2012 Nissan Altima Exhaust System Diagram
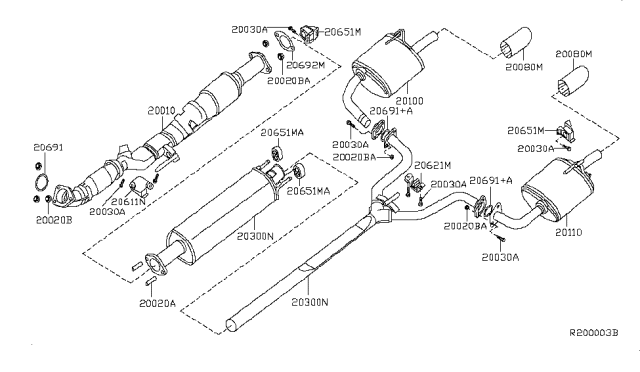
Welcome, fellow wrench-turners! Today, we’re diving deep into the heart of your 2012 Nissan Altima: its exhaust system. This isn't just about making noise; it's a critical component that affects performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. Understanding the exhaust system is crucial for everything from routine maintenance to diagnosing that pesky check engine light. We've got the detailed 2012 Nissan Altima exhaust system diagram available for you (details on downloading it are at the end of this article), and this guide will help you decipher it and use it effectively.
Purpose of Understanding the Exhaust System Diagram
Why bother understanding this diagram? Plenty of reasons! First, it's invaluable for diagnosing and repairing exhaust-related issues. Is your car suddenly louder? Are you experiencing a loss of power? The diagram will help you pinpoint the source. Second, if you're considering any modifications, such as installing an aftermarket exhaust, knowing the system's layout is essential to ensure a proper and legal installation. Finally, even if you're not planning any major work, studying the diagram provides a deeper understanding of how your car works, making you a more informed and capable car owner.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 2012 Altima Exhaust System
Let's break down the 2012 Altima's exhaust system. Keep in mind that specific configurations might vary slightly depending on the engine (2.5L I4 or 3.5L V6), but the fundamental components remain the same:
- Exhaust Manifold (or Headers): Bolted directly to the engine's cylinder head, the manifold collects exhaust gases from each cylinder. The 2.5L engine typically has an integrated exhaust manifold with the catalytic converter. The V6 usually has separate manifolds for each bank.
- Catalytic Converter(s): A critical emission control device. It uses chemical reactions to convert harmful pollutants like hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and nitrogen (N2). The Altima may have one or two catalytic converters depending on the engine.
- Resonator: This component helps to reduce specific frequencies of sound, contributing to a quieter and more refined exhaust note. It's essentially a pre-muffler that dampens certain sound waves.
- Muffler: The primary device for reducing exhaust noise. It uses a series of chambers and baffles to dampen sound waves.
- Piping: Connects all the exhaust components. Typically made of steel, the piping needs to be durable enough to withstand high temperatures and corrosive gases. Pay attention to pipe diameter as this affects exhaust flow.
- Oxygen Sensors (O2 Sensors): Located before (upstream) and after (downstream) the catalytic converter(s). They measure the oxygen content in the exhaust gas and provide feedback to the engine control unit (ECU) to optimize the air-fuel mixture and monitor the converter's efficiency.
- Flanges and Gaskets: Used to connect different exhaust components. Gaskets ensure a tight seal to prevent exhaust leaks.
- Hangers and Mounts: Support the exhaust system and dampen vibrations.
Symbols on the Exhaust System Diagram
The diagram uses specific symbols to represent different components and features. Here’s a general guide:
- Solid Lines: Usually represent the exhaust piping itself. The thickness of the line might indicate the diameter of the pipe.
- Dashed Lines: Might indicate heat shields or other non-structural components. They can also show wiring harnesses for sensors.
- Boxes or Rectangles: Typically represent the catalytic converter, resonator, or muffler. The diagram may include internal details of these components.
- Circles or Ovals: Usually represent sensors, such as oxygen sensors.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of exhaust gas flow.
- Numbers and Labels: Identify specific components, bolt sizes, torque specifications, and part numbers. Refer to the key or legend on the diagram for specific interpretations.
- Color Coding: While not always present, color might indicate different materials (e.g., stainless steel vs. regular steel) or temperature zones. Refer to the diagram's key for details.
Remember to carefully examine the specific diagram for your 2012 Altima, as conventions can vary slightly.
How the Exhaust System Works
The exhaust system's primary function is to remove combustion byproducts from the engine. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
- Exhaust Gases Exit the Engine: Hot exhaust gases are expelled from the engine cylinders and enter the exhaust manifold.
- Catalytic Conversion: The gases flow through the catalytic converter, where harmful pollutants are converted into less harmful substances. The effectiveness of this process is monitored by the downstream O2 sensor.
- Sound Damping: The gases then pass through the resonator and muffler, which dampen the sound waves to reduce noise.
- Exhaust Gases Exit: Finally, the exhaust gases are released into the atmosphere through the tailpipe.
- O2 Sensor Feedback: Upstream O2 sensor(s) measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas coming directly from the engine. This information is sent to the ECU (Engine Control Unit) which adjusts the air/fuel mixture to optimize combustion efficiency.
The O2 sensors play a crucial role in this process. The upstream sensor(s) help the ECU maintain the optimal air-fuel ratio for efficient combustion. The downstream sensor monitors the catalytic converter's performance. If the downstream sensor detects similar oxygen levels as the upstream sensor, it indicates that the converter is not functioning correctly and may trigger a check engine light.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how you can use the diagram to diagnose common exhaust system problems:
- Loud Exhaust: Visually inspect the exhaust system for obvious leaks or damage. Start at the exhaust manifold and work your way back. Pay close attention to joints, welds, and areas prone to rust. The diagram will help you identify the location of specific components. A hissing sound often indicates a leak near the manifold or a cracked manifold. A rattling sound can indicate a loose heat shield or a failing catalytic converter.
- Check Engine Light: Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the trouble codes. Many codes relate to the exhaust system, such as P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold), P0131 (O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage), or P0442 (Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected). The diagram will help you locate the relevant sensor or component.
- Reduced Performance or Fuel Economy: A clogged catalytic converter can restrict exhaust flow, leading to reduced engine performance and fuel economy. The diagram can help you locate the converter and visually inspect it for damage. A backpressure test can also help confirm a clogged converter.
Before replacing any components, always double-check your diagnosis and consult the repair manual for specific procedures. Remember that a faulty O2 sensor can also trigger various trouble codes, so accurate diagnosis is key.
Safety Precautions
Working on the exhaust system can be dangerous. Here are some important safety precautions:
- Hot Exhaust: Always allow the exhaust system to cool completely before working on it. Exhaust components can reach extremely high temperatures, causing severe burns.
- Exhaust Gases: Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling harmful exhaust fumes.
- Lifting the Vehicle: Use jack stands to properly support the vehicle. Never work under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
- Gloves: Wear gloves to protect your hands from sharp edges and contaminants.
- Catalytic Converter Handling: Be cautious when handling catalytic converters, as they may contain precious metals. Follow local regulations for disposal.
When dealing with O2 sensors, be careful not to damage the sensitive sensing element. Avoid dropping them or contaminating them with grease or solvents.
The catalytic converter is a particularly risky component. It operates at high temperatures and contains potentially hazardous materials. Handle it with care and dispose of it properly.
Remember, safety should always be your top priority when working on your car.
Download the 2012 Nissan Altima Exhaust System Diagram
We have the detailed 2012 Nissan Altima exhaust system diagram ready for you to download. This diagram will provide you with the specific layout and component locations for your vehicle. [Provide instructions here on how to download the file, e.g., "Click the link below to download the PDF file." or "Send an email to [email protected] with the subject '2012 Altima Exhaust Diagram' to receive the diagram via email."]. This diagram, coupled with the information provided in this article, should give you a solid foundation for understanding and maintaining your 2012 Altima's exhaust system. Happy wrenching!
