2012 Silverado 3500 Rear Lighting Plug Wiring Diagram
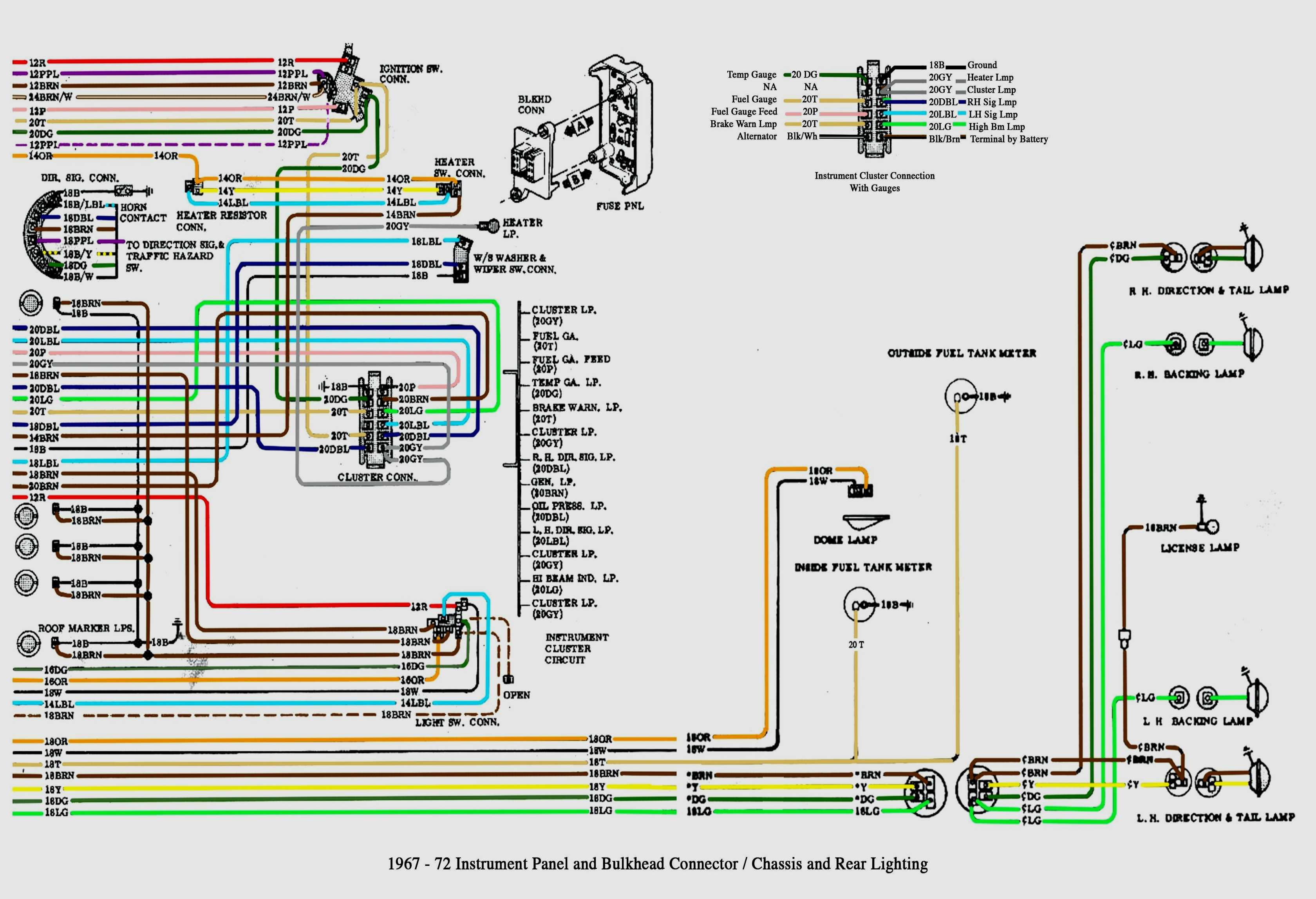
Alright, let's dive into the rear lighting plug wiring diagram for your 2012 Silverado 3500. Understanding this wiring is crucial whether you're tackling a repair, adding aftermarket accessories like a trailer brake controller, diagnosing a faulty signal, or just expanding your automotive knowledge. This document will give you a solid foundation, covering the key aspects from symbols to troubleshooting, so you can approach the job with confidence. And remember, safety always comes first when dealing with electrical systems.
Purpose: Why This Diagram Matters
Think of the wiring diagram as a roadmap for your truck's rear lighting system. Its purpose is multi-faceted:
- Repairing Faulty Lights: Perhaps your brake lights are intermittent, or a turn signal isn't working. The diagram helps you trace the circuit to pinpoint the break or short.
- Adding Accessories: Need to install a trailer hitch wiring harness or auxiliary lighting? This diagram shows you where to tap into the existing circuits.
- Troubleshooting Electrical Issues: Unexpected electrical behavior in the rear of the truck might be traced to the wiring itself. The diagram allows systematic testing.
- Understanding the System: Even if everything is working perfectly, studying the diagram gives you a better understanding of how the rear lighting is designed, which can be invaluable for future maintenance.
Having this information at your fingertips can save you time, money, and frustration, enabling you to perform repairs or modifications yourself rather than relying solely on a mechanic.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2012 Silverado 3500's rear lighting system, like most vehicles, relies on a 12-volt direct current (DC) electrical system. The diagram will detail the connections to several key components:
- Tail Lights: The primary lights visible from the rear, typically including running lights, brake lights, and turn signals.
- Brake Lights: Activated when the brake pedal is pressed, providing a clear signal to following vehicles.
- Turn Signals: Indicate the driver's intention to turn or change lanes. They're often combined with the hazard lights.
- Reverse Lights: Illuminate the area behind the vehicle when it's in reverse, and act as a warning signal.
- License Plate Lights: Illuminate the license plate, ensuring it's visible at night.
- Trailer Wiring Connector: A dedicated plug for connecting a trailer's lighting system (brake lights, turn signals, etc.). This is an area where modification is common.
- Grounding Points: Crucial for completing the electrical circuits. Poor grounding can lead to all sorts of unpredictable lighting issues.
- Fuses and Relays: Protective devices that interrupt the circuit in case of overcurrent or electrical faults. These are a key area to check when troubleshooting.
The wiring diagram will show how these components are interconnected, including wire gauges, connector types, and grounding locations.
Symbols: Understanding the Language of the Diagram
Wiring diagrams use standardized symbols to represent components, connections, and wire characteristics. Let's break down the most common ones you'll encounter in the 2012 Silverado 3500's rear lighting diagram:
- Solid Lines: Represent wires. The thickness of the line may (but doesn't always) indicate the wire gauge (thickness). Thicker wires carry more current.
- Dashed Lines: Often represent shielded wires or connections that are not directly involved in the primary circuit but may be related (e.g., a connection to a control module).
- Circles/Ovals: Can represent lights (tail light bulbs, reverse lights, etc.). The symbol might be filled or unfilled, or have a specific mark within to indicate the type of bulb.
- Squares/Rectangles: Frequently represent connectors, relays, or control modules.
- Triangles (pointing down): Commonly represent grounding points.
- Color Codes: Wires are typically identified by color codes (e.g., BRN for Brown, GRN for Green, YEL for Yellow, BLU for Blue, BLK for Black). The diagram will include a key explaining these abbreviations.
- Pin Numbers: Each connector pin is numbered, allowing you to precisely identify which wire connects to which terminal. This is critical when testing continuity.
- Splices: Represented by dots or small circles where wires connect to each other.
Pay close attention to the legend or key provided with the diagram. It will define the specific symbols and color codes used in that particular document.
How It Works: Tracing the Circuit
The rear lighting system operates on basic electrical principles. Power flows from the battery, through a fuse (for protection), to the various lighting components. A switch (e.g., the headlight switch, brake light switch) controls the flow of current to activate the lights.
Here's a simplified example: When you press the brake pedal, the brake light switch closes, completing the circuit to the brake lights. Current flows from the battery, through the fuse, through the brake light switch, and then to the brake light bulbs. The bulbs illuminate, signaling that you're braking. The circuit is completed through a grounding point, returning the current to the vehicle's chassis (negative terminal of the battery).
The wiring diagram shows the exact path of each circuit, including the components involved and the wire colors. By tracing the circuit on the diagram, you can identify potential points of failure, such as a broken wire, a faulty switch, or a blown fuse.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Let's say your right rear turn signal isn't working. Here's how you might use the wiring diagram to troubleshoot:
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the section of the diagram that shows the right rear turn signal circuit.
- Check the Bulb: The most obvious step, but worth mentioning. Is the bulb burned out? Replace it and test.
- Check the Fuse: Identify the fuse that protects the turn signal circuit. Use a multimeter to check for continuity across the fuse. If it's blown, replace it with the correct amperage fuse.
- Inspect the Wiring: Visually inspect the wiring and connectors associated with the right rear turn signal. Look for broken wires, corroded connectors, or loose connections.
- Test for Voltage: Use a multimeter to check for voltage at the turn signal bulb socket when the turn signal is activated. If there's no voltage, the problem lies upstream.
- Check the Ground Connection: Ensure the ground connection for the right rear turn signal is clean and secure. A poor ground can cause all sorts of lighting problems.
- Trace the Circuit: Using the wiring diagram, trace the circuit back to the turn signal switch or flasher relay. Test for voltage and continuity at each point along the way to isolate the fault.
Remember to use a multimeter safely and accurately. Set it to the correct voltage range and test the leads before taking measurements.
Safety: A Word of Caution
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some crucial safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical circuit, disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent accidental shocks or shorts.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools designed for automotive electrical work.
- Don't Work in Wet Conditions: Water conducts electricity, increasing the risk of shock.
- Be Careful with Wiring: Damaged or frayed wiring can create shorts and fire hazards. Replace damaged wiring promptly.
- Fuses are Crucial: Never bypass a fuse or replace it with one of a higher amperage. Fuses protect the circuit from overcurrent.
- Specifically, handling the trailer wiring connector requires extra caution. Incorrect wiring can damage both the truck's electrical system and the trailer's. Always double-check your connections.
High-intensity discharge (HID) or light-emitting diode (LED) lights can operate at higher voltages than traditional incandescent bulbs. Be extra careful when working with these systems.
Remember, if you're uncomfortable working with electrical systems, it's best to consult a qualified mechanic.
We have the full wiring diagram file available for download. It contains all the details you'll need for troubleshooting and modification of your 2012 Silverado 3500's rear lighting system. Proceed with caution and enjoy the process!
