2013 Hyundai Santa Fe 2.4 Serpentine Belt Diagram
Alright, let's dive into the serpentine belt system of the 2013 Hyundai Santa Fe with the 2.4L engine. Whether you're planning on replacing the belt yourself, troubleshooting a squealing noise, or simply expanding your automotive knowledge, understanding the serpentine belt diagram is crucial. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know, from the diagram's purpose to practical troubleshooting.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
The serpentine belt diagram serves as a visual roadmap for the belt's routing. It's not just a pretty picture; it's essential for several reasons:
- Correct Installation: Ensuring the belt is routed correctly is paramount. An incorrectly routed belt can lead to component failure, reduced performance, or even engine damage.
- Troubleshooting: The diagram helps diagnose issues like belt slippage, noise, or component failure by identifying the components driven by the belt.
- Component Identification: The diagram labels each pulley and its associated component (alternator, power steering pump, AC compressor, etc.), helping you understand the system's layout.
- Preventative Maintenance: Knowing the routing and the components allows for easier inspection of the belt and pulleys for wear, damage, or misalignment.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 2013 Hyundai Santa Fe 2.4L Serpentine Belt System
Before we dissect the diagram, let's identify the key components involved:
- Serpentine Belt: This is the single, continuous belt that drives multiple engine accessories. It's typically made of reinforced rubber.
- Crankshaft Pulley (or Crank Pulley): Located at the bottom of the engine, this pulley is directly connected to the crankshaft and provides the driving force for the belt.
- Alternator Pulley: The alternator generates electrical power for the vehicle. The serpentine belt drives the alternator to keep the battery charged and power electrical components.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: This pulley drives the power steering pump, which provides hydraulic assistance to make steering easier.
- Air Conditioning (AC) Compressor Pulley: This pulley drives the AC compressor, which circulates refrigerant to cool the vehicle's cabin.
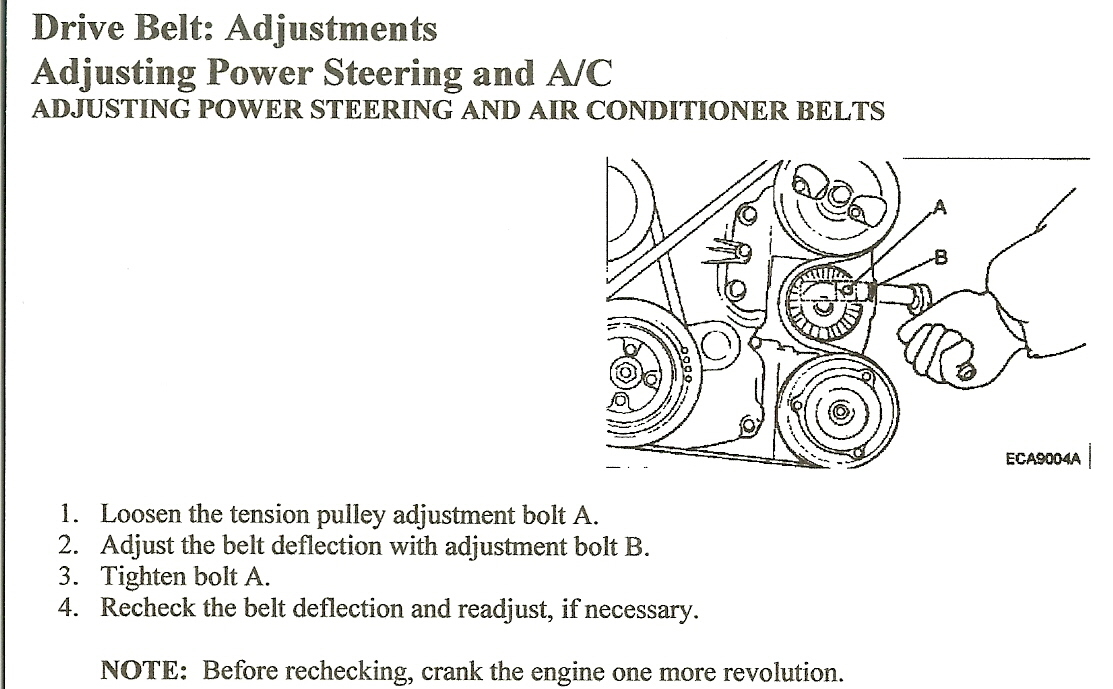
- Tensioner Pulley: The tensioner pulley maintains the correct tension on the serpentine belt. It's often spring-loaded or hydraulically adjusted. This pulley is *critical* for the belt's lifespan and performance.
- Idler Pulley (Optional): Some configurations may include an idler pulley, which serves only to guide the belt's path and provide the necessary wrap angle around other pulleys.
Understanding the Serpentine Belt Diagram Symbols
The diagram uses a standardized set of symbols to represent the different components and belt routing. Here’s what to look for:
- Solid Lines: Represent the path of the serpentine belt. The width of the line doesn't necessarily indicate the belt's physical width.
- Circles: Represent pulleys. These are usually labeled with abbreviations to indicate the component they're connected to (e.g., ALT for alternator, P/S for power steering).
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of rotation of each pulley. This is important for understanding how the belt transfers power.
- Text Labels: Identify each component by name or abbreviation. Pay close attention to these labels to ensure you're identifying the correct pulley.
- Tensioner Symbol: The tensioner pulley is typically represented by a symbol that indicates its adjustable nature, often a spring or a pivoting arm.
How the Serpentine Belt System Works
The serpentine belt system is a clever piece of engineering. The crankshaft pulley, driven by the engine's rotation, powers all the accessories via a single belt. The tensioner pulley is crucial, as it maintains the optimal tension on the belt. Too little tension, and the belt will slip, leading to reduced performance and potential overheating. Too much tension, and it will accelerate wear on the belt and pulleys. The specific routing of the belt is designed to provide sufficient wrap angle around each pulley, ensuring adequate grip and preventing slippage. A proper wrap angle is the angle of the belt in contact with the pulley. A greater wrap angle, usually measured in degrees, means a larger contact area and better friction between the belt and pulley, reducing slippage.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common issues and how the serpentine belt diagram can help:
- Squealing Noise: A squealing noise, especially when the engine is first started or under heavy load (like turning the steering wheel all the way), often indicates a slipping serpentine belt. The diagram can help you inspect the belt for wear, cracks, or glazing. Also, inspect the tensioner pulley to ensure it's functioning correctly. Look for excessive wobble or looseness.
- Battery Not Charging: If the alternator isn't being driven properly, the battery won't charge. Use the diagram to verify the belt is correctly routed around the alternator pulley and that the belt isn't slipping.
- Power Steering Failure: Loss of power steering assistance can be caused by a broken or slipping belt. The diagram will show you the belt's routing to the power steering pump pulley.
- AC Not Cooling: Similarly, a malfunctioning AC system can be caused by a belt issue. Check the diagram to confirm the belt is driving the AC compressor.
- Visual Inspection with the Diagram: Before even starting the engine, use the diagram to visually inspect the entire system. Check for cracks, fraying, missing chunks, or signs of wear on the belt. Examine the pulleys for rust, corrosion, and damage. Make sure all pulleys are aligned and rotate smoothly.
Safety Precautions
Working on the serpentine belt system involves potential hazards. Here are some important safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on any electrical components or the serpentine belt system. This prevents accidental electrical shorts.
- Hot Engine: Allow the engine to cool completely before working on the serpentine belt. The engine components can get extremely hot.
- Moving Parts: Never put your hands or tools near the serpentine belt while the engine is running. This could cause serious injury.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
- Tensioner Tool: Use the correct tool to relieve tension on the belt. Improvising can be dangerous. A serpentine belt tool usually fits into the tensioner. Using a long handled wrench for leverage, rotate the tool in the correct direction to slack the belt, then slip the belt off the pulley.
- Belt Tension: Serpentine belts are under a great deal of tension. When a belt breaks it can do a great deal of damage, and even injury. Wear safety glasses and thick gloves when working with or replacing a serpentine belt to protect yourself.
Replacing the Serpentine Belt
If you need to replace the serpentine belt, the diagram is essential. Follow these steps:
- Locate the tensioner pulley using the diagram.
- Use a serpentine belt tool (or appropriate wrench) to relieve tension on the belt.
- Carefully remove the old belt, noting its routing. It is helpful to draw a diagram on a piece of paper of the original routing, or take a picture of the current belt setup with your phone.
- Install the new belt, ensuring it's correctly routed around all the pulleys according to the diagram.
- Release the tension on the tensioner pulley.
- Double-check the belt's routing to ensure it's properly seated on all pulleys.
- Start the engine and listen for any unusual noises.
- Inspect the belt after a few minutes of running to ensure it's tracking correctly.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the 2013 Hyundai Santa Fe 2.4L serpentine belt diagram is a valuable skill for any DIY mechanic. By following this guide and using the diagram as your reference, you can confidently troubleshoot issues, perform maintenance, and even replace the belt yourself. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult a professional if you're unsure about any aspect of the repair. Armed with this knowledge and the diagram, you're well-equipped to tackle serpentine belt issues on your Santa Fe.
And remember, we have a high-resolution, printable version of the 2013 Hyundai Santa Fe 2.4L Serpentine Belt Diagram ready for you to download. It will be a useful reference for your future repairs and maintenance.
