2012 Dodge Grand Caravan 3.6 Serpentine Belt Diagram
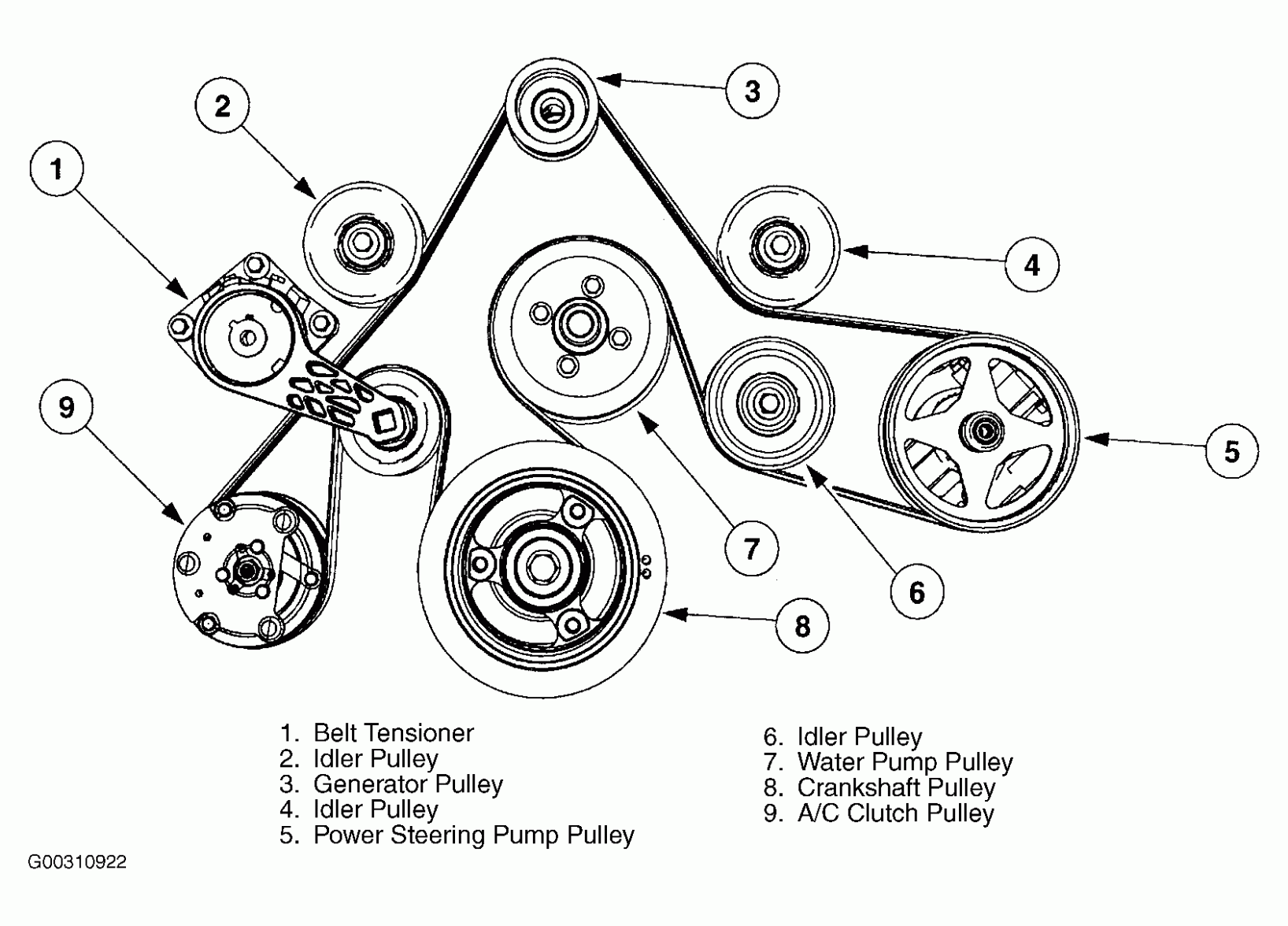
Alright, let's dive into the serpentine belt diagram for a 2012 Dodge Grand Caravan with the 3.6L Pentastar V6 engine. Understanding this diagram is crucial for anyone tackling repairs, preventative maintenance, or even just expanding their automotive knowledge. It's your roadmap to successfully navigating the belt system, ensuring everything runs smoothly and preventing costly breakdowns.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
The serpentine belt diagram, also known as a belt routing diagram, serves as a visual guide for the correct installation and routing of the serpentine belt around various engine components. Its primary purpose is to ensure the belt is installed correctly, driving the accessories at the proper speeds and in the correct direction. Without the diagram, you risk incorrect installation, leading to premature belt wear, accessory malfunction, and potentially serious engine damage. Consider it the "treasure map" for your engine bay's belt system.
You'll need this diagram for several situations:
- Belt Replacement: Obviously, when replacing a worn or damaged serpentine belt, the diagram ensures you route the new belt exactly as the old one was.
- Accessory Repair/Replacement: If you're replacing the alternator, power steering pump, AC compressor, or any other accessory driven by the belt, you'll need to remove and reinstall the belt, relying on the diagram for correct routing.
- Troubleshooting: The diagram can help you identify potential issues, like a misrouted belt causing noise or accessory malfunction.
- General Understanding: Even if you aren't actively working on the system, knowing the belt's path helps you understand how the engine accessories are powered and how to diagnose related problems.
Key Specs and Main Parts (2012 Grand Caravan 3.6L)
For the 2012 Dodge Grand Caravan with the 3.6L Pentastar V6, you'll generally find the belt routing diagram sticker under the hood, often near the radiator support or on the underside of the hood itself. Always refer to *that* diagram if available, as variations can exist. However, a general understanding of the key components is essential.
- Serpentine Belt: This is the main driving force, a long, continuous belt made of rubber and reinforced cords.
- Crankshaft Pulley (or Harmonic Balancer): The crankshaft pulley is directly connected to the engine's crankshaft. It's the primary driver of the serpentine belt system.
- Alternator Pulley: The alternator generates electricity to power the car's electrical system and charge the battery.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: The power steering pump provides hydraulic pressure to assist steering.
- AC Compressor Pulley: The AC compressor circulates refrigerant in the air conditioning system.
- Idler Pulley(s): Idler pulleys are smooth pulleys that guide the belt and maintain proper tension. They don't drive any accessories.
- Tensioner Pulley: The tensioner pulley is spring-loaded to maintain constant tension on the serpentine belt. This is *critical* for proper operation. A weak tensioner can cause belt slippage, noise, and premature wear.
- Water Pump Pulley: The water pump circulates coolant through the engine to prevent overheating.
Belt Length: The exact belt length will vary depending on the specific configuration of your van (e.g., with or without rear air conditioning). However, it typically falls within the range of 90-95 inches. Always use the part number specified for your vehicle's VIN to ensure the correct fit. A belt that's too long will slip, and one that's too short won't fit at all.
Symbols and Markings on the Diagram
Diagrams use standardized symbols to represent different components and the belt's path. Here's what to look for:
- Solid Lines: A solid line represents the outer surface of the serpentine belt. This is the side that makes contact with the grooved pulleys.
- Dotted Lines: A dotted line usually indicates the backside of the belt. This smooth side typically contacts idler pulleys.
- Arrows: Arrows on the belt path show the direction of belt rotation. This is crucial for understanding how each accessory is driven.
- Component Labels: Abbreviations like "ALT" (alternator), "P/S" (power steering), "A/C" (air conditioning), "CRANK" (crankshaft), "IDLR" (idler), "TENS" (tensioner), and "W/P" (water pump) are used to identify each pulley.
- Grooved vs. Smooth Pulleys: The diagram might subtly indicate grooved pulleys (which contact the ribbed side of the belt) and smooth pulleys (which contact the back of the belt). Look for slightly different shading or texture on the pulley representation.
How It Works
The serpentine belt system is a relatively simple, yet ingenious, mechanism. The crankshaft pulley, driven by the engine's rotation, transfers power to the other accessories via the serpentine belt. The belt wraps around each pulley, and friction between the belt and the pulley surface causes the accessory to rotate. The tensioner pulley maintains constant tension on the belt, preventing slippage. If the belt is too loose, it will slip, leading to reduced accessory performance (e.g., dim headlights from a poorly charging alternator, weak power steering, or ineffective air conditioning). If the belt is too tight, it can put excessive stress on the accessory bearings, leading to premature failure.
Real-World Use and Basic Troubleshooting
Here are some practical troubleshooting tips using the serpentine belt diagram:
- Squealing Noise: A squealing noise, especially when the engine is cold or under load (e.g., turning the steering wheel at low speeds), is a common symptom of a loose or worn serpentine belt. Check the tensioner to ensure it's applying adequate pressure. Also, inspect the belt for cracks, glazing (a shiny appearance), or missing ribs. A worn belt will lose its grip.
- Accessory Malfunction: If an accessory suddenly stops working (e.g., the air conditioning stops blowing cold), check the belt routing and condition. Make sure the belt is still intact and properly routed around the affected accessory's pulley. A broken belt will immediately disable all accessories.
- Belt Wear Patterns: Examine the old belt for uneven wear. If one side of the belt is more worn than the other, it could indicate a misaligned pulley. Use a straight edge to check the alignment of the pulleys. Misalignment creates friction and premature wear.
- Tensioner Movement: Observe the tensioner pulley while the engine is running. Excessive "bouncing" or movement of the tensioner can indicate a worn tensioner or a problem with the belt itself. A faulty tensioner can cause the belt to slip and wear out quickly.
Safety Precautions
Working with the serpentine belt system involves some inherent risks. Here's what to keep in mind:
- Engine Off: Always work on the serpentine belt system with the engine off and the key removed from the ignition. Accidental engagement of the engine while your hands are near the belt or pulleys can result in serious injury.
- Battery Disconnect: Disconnecting the negative battery cable is a good practice to prevent accidental starting and protect electrical components.
- Moving Parts: Be extremely cautious of the moving parts when the engine is running. Never reach near the belt or pulleys while the engine is on.
- Hot Engine: Allow the engine to cool down before working on the serpentine belt system. Components can get very hot, leading to burns.
- Protective Gear: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
The tensioner pulley is under significant spring pressure. When releasing the tension on the belt, use the correct tool (usually a wrench or socket on the tensioner pulley's bolt) and apply steady, controlled pressure. Releasing the tension too quickly can cause the tensioner to snap back with considerable force, potentially causing injury.
Remember, this is a guide, and every vehicle can have slight variations. Refer to your vehicle's specific diagram whenever possible. If you're uncomfortable performing this work yourself, consult a qualified mechanic.
We have the serpentine belt diagram file available for download. Please reach out to access it.
