2014 Dodge Dart Coolant Hose Diagram
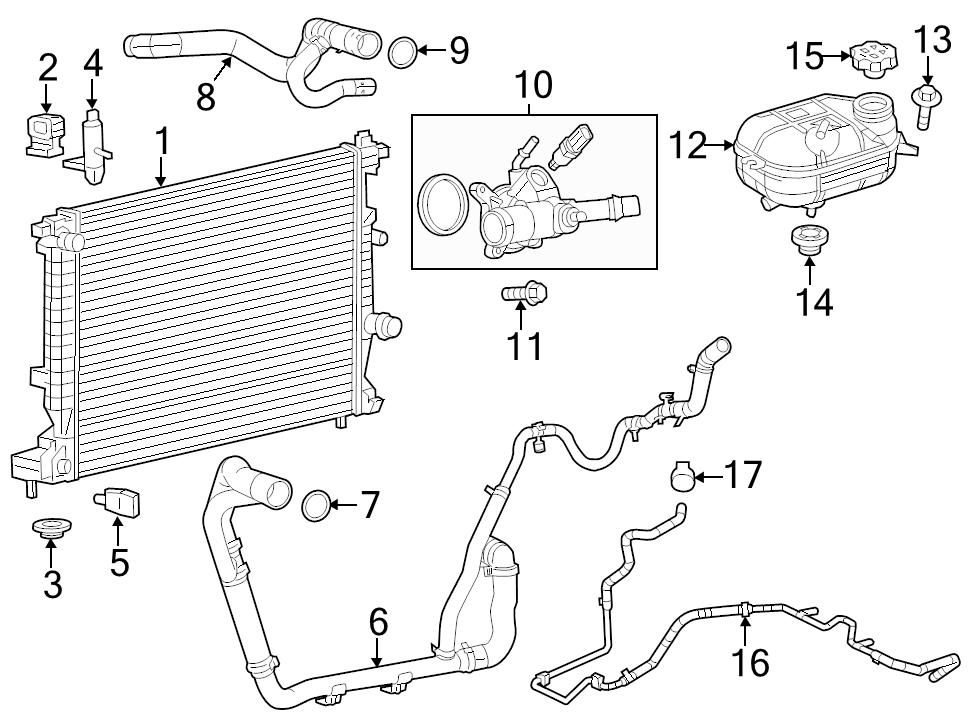
Let's dive into the cooling system of your 2014 Dodge Dart, specifically focusing on understanding the coolant hose diagram. This information is crucial for various reasons, from diagnosing leaks and performing routine maintenance to understanding the overall thermal management of your engine. Whether you're a seasoned DIYer tackling a coolant flush or trying to pinpoint the source of overheating, a clear understanding of the hose routing is essential.
Purpose: Why You Need This Diagram
A coolant hose diagram for your 2014 Dodge Dart serves several vital purposes:
- Troubleshooting Leaks: The diagram helps you trace the path of coolant, allowing you to identify the specific hose or connection point where a leak is occurring. Without it, you're essentially guessing and potentially wasting time replacing the wrong components.
- Performing Maintenance: When flushing the cooling system or replacing a thermostat, knowing the hose routing is critical for proper draining and refilling.
- Understanding System Operation: The diagram provides a visual representation of how the cooling system works, allowing you to grasp the flow of coolant through the engine, radiator, and heater core.
- Modification and Repair: If you're planning any engine modifications that might affect the cooling system, or if you need to replace damaged hoses, the diagram is indispensable for ensuring correct reassembly.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2014 Dodge Dart cooling system, particularly concerning its hose routing, centers around the following key components:
- Radiator: This is the primary heat exchanger. Coolant flows through the radiator's core, dissipating heat into the atmosphere.
- Engine Block: Coolant circulates through passages within the engine block and cylinder head(s) to absorb heat generated by combustion.
- Thermostat: A temperature-sensitive valve that regulates coolant flow to maintain optimal engine operating temperature. It's usually housed in a thermostat housing, where the upper radiator hose connects.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant throughout the system. Its located at the front of the engine, driven by the serpentine belt.
- Heater Core: A small radiator located inside the passenger compartment. It provides heat by allowing hot coolant to flow through it.
- Expansion Tank (Coolant Reservoir): Holds excess coolant and compensates for expansion and contraction due to temperature changes. It is also important for air removal from system.
- Coolant Hoses: These are the flexible rubber or silicone tubes that connect all the components. They're designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures. Common sizes range from ¾ inch to 1 ½ inches inner diameter, depending on their location and function. Hose clamps secure them to the fittings.
- Hose Clamps: Typically spring-loaded or screw-type clamps used to secure the hoses to their connections.
The specific layout and number of hoses can vary slightly depending on the engine configuration of your 2014 Dart (e.g., 2.0L, 1.4L Turbo, or 2.4L). The diagram we're discussing will generally cover the common configurations.
Symbols and Conventions
Understanding the symbols used in a coolant hose diagram is crucial for accurate interpretation. Here's a breakdown of common symbols:
- Solid Lines: Typically represent the main coolant hoses. Their thickness may indicate the hose diameter, with thicker lines representing larger hoses.
- Dashed Lines: Often indicate vacuum lines or secondary coolant lines, such as those for the overflow tank.
- Arrows: Show the direction of coolant flow. Pay close attention to these, as incorrect hose connections can lead to serious engine damage.
- Component Symbols: Radiators are typically represented by a rectangular shape with fins, the water pump might be symbolized by a circle with a pump icon, and the thermostat housing will be a stylized representation of its physical form.
- Color Coding (Less Common, But Possible): Some diagrams use color coding to differentiate between hot and cold coolant lines. Red might indicate hot coolant flowing *away* from the engine, while blue indicates cooled coolant returning *to* the engine.
How It Works: The Cooling System in Action
The cooling system's operation is based on a simple principle: removing heat from the engine and dissipating it into the atmosphere. Here's a step-by-step breakdown:
- The water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine block and cylinder head.
- As the coolant flows through the engine, it absorbs heat generated by combustion.
- The heated coolant flows towards the thermostat.
- If the engine is cold, the thermostat remains closed, restricting coolant flow to the radiator and allowing the coolant to circulate only within the engine block, allowing the engine to heat up quickly.
- Once the engine reaches its operating temperature, the thermostat opens, allowing coolant to flow to the radiator.
- In the radiator, the hot coolant flows through the core, and heat is transferred to the surrounding air. The radiator fan (if equipped) helps to draw air through the radiator, increasing the rate of heat transfer.
- The cooled coolant then returns to the engine block to repeat the cycle.
- The heater core receives hot coolant and provides heat to the passenger compartment.
- The expansion tank accommodates changes in coolant volume due to temperature fluctuations.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common troubleshooting scenarios where the coolant hose diagram proves invaluable:
- Locating Leaks: If you notice a coolant leak, use the diagram to trace the hoses and connections near the leak's origin. Look for cracks, bulges, or loose clamps. A pressure tester can help pinpoint elusive leaks.
- Overheating: If your engine is overheating, check the thermostat, water pump, and radiator. The diagram helps you understand the flow path and identify potential blockages or malfunctions. Low coolant levels are, of course, a common culprit, easily checked using the diagram to identify the expansion tank.
- Coolant Loss: If you're constantly adding coolant, there's likely a leak somewhere in the system. Use the diagram to systematically inspect all hoses, connections, and components. Don't forget to check the water pump weep hole for signs of leakage, as that indicates the pump is failing.
- Heater Not Working: If your heater isn't producing heat, check the heater core hoses and the blend door actuator. Use the diagram to ensure proper coolant flow to the heater core.
Safety Considerations
Working with the cooling system involves several safety risks. Always allow the engine to cool completely before opening the cooling system. Pressurized hot coolant can cause severe burns.
- Hot Coolant: As mentioned, hot coolant is extremely dangerous. Never open the radiator cap or any coolant hoses while the engine is hot.
- Pressure: The cooling system is pressurized. Even when cool, there may be residual pressure. Release the pressure slowly by carefully opening the radiator cap (covered with a thick rag for protection).
- Chemical Exposure: Coolant is toxic. Avoid skin contact and never ingest it. Clean up any spills immediately and dispose of used coolant properly at a recycling center.
- Sharp Edges: Be mindful of sharp edges on hoses, clamps, and other components. Wear gloves to protect your hands.
Understanding the 2014 Dodge Dart coolant hose diagram is a valuable skill for any DIY mechanic or car enthusiast. It empowers you to diagnose problems, perform maintenance, and ensure the proper operation of your vehicle's cooling system.
We have the 2014 Dodge Dart coolant hose diagram available for download. Use it as a reference for your repairs. Good luck!
