2012 Silverado 3500 Rear Lighting Plug Wiring Diagram Pdf
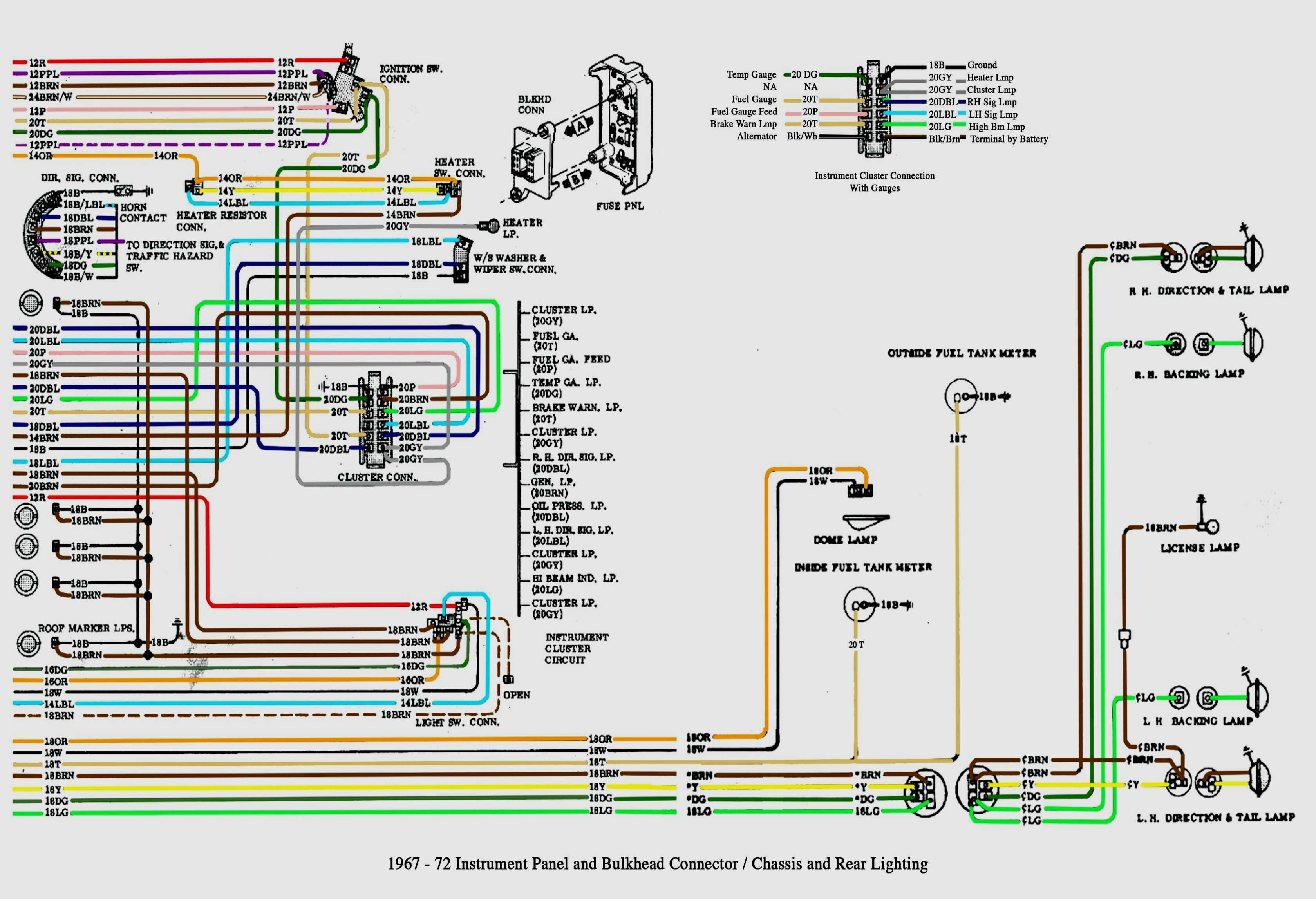
Understanding the rear lighting wiring on your 2012 Silverado 3500 is crucial for a variety of reasons. Whether you're tackling a repair, adding aftermarket accessories like a trailer brake controller or custom taillights, or simply trying to diagnose a lighting problem, having access to and understanding the wiring diagram is invaluable. This article aims to break down the 2012 Silverado 3500 rear lighting plug wiring diagram, offering an expert-level explanation in a way that's accessible to the experienced DIY enthusiast.
Purpose of the Wiring Diagram
A wiring diagram, specifically for the rear lighting plug, serves as a roadmap for the electrical system responsible for your taillights, brake lights, turn signals, reverse lights, and auxiliary trailer connections. Its primary purposes include:
- Repair and Troubleshooting: Pinpointing the exact wire responsible for a malfunctioning light. Instead of blindly guessing, you can trace the circuit and identify the source of the problem, be it a broken wire, a faulty connector, or a blown fuse.
- Modification and Upgrades: Safely and correctly connecting aftermarket accessories, like LED taillights, trailer brake controllers, or auxiliary lighting. Knowing the function of each wire prevents accidental shorts or damage to the vehicle's electrical system.
- Understanding the System: Gaining a deeper knowledge of how your vehicle's electrical system functions, allowing you to perform preventative maintenance and anticipate potential issues.
- Trailer Wiring: Ensuring proper connection of trailer lights, which is essential for safe towing and avoiding legal issues.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2012 Silverado 3500 rear lighting system comprises several key components, and understanding their roles is essential for interpreting the wiring diagram:
- Battery: The power source for the entire electrical system.
- Fuses: Overcurrent protection devices designed to interrupt the circuit if there's a short or overload. Identifying the correct fuse for the rear lighting circuit is critical.
- Lighting Control Module (LCM): A computer module that controls various lighting functions, including turning lights on and off, dimming, and providing turn signal flash patterns. This module interprets signals from the brake pedal, turn signal stalk, and headlights switch.
- Taillight Assemblies: Enclosures containing the brake lights, turn signals, taillights, and sometimes reverse lights.
- Rear Lighting Plug/Connector: The physical connector that provides the electrical interface between the vehicle's wiring harness and the taillight assembly (or trailer wiring). The wiring diagram details the pinout of this connector.
- Wiring Harness: A bundle of wires that connects all the components of the rear lighting system.
- Ground Points: Locations where the electrical circuits are connected to the vehicle's chassis, providing a return path for the current.
Symbols in the Wiring Diagram
Wiring diagrams use standardized symbols to represent different components and connections. Here's a breakdown of common symbols you'll encounter:
- Solid Lines: Represent wires. The thickness of the line may indicate the wire gauge (thickness).
- Dashed Lines: Often indicate shielded wires or connections to ground.
- Circles: Can represent bulbs, connectors, or other components depending on their content.
- Squares or Rectangles: Typically represent switches, relays, or control modules.
- Color Codes: Each wire is assigned a color code, often abbreviated (e.g., BLU for blue, GRN for green). Matching wire colors in the diagram to the actual wires on your truck is crucial. The diagram will include a key explaining the color codes.
- Numbers and Letters: Indicate wire gauge, circuit numbers, and pin numbers on connectors. The wire gauge indicates the current-carrying capacity of the wire.
- Ground Symbol: A series of downward-pointing lines indicating a connection to ground. A good ground connection is essential for proper circuit operation.
How It Works
The rear lighting system works by completing electrical circuits that allow current to flow from the battery, through a control device (like a switch or the LCM), to the lights, and then back to the battery through a ground connection. The wiring diagram shows the path of each circuit.
For example, when you press the brake pedal, a switch activates, sending a signal to the LCM. The LCM then energizes the brake light circuit, sending power through the appropriate wire in the wiring harness to the brake light bulbs in the taillight assemblies. The current flows through the bulbs, causing them to illuminate, and then returns to the battery through a ground connection. The same principle applies to the turn signals, taillights, and reverse lights.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting tips using the wiring diagram:
- No Brake Lights: Check the brake light fuse first. If the fuse is blown, replace it and test. If the new fuse blows immediately, there's likely a short circuit. Use the wiring diagram to trace the brake light circuit and look for damaged wires or connections. Also consider the brake light switch itself.
- One Turn Signal Not Working: Check the bulb first. If the bulb is good, use the wiring diagram to trace the turn signal circuit. Check the wiring and connections to the turn signal bulb socket. A common cause is a corroded ground connection.
- Trailer Lights Not Working: Begin by verifying the trailer lights themselves work on another vehicle, then inspect the trailer wiring plug and harness on your Silverado. Use a multimeter to test for voltage at the trailer plug pins, referencing the wiring diagram to identify the correct pin for each function (taillights, brake lights, turn signals). Check the trailer tow fuses.
- Tail lights not illuminating: Check the tail light bulbs and tail light fuse. Use wiring diagram to isolate possible broken wires.
When troubleshooting, always use a multimeter to test for voltage and continuity. Continuity testing verifies that a circuit is complete and doesn't have any breaks. Voltage testing verifies that power is reaching the correct point in the circuit.
Safety Considerations
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some important safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on any electrical component. This prevents accidental shorts and potential electrical shocks.
- Work in a Well-Lit Area: Adequate lighting allows you to see clearly and avoid mistakes.
- Use Insulated Tools: Using insulated tools minimizes the risk of electrical shock.
- Avoid Working in Wet Conditions: Water conducts electricity, increasing the risk of shock.
- Properly Identify Wires: Double-check wire colors and pin locations on the wiring diagram before making any connections. Incorrect connections can damage the vehicle's electrical system.
- Be Aware of Airbag Systems: The wiring diagram may show the location of airbag sensors and wiring. Avoid disturbing these components, as accidental deployment can cause serious injury.
- High-Intensity Discharge (HID) Systems: Be extremely cautious when dealing with HID lighting. The ballasts can store a dangerous amount of voltage even when the vehicle is turned off.
The rear lighting system, while relatively simple, can be complex to diagnose without the proper resources. The 2012 Silverado 3500 rear lighting plug wiring diagram is an indispensable tool for anyone working on this system. With careful study and proper safety precautions, you can confidently troubleshoot and repair lighting issues on your truck.
We have the complete 2012 Silverado 3500 rear lighting plug wiring diagram available for download. Having this document will save you time and frustration during repairs or modifications.
