2012 Nissan Rogue Fuse Box Diagram
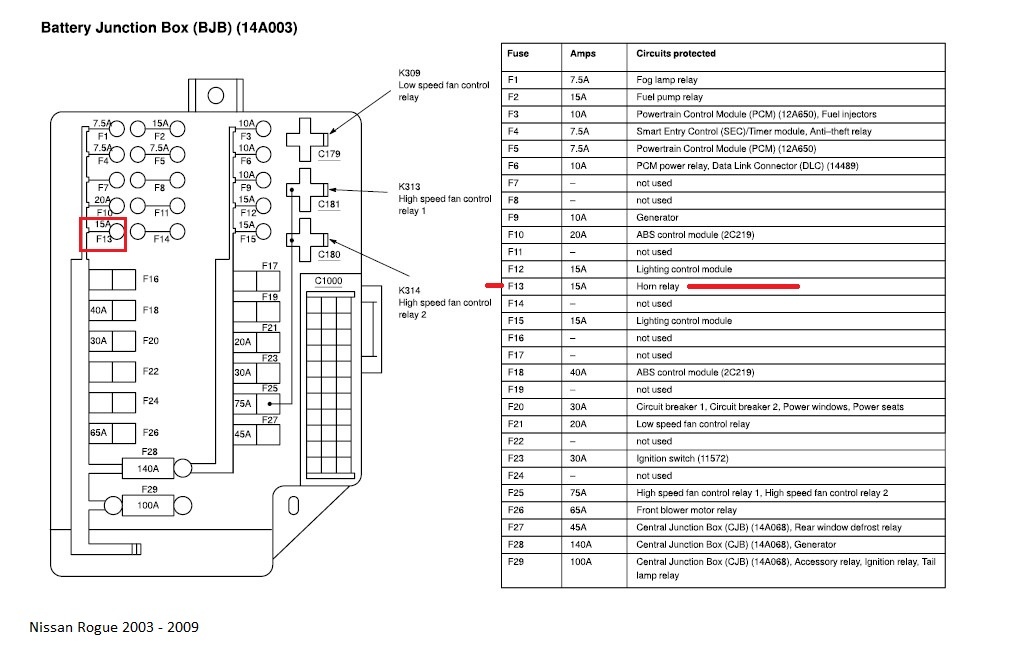
Understanding your vehicle's electrical system is crucial for both routine maintenance and tackling more complex repairs. A key component of that system is the fuse box. Specifically, understanding the 2012 Nissan Rogue fuse box diagram can save you time, money, and potential headaches. This article will serve as a comprehensive guide, demystifying the diagram and empowering you to troubleshoot electrical issues in your Rogue.
Purpose of the 2012 Nissan Rogue Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram is essentially a roadmap to your vehicle's electrical protection system. Its primary purpose is to provide a clear and concise visual representation of each fuse's location and the specific circuit it protects. This is invaluable for several reasons:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: When an electrical component malfunctions (e.g., a blown taillight, a non-functioning radio), the fuse box diagram helps you quickly identify and check the corresponding fuse.
- Performing Repairs: If you're replacing a component or wiring, the diagram shows you which fuse to remove to de-energize the circuit, preventing shorts and potential damage.
- Adding Aftermarket Accessories: If you're adding an aftermarket accessory like a dashcam or upgraded headlights, the diagram can help you find a suitable power source and ensure you're using an appropriately sized fuse to protect the circuit.
- Understanding Vehicle Systems: Even without immediate problems, studying the diagram helps you understand how the different electrical systems in your Rogue are connected and protected.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the Fuse Box
The 2012 Nissan Rogue typically has two fuse boxes: one located inside the cabin (usually under the dashboard on the driver's side) and another in the engine compartment. Each fuse box contains a collection of fuses, relays, and sometimes other electrical components.
- Fuses: These are the primary protective devices. They contain a thin wire that melts and breaks the circuit if the current exceeds a predetermined limit. Fuses are rated in amperes (amps), indicating the maximum current they can handle. Common ratings range from 5A to 30A or higher.
- Relays: These are electromechanical switches that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. They're used to power components like headlights, the starter motor, and the horn.
- Fuse Box Housing: This is the physical enclosure that houses the fuses and relays, protecting them from the environment.
- Fuse Puller: Many fuse boxes include a small plastic tool for removing fuses. Using the correct tool prevents damage to the fuse or the fuse box.
The fuse box diagram itself is typically printed on a label affixed to the inside of the fuse box cover or found in the owner's manual. This label provides a map of the fuse locations and their corresponding circuits.
Understanding Fuse Box Diagram Symbols and Conventions
Fuse box diagrams use a combination of symbols, lines, colors, and text to convey information. Here's a breakdown of common symbols and conventions:
- Fuse Symbols: Fuses are typically represented by a rectangle or a simplified drawing of a fuse. The amperage rating is often printed next to the symbol.
- Relay Symbols: Relays are usually depicted as a square or a rectangle with internal components shown schematically.
- Lines: Lines indicate the electrical connections between the fuses and the components they protect.
- Colors: While not universally standardized, some diagrams use colors to differentiate between different types of circuits (e.g., red for power, black for ground). However, rely primarily on the text labels for circuit identification.
- Text Labels: These are the most crucial part of the diagram. They identify the circuit protected by each fuse, such as "Headlight (Right)," "Radio," or "Fuel Pump."
It's important to note that diagrams can vary slightly depending on the vehicle's trim level and optional equipment. Always refer to the diagram specific to your 2012 Nissan Rogue.
How the Fuse Box Works: A Simplified Explanation
The fuse box serves as a central distribution point for electrical power in your vehicle. Power from the battery is routed through the fuse box, and each circuit is protected by a fuse. When a short circuit or overload occurs, the excessive current causes the fuse's internal wire to melt, breaking the circuit and preventing damage to the wiring and components.
Think of it like a series of small bridges. Each bridge (fuse) is designed to collapse if too much weight (current) is applied, preventing damage to the road (wiring) and the vehicles (components) traveling on it.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how to use the fuse box diagram for basic troubleshooting:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which electrical component is malfunctioning (e.g., the cigarette lighter isn't working).
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse box diagram (usually on the fuse box cover or in the owner's manual).
- Locate the Fuse: Find the fuse that corresponds to the malfunctioning component on the diagram. The diagram might label it "Accessory Power," "Cig Lighter," or something similar.
- Inspect the Fuse: Use a fuse puller to carefully remove the fuse. Visually inspect it. A blown fuse will have a broken or blackened wire inside.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating. Using a higher amperage fuse can damage the circuit.
- Test the Component: Turn on the ignition and test the component to see if it's working.
- If the Fuse Blows Again: If the new fuse blows immediately, there's likely a short circuit in the wiring or the component itself. Further diagnosis and repair are needed. This might involve checking the wiring for damage, disconnecting the component to see if the short disappears, or having the component professionally tested.
Safety Precautions: Handling Risky Components
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some crucial safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative (-) battery terminal to prevent accidental shorts.
- Use the Correct Fuse Rating: Always replace a blown fuse with a fuse of the same amperage rating. Using a higher amperage fuse can overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- Avoid Working in Wet Conditions: Never work on electrical systems in wet or damp environments.
- Be Careful with High-Current Circuits: Circuits related to the starter motor, alternator, and battery carry high currents. Exercise extreme caution when working on these circuits.
- When in doubt, consult a professional: If you're not comfortable working on electrical systems, consult a qualified mechanic.
Specifically, the circuits related to the ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) and airbags should be handled with extreme care. These systems are critical for safety, and improper handling can lead to malfunction or injury. If you suspect a problem with these systems, it's best to take your Rogue to a qualified technician.
Remember: Electricity can be dangerous. Always prioritize safety when working on your vehicle's electrical system. Never attempt to bypass a fuse with a wire or other conductive material. This can create a severe fire hazard.
We understand the importance of having access to the right information. To help you further, we have the complete 2012 Nissan Rogue fuse box diagram file available for download. This diagram is high-resolution and easy to read, ensuring you have the necessary information at your fingertips for any electrical project or repair. Please note that while we strive for accuracy, the diagram should always be verified against the diagram found in your specific vehicle or the official Nissan service manual.
