2013 Subaru Impreza Fuse Box Diagram
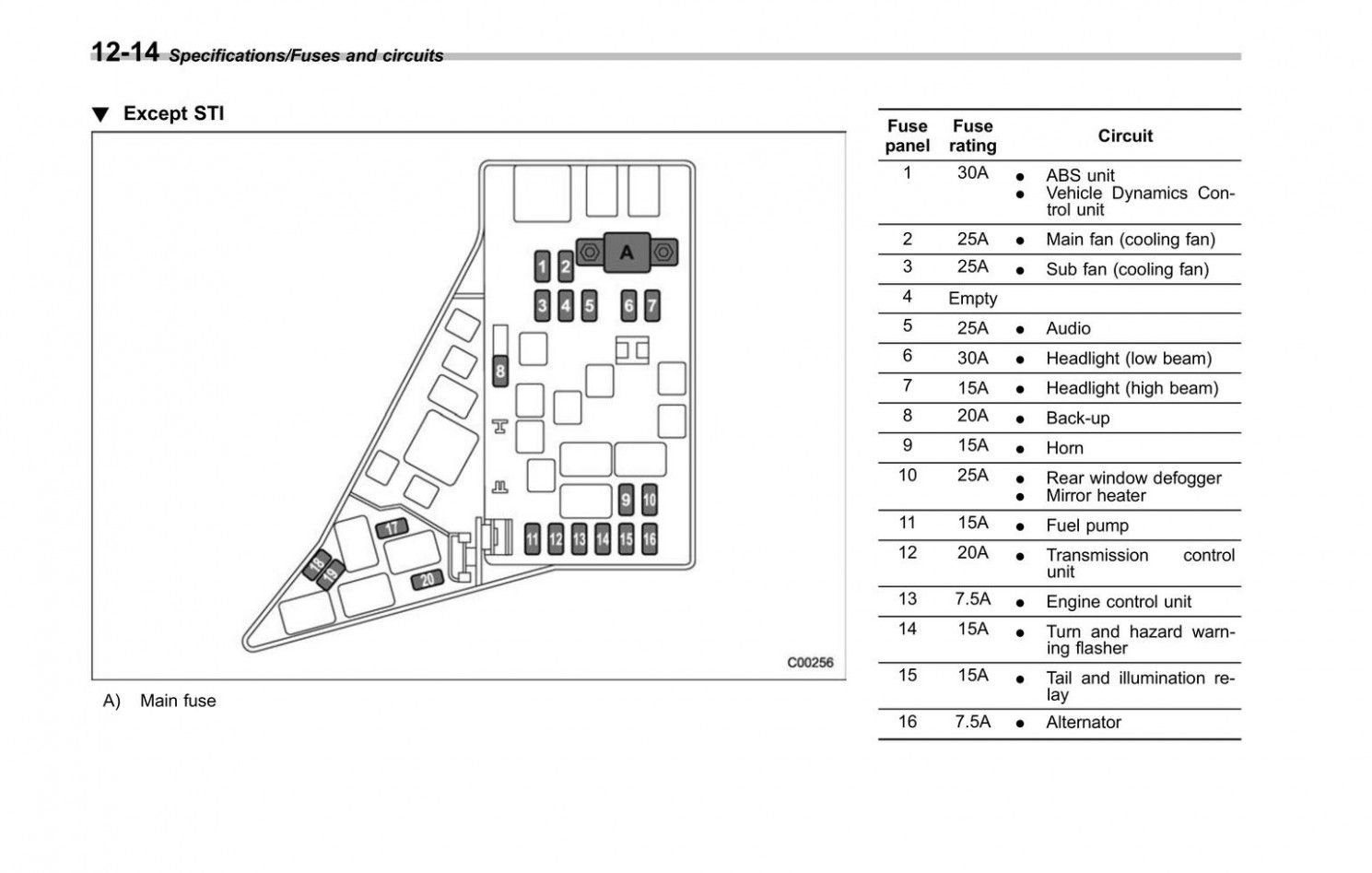
Alright, let's dive into the fuse box diagram for the 2013 Subaru Impreza. Understanding this diagram is crucial for anyone who wants to perform electrical repairs, add aftermarket accessories, diagnose electrical problems, or simply understand their car's electrical system better. Think of it as the Rosetta Stone for your Impreza's electricals.
Why You Need This Diagram
The fuse box diagram is more than just a pretty picture; it's the key to:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Issues: Quickly identify which fuse protects a specific circuit. If your radio suddenly stops working, you'll know which fuse to check first.
- Performing Electrical Repairs: Locate the correct fuse for a damaged component, ensuring a safe and effective repair.
- Adding Aftermarket Accessories: Safely tap into the electrical system to power accessories like aftermarket lighting, stereos, or security systems. Knowing which fuse to use and how to protect the new circuit is essential.
- Understanding Your Car's Electrical System: Gain a deeper understanding of how various components are powered and protected, increasing your overall knowledge of vehicle maintenance.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2013 Impreza typically has two main fuse box locations:
- Interior Fuse Box: Located inside the cabin, often under the dashboard on the driver's side. This box primarily houses fuses for interior components like the radio, power windows, lights, and the ECU (Engine Control Unit).
- Engine Bay Fuse Box: Found under the hood, usually near the battery or firewall. This box houses fuses for engine components, headlights, horn, and other critical systems.
The fuse boxes themselves are plastic housings containing a series of terminals that accept various types of fuses. The diagram provides a map indicating what each fuse protects. This is critical because replacing a blown fuse with one that is rated for higher amperage could cause serious damage, even a fire!
Important specifications to be aware of include the fuse amperage rating (measured in amps – A) and the fuse type (e.g., ATO, Mini-blade). Each fuse is designed to protect a specific circuit from overcurrent. The amperage rating indicates the maximum current the fuse can handle before it blows, interrupting the circuit. Using the incorrect amperage rating can lead to either nuisance fuse blowing or, far worse, a failure to protect the circuit from a dangerous overload. Remember: the fuse amperage rating is always printed directly on the fuse itself.
Understanding the Symbols, Lines, and Colors
Fuse box diagrams use a standardized set of symbols, lines, and colors to represent different electrical components and their connections. Understanding these symbols is vital for interpreting the diagram correctly:
- Lines: Solid lines generally represent wiring connections. Thicker lines may indicate heavier gauge wiring for higher current circuits. Dashed lines might indicate less direct connections or ground paths.
- Colors: Wire colors are often indicated on the diagram. Common colors include red (power), black (ground), and various other colors to distinguish different circuits. These color codes often correspond to the actual wire colors used in the vehicle, making it easier to trace wires.
- Icons/Symbols: These represent the component being protected. Common symbols include:
- Headlight: A stylized headlight icon indicates the fuse protects the headlight circuit.
- Radio: A speaker icon or similar represents the radio circuit.
- ECU: Often labelled with the acronym "ECU" or a stylized computer chip icon.
- Power Windows/Locks: Typically, a window or lock symbol signifies circuits for those components.
- ABS: For the anti-lock braking system.
The diagram itself is usually organized in a grid-like pattern, with each fuse location clearly numbered or labelled. The legend accompanying the diagram provides a detailed description of what each fuse protects, along with its amperage rating. Pay close attention to the legend to avoid misinterpreting the diagram. A quick example, you might find "Fuse #12 - Interior Lights - 10A".
How It Works: The Electrical Circuit and Fuse Function
To truly understand the fuse box diagram, you need a basic understanding of how electrical circuits work. A circuit is a complete path that allows electricity to flow from a power source (battery) through a component (e.g., headlight) and back to the power source. The fuse is placed in this circuit to protect it from overcurrent – a situation where too much electricity flows through the circuit, potentially causing damage or a fire.
When the current exceeds the fuse's amperage rating, the thin metal strip inside the fuse melts, breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity. This prevents the overcurrent from reaching the component and causing damage. When a fuse blows, it's usually an indication of a problem in the circuit, such as a short circuit (where the current flows directly to ground, bypassing the component) or a faulty component drawing too much current. Always investigate the cause of a blown fuse before replacing it. Simply replacing the fuse without addressing the underlying problem will likely result in the new fuse blowing as well.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting tips for using the fuse box diagram:
- Symptom-Based Troubleshooting: If a specific component isn't working, consult the fuse box diagram to identify the corresponding fuse. Check the fuse to see if it's blown.
- Visual Inspection: A blown fuse will typically have a broken filament or a darkened appearance. Some fuses have a clear plastic window that allows you to visually inspect the filament.
- Fuse Tester: Use a fuse tester (a simple tool with a probe and a light) to check if a fuse is good. You can test the fuse without removing it by probing the test points on the top of the fuse. If the light on the tester illuminates, the fuse is good.
- Fuse Puller: Use a fuse puller (a small plastic tool) to safely remove and replace fuses.
- Replacement Fuses: Always replace a blown fuse with a fuse of the same type and amperage rating. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can be extremely dangerous.
Let's say your interior lights aren't working. Consult the diagram, find the fuse labelled "Interior Lights" (or similar), and check its amperage rating. Locate the fuse in the interior fuse box and visually inspect it. If it's blown, replace it with a fuse of the correct type and amperage rating. If the new fuse blows immediately, there's likely a short circuit in the interior lighting circuit that needs further investigation.
Safety Considerations
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Always take the following precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical system, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent accidental shorts and electrical shocks.
- Avoid Water: Never work on electrical systems in wet conditions.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Protect your eyes from sparks or debris.
- High-Current Circuits: Be extremely cautious when working with circuits that handle high current, such as the starter motor or alternator circuits. These circuits can deliver a significant electrical shock.
- Airbag Circuits: Never tamper with airbag circuits. These circuits are highly sensitive and can deploy the airbags unexpectedly, causing serious injury. Leave airbag repairs to qualified professionals. The diagrams pertaining to airbag circuits are particularly risky. Even a static discharge can trigger the airbag.
- ECU: Be careful around the ECU. Static discharge can fry the ECU.
Remember, if you're not comfortable working with electrical systems, it's always best to consult a qualified mechanic.
We have a detailed, high-resolution PDF of the 2013 Subaru Impreza fuse box diagram available for download. This diagram provides a clear and comprehensive map of all the fuses in your vehicle, making it easier to troubleshoot electrical problems and perform electrical repairs. With this diagram, you'll be well-equipped to tackle most electrical issues yourself, saving you time and money. Remember safety first!
