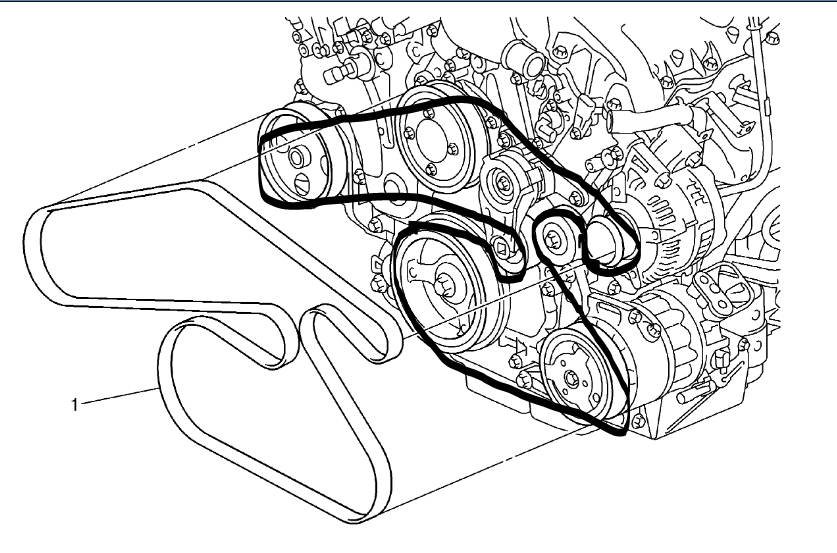
Alright, let's dive into the serpentine belt diagram for your 2012 Chevy Impala equipped with the 3.6L V6 engine. This isn't just a pretty picture; it's your roadmap to understanding, diagnosing, and potentially fixing issues related to your car's vital accessories. Whether you're tackling a squealing belt, replacing a failing component, or simply want a better understanding of how your engine bay is laid out, having a solid grasp of this diagram is crucial.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
The serpentine belt diagram serves several critical purposes. Its primary role is to illustrate the belt's routing path. Without it, reassembling the belt after replacement or repairs becomes a frustrating guessing game. It also helps in diagnosing issues. For example, a specific component's failure can lead to a chain reaction affecting others in the belt's path. Furthermore, understanding the diagram helps in identifying potential wear points and anticipating future maintenance needs. It's invaluable for anyone looking to perform preventative maintenance or troubleshoot existing problems.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2012 Impala 3.6L uses a single serpentine belt to drive several essential accessories. Knowing these components and their roles is key to interpreting the diagram:
- Crankshaft Pulley (Harmonic Balancer): This is the driving force behind the entire system. Connected directly to the engine's crankshaft, it's the starting point for the belt's journey. It absorbs torsional vibrations from the engine's firing pulses, minimizing wear and tear on other components.
- Alternator Pulley: The alternator generates the electrical power needed to run your car's electrical system and charge the battery. A failing alternator can lead to a dead battery and a host of electrical issues.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: This pump provides the hydraulic pressure necessary for power-assisted steering. Problems here can result in hard steering, especially at low speeds.
- Air Conditioning (A/C) Compressor Pulley: The A/C compressor circulates refrigerant to cool the cabin. A faulty compressor can mean no cold air.
- Water Pump Pulley: The water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine, preventing overheating. Overheating can cause severe engine damage.
- Tensioner Pulley: This spring-loaded pulley maintains proper tension on the serpentine belt, preventing slippage and premature wear. A weak tensioner can lead to squealing belts and reduced component performance. This tensioner is critical for the system to work correctly.
- Idler Pulley (if equipped): Some Impalas might have an idler pulley. This is a smooth pulley that guides the belt around other components, optimizing the wrap angle and preventing interference.
The serpentine belt itself is typically made of a durable, reinforced rubber compound. The belt's length and width are specific to the 2012 Impala 3.6L, so ensure you get the correct replacement part. Incorrect belt dimensions can lead to improper tension and component damage.
Symbols and Diagram Interpretation
Serpentine belt diagrams use specific conventions to convey information clearly:
- Solid Lines: Typically represent the path of the serpentine belt itself. Follow the line to trace the belt's routing around the various pulleys.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of belt travel around each pulley. This is crucial for ensuring correct installation.
- Component Symbols: Each component is represented by a simplified symbol, usually a circle or pulley shape, labeled with its corresponding name (e.g., ALT for alternator, P/S for power steering).
- Tensioner Symbol: The tensioner is often represented with a spring symbol, indicating its spring-loaded mechanism.
- Routing Details: Some diagrams show the grooved side and smooth side of the belt to help guide the installer.
Understanding these symbols allows you to effectively "read" the diagram and visualize the belt's routing in your engine bay. Pay close attention to the arrows and component labels.
How It Works
The serpentine belt system is a relatively simple, yet vital system. The crankshaft pulley, driven by the engine, provides the rotational power. This power is transferred via the serpentine belt to all the accessory pulleys. The belt's friction against each pulley causes it to spin, powering the attached component. The tensioner pulley keeps the belt taut, ensuring consistent contact with each pulley and preventing slippage. A properly tensioned belt is essential for optimal component performance and longevity.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting
The serpentine belt diagram becomes invaluable when troubleshooting issues. Here are a few scenarios:
- Squealing Belt: A squealing belt often indicates slippage. Using the diagram, inspect the tensioner pulley. Is it moving freely? Is the belt properly seated in all the pulleys? Check for signs of oil or coolant contamination on the belt, which can reduce friction.
- Accessory Failure: If the A/C isn't blowing cold, the power steering is difficult, or the alternator isn't charging, use the diagram to check the belt's routing to the corresponding pulley. Is the belt intact? Is it properly engaged? Sometimes, a failing component can seize, causing the belt to break.
- Belt Replacement: Before removing the old belt, carefully study the diagram or take a photo of the belt's routing. This will save you a lot of headaches during reinstallation. Use the diagram to confirm the new belt is routed correctly before releasing the tensioner.
If a component is failing, the diagram will help you to determine if its failure is directly related to the serpentine belt system or if other causes are in play. For instance, a faulty alternator is likely an electrical problem in the alternator itself, but you can still check the belt path to rule out an obvious mechanical issue. If the belt is very worn or frayed, it may affect voltage output and performance.
Safety Considerations
Working around the serpentine belt system involves inherent risks. Here are some critical safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on the serpentine belt system. This prevents accidental starting and potential injury from moving parts.
- Engine Cooling: Never work on the system when the engine is hot. Allow the engine to cool completely before attempting any repairs. The engine and coolant will burn you.
- Moving Parts: Keep hands, tools, and loose clothing away from the belt and pulleys when the engine is running. Even a momentarily engaged engine with the belt running can cause serious injury.
- Tensioner Spring: The tensioner pulley spring is under considerable tension. Use the correct tools and techniques to release the tension safely. Improper handling can result in injury or damage to the tensioner.
Special care should be taken around the crankshaft pulley. It's directly linked to the engine and will start spinning immediately upon ignition. Avoid any contact with it when the engine is running.
Always wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris. Consider wearing gloves to protect your hands from grease and sharp edges.
With this knowledge and the right serpentine belt diagram, you are well-equipped to diagnose and tackle serpentine belt-related issues on your 2012 Chevy Impala 3.6L. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult a qualified mechanic if you're unsure about any aspect of the repair.
For your convenience, we have the complete serpentine belt diagram for the 2012 Chevy Impala 3.6L V6 engine available for download. This high-resolution file will provide you with a clear and detailed reference for all your repairs and maintenance needs.
