2012 Infiniti Qx56 Fuse Box Diagram
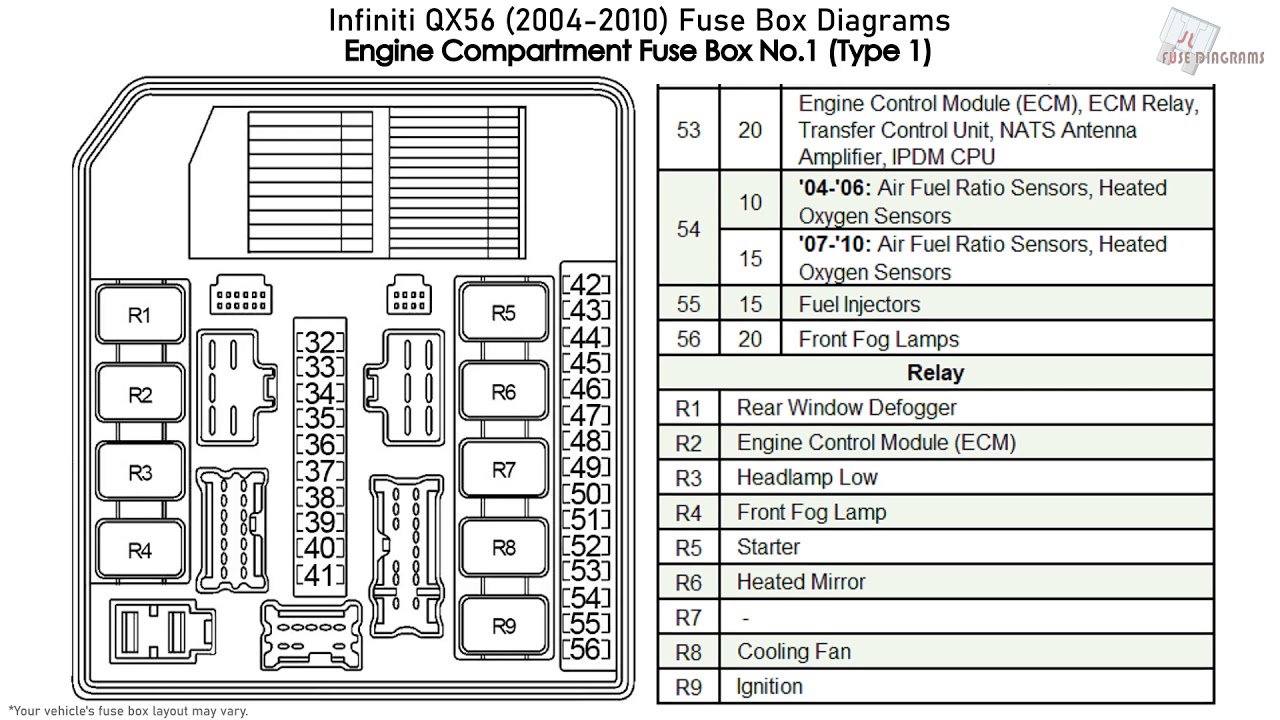
Alright, let's dive into the fuse box diagram for the 2012 Infiniti QX56. If you're tinkering with your electrical system, doing some modifications, or just trying to diagnose a pesky issue, understanding this diagram is absolutely crucial. It's your roadmap to the electrical arteries of your vehicle.
Why You Need This Diagram
Think of the fuse box diagram as the Rosetta Stone of your QX56's electrical system. It's essential for:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Issues: Identify blown fuses quickly to resolve problems like malfunctioning lights, power windows, or the audio system.
- Installing Aftermarket Accessories: Safely tap into the electrical system to add new components like auxiliary lights, subwoofers, or a remote starter.
- Understanding the Electrical System: Gain a deeper understanding of how different circuits are protected and interconnected.
- Preventing Further Damage: Replacing a fuse with the wrong amperage can cause serious damage to components and even lead to a fire. The diagram helps you avoid this.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2012 QX56 typically has multiple fuse boxes located in different areas of the vehicle. The most common locations are:
- Interior Fuse Box: Usually located under the dashboard, on the driver's side, or sometimes in the passenger side footwell. This box generally controls circuits for interior components like lights, power windows, and the infotainment system.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Found under the hood, near the engine. This box protects critical engine management systems, headlights, and other high-current circuits.
- Battery Junction Box (BJB): Some models also have a BJB located near the battery itself. This handles very high-current circuits like the starter motor and alternator.
Key Specifications:
- Fuse Types: The QX56 typically uses blade-type fuses (ATO, ATC, mini-blade) and some cartridge fuses for higher amperage circuits.
- Voltage: All circuits are designed for a 12V DC (Direct Current) system.
- Amperage Ratings: Fuses are rated in Amps (A). Common ratings include 5A, 7.5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, 30A, and higher. Always replace a blown fuse with one of the same amperage rating.
Decoding the Symbols: Lines, Colors, and Icons
The fuse box diagram uses a specific set of symbols to represent different components and connections. Here's a breakdown of the common elements:
- Lines: Solid lines represent electrical wires. Dashed lines may indicate a shielded wire or a ground connection.
- Colors: Wire colors are often indicated on the diagram using abbreviations (e.g., BLK for black, RED for red, BLU for blue, GRN for green, YEL for yellow). These colors help you trace wires physically in the vehicle.
- Icons: Icons represent specific components. Common icons include:
- Fuse Symbol: A zigzag line inside a rectangle.
- Relay Symbol: A rectangle with a coil and switch depicted inside. A relay is an electrically operated switch that allows a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit.
- Connector Symbol: A circle or rectangle with pins indicating where wires connect.
- Ground Symbol: A series of horizontal lines decreasing in size, representing a connection to the vehicle's chassis (ground).
- Component Symbols: Specific icons for lights, motors, sensors, and other electrical devices. Consult the diagram's legend for a full list.
- Numbers and Letters: Each fuse, relay, and connector is usually assigned a number or letter code for easy identification.
How It Works: The Circuit Protection System
The fuse box is designed to protect the electrical circuits of your QX56 from overcurrent conditions. Here's how it works:
- Normal Operation: Under normal operating conditions, electricity flows through the circuit, including the fuse. The fuse acts as a weak point in the circuit.
- Overcurrent Condition: If there's a short circuit (e.g., a wire chafes and touches the chassis) or an overload (e.g., too many devices drawing power from the same circuit), the current flow dramatically increases.
- Fuse Blows: The excessive current causes the fuse element (a thin strip of metal inside the fuse) to melt and break the circuit. This stops the flow of electricity and prevents damage to the wiring and components.
- Circuit Isolation: By blowing the fuse, the faulty circuit is isolated from the rest of the electrical system, preventing a cascading failure.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting tips using the fuse box diagram:
- Identify the Symptom: What's not working? (e.g., headlights, radio, power windows).
- Locate the Relevant Fuse: Consult the fuse box diagram to find the fuse associated with the malfunctioning component. The diagram will tell you the fuse location (e.g., "Fuse #12, Interior Fuse Box") and its amperage rating (e.g., "15A").
- Inspect the Fuse: Remove the fuse using a fuse puller (a small plastic tool designed for this purpose) and visually inspect it. A blown fuse will have a broken filament.
- Test the Fuse: Use a multimeter set to continuity mode to test the fuse. A good fuse will show continuity (a beep or a reading close to zero ohms). A blown fuse will show no continuity (an open circuit).
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating. Never use a higher amperage fuse.
- Test the Circuit: After replacing the fuse, test the circuit to see if the problem is resolved.
- If the Fuse Blows Again: If the new fuse blows immediately or shortly after replacement, there's likely a more serious problem in the circuit, such as a short circuit or an overloaded circuit. Further diagnosis by a qualified technician is recommended.
Safety: Proceed with Caution
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative terminal of the battery before working on the electrical system. This prevents accidental short circuits and electrical shocks.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools designed for automotive electrical work.
- Never Bypass a Fuse: Never replace a fuse with a wire or other conductive material. This can overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- Be Careful Around High-Current Circuits: The battery and starter motor circuits carry very high currents. Avoid touching these circuits while the battery is connected. The Battery Junction Box (BJB) houses these high-current fuses and relays. Proceed with extreme caution around this area.
- If You're Unsure, Seek Professional Help: If you're not comfortable working on the electrical system, consult a qualified automotive technician.
Remember, the fuse box diagram is your guide, but it's only as good as your understanding of it. Take your time, be methodical, and prioritize safety.
We have a high-resolution, downloadable version of the 2012 Infiniti QX56 fuse box diagram ready for you. Having it on hand will be a great asset when you're working on your vehicle.
