2012 Hyundai Tucson Fuse Box Diagram
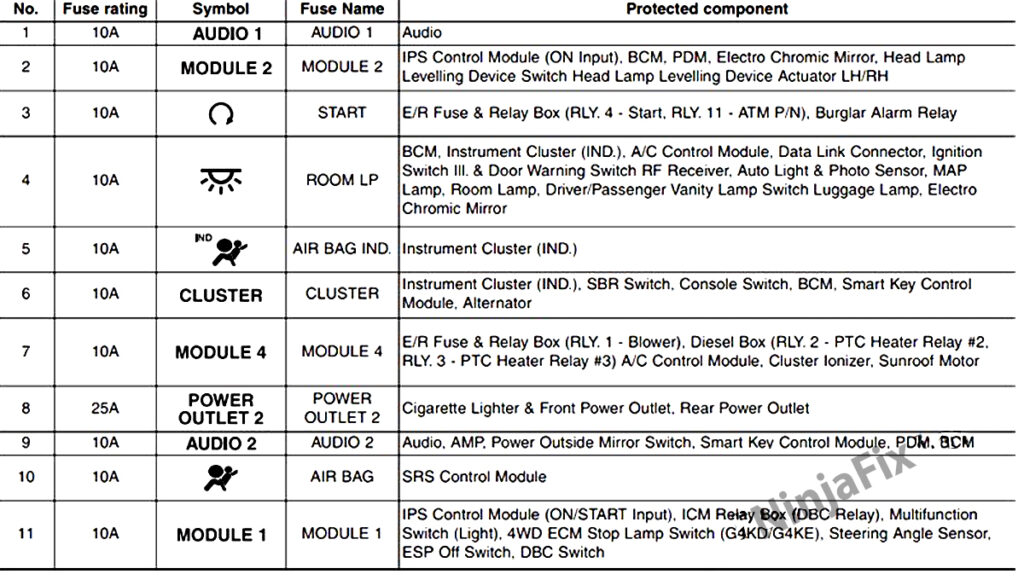
Alright, let's dive into the 2012 Hyundai Tucson fuse box diagram. If you're tinkering with your Tucson's electrical system, whether it's for routine repairs, installing aftermarket accessories, or just understanding how things work, knowing your way around the fuse box is absolutely crucial. This article will equip you with the knowledge to decipher the diagram, understand the function of each fuse, and troubleshoot common electrical issues.
Why Bother with the Fuse Box Diagram?
Why should you care about this seemingly arcane piece of paper? The fuse box diagram is your roadmap to the electrical system. Without it, you're basically poking around in the dark. Here's why it's indispensable:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: When something electrical malfunctions – a light bulb stops working, the radio cuts out, or the power windows fail – the first place to check is the fuse box. The diagram identifies which fuse controls that circuit.
- Installing Aftermarket Accessories: Adding a new stereo, amplifier, lighting, or any other electrical component requires tapping into the existing electrical system. The diagram helps you find appropriate circuits and ensure you're using the correct fuse amperage to protect your vehicle.
- Understanding Vehicle Systems: Even if you're not currently experiencing any problems, studying the fuse box diagram offers valuable insight into how your Tucson's electrical systems are organized and interconnected. It helps you understand what each system controls and how it's protected.
- Preventing Further Damage: Replacing a blown fuse with the wrong amperage can overload the circuit and cause damage to wiring, components, or even start a fire. The diagram provides the correct fuse ratings for each circuit.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2012 Hyundai Tucson actually has multiple fuse boxes. The primary one we'll focus on is the interior fuse box, usually located under the dashboard on the driver's side. There's also a engine compartment fuse box, typically situated near the battery. The diagram encompasses both, detailing the fuses and relays in each location. Key specs to note include:
- Fuse Amperage: Fuses are rated in amperes (A), which indicates the maximum current they can handle before blowing. Common ratings include 5A, 7.5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, 30A, and even higher for specific components.
- Fuse Types: The 2012 Tucson primarily uses blade-type fuses, which are color-coded to indicate their amperage. Mini blade fuses may also be present.
- Relays: Relays are electromechanical switches that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. They're used for components like headlights, fuel pump, and starter motor. The diagram shows their location and function.
- Main ECU (Engine Control Unit) Fuses: Protecting the ECU is paramount. These fuses are crucial for the vehicle's overall operation and should be checked carefully if you suspect engine-related issues.
The main parts of a typical fuse box diagram are:
- Layout Diagram: A visual representation of the fuse box, showing the physical location of each fuse and relay.
- Fuse/Relay Table: A table that lists each fuse and relay, along with its amperage rating and the component or system it protects. This table is usually cross-referenced to the layout diagram using numbers or letters.
Decoding the Symbols: Lines, Colors, and Icons
Understanding the symbols on the diagram is essential for accurate interpretation. Here's a breakdown of common symbols:
- Fuse Representation: Fuses are typically represented by a rectangular box with a line running through it, often accompanied by the amperage rating.
- Relay Representation: Relays are usually depicted as a square or rectangle with internal symbols representing the coil and contacts.
- Lines: Lines indicate the electrical circuits. Thicker lines might represent higher current circuits.
- Colors: Color-coding on the diagram can sometimes indicate the wire color in the actual vehicle harness. While not always a perfect match, it can be a helpful reference.
- Icons: Icons are used to represent the component or system that the fuse protects. For example, a headlight icon, a radio icon, or a window icon. The manual typically lists what all the icons mean.
Pay close attention to the abbreviations used. Some common ones include:
- ECU: Engine Control Unit
- ABS: Anti-lock Braking System
- SRS: Supplemental Restraint System (Airbags)
- IGN: Ignition
- ACC: Accessory
How It Works: From Battery to Component
Let's trace the path of electricity through a simplified circuit to illustrate how the fuse box functions. Imagine you want to power your radio. The process goes something like this:
- Power Source: The battery provides the initial electrical power.
- Circuit Path: The electricity flows from the battery, through the wiring harness, to the fuse box.
- Fuse Protection: The electricity passes through the fuse that's designated for the radio circuit. If the current draw exceeds the fuse's amperage rating (e.g., 15A), the fuse's internal element melts, breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity. This protects the radio and the wiring from damage.
- Radio Operation: If the fuse is intact, the electricity continues to the radio, allowing it to function.
- Ground Path: After powering the radio, the electricity returns to the battery through a ground connection, completing the circuit.
The fuse box acts as a central distribution point and a safety mechanism, preventing overloads and short circuits from damaging sensitive electrical components.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some practical troubleshooting tips using the fuse box diagram:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which component or system is malfunctioning.
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse or relay associated with the affected component in the fuse box diagram.
- Inspect the Fuse: Visually inspect the fuse. A blown fuse will have a broken filament inside.
- Test the Fuse: Use a multimeter to test the fuse for continuity. A working fuse will have continuity; a blown fuse will not. Set your multimeter to the continuity setting (usually indicated by a diode symbol or a sound wave symbol). Place the probes on each metal contact of the fuse. A beep or a reading of close to 0 ohms indicates continuity.
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a fuse of the same amperage rating. Never use a higher amperage fuse, as this could damage the circuit.
- Check for Shorts: If the new fuse blows immediately, there's likely a short circuit in the wiring or the component itself. Further investigation is needed to locate and repair the short before replacing the fuse again.
Important Note: If you're repeatedly blowing fuses, it's a sign of a more serious electrical problem that requires professional diagnosis and repair.
Safety First: Risky Components
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some safety precautions to keep in mind:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on the fuse box, disconnect the negative (-) terminal of the battery to prevent accidental shorts or electrical shocks.
- Airbag System: The airbag (SRS) system is highly sensitive. Incorrectly handling airbag-related fuses or wiring can cause accidental deployment, resulting in serious injury. If you're unsure, consult a qualified technician.
- High-Current Circuits: Be cautious when working with high-current circuits, such as those for the starter motor or alternator. These circuits can deliver a powerful shock.
- Proper Tools: Use insulated tools and wear appropriate safety gear, such as safety glasses and gloves.
- Never bypass a fuse: Bypassing a fuse with a wire or other conductive material is extremely dangerous and can cause a fire.
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) fuses and relays are essential. Handle with care. A faulty ECU can lead to a no-start condition or major performance issues.
By understanding the 2012 Hyundai Tucson fuse box diagram, you'll be better equipped to maintain and troubleshoot your vehicle's electrical system safely and effectively. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult a qualified technician if you're unsure about any aspect of the repair process.
