2020 Nissan Rogue Fuse Box Diagram
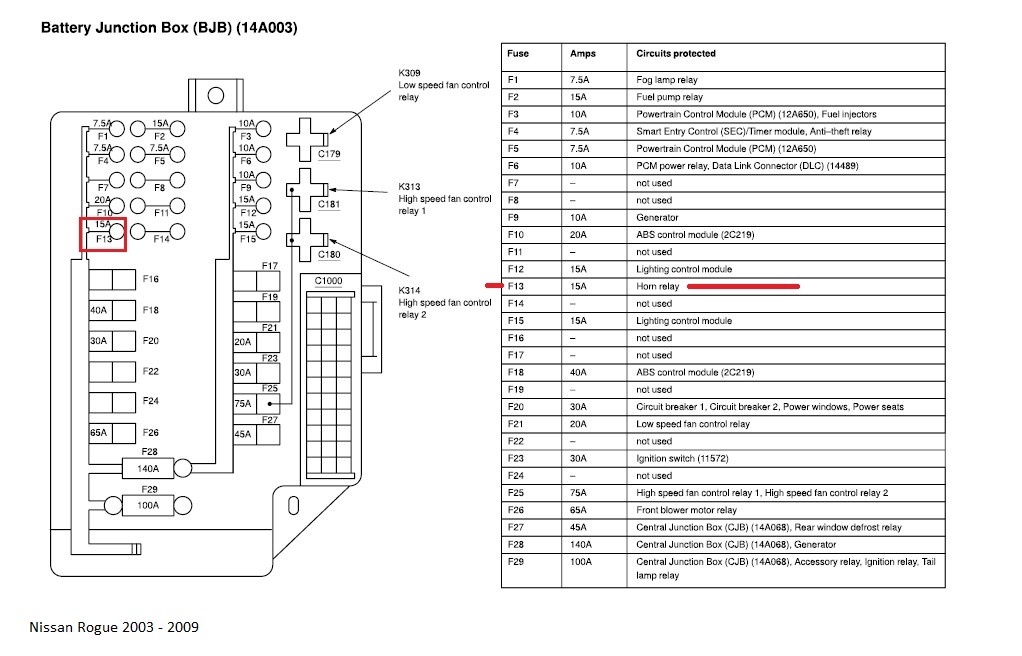
Understanding your vehicle's electrical system is crucial for both routine maintenance and troubleshooting unexpected issues. The fuse box diagram is your roadmap to this system, allowing you to identify and address problems quickly and safely. This guide focuses on the 2020 Nissan Rogue fuse box diagram, providing the knowledge you need to navigate its complexities.
Purpose of the 2020 Nissan Rogue Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram serves several critical purposes:
- Repair and Troubleshooting: Identifying a blown fuse associated with a specific component (e.g., headlights, power windows) is the most common use.
- Modification and Accessory Installation: When adding aftermarket accessories (e.g., dash cams, upgraded audio systems), knowing the location of suitable power sources and the amperage rating of existing circuits is essential.
- Preventative Maintenance: Periodically inspecting fuses for signs of corrosion or damage can prevent future electrical problems.
- General Understanding: Familiarizing yourself with the fuse box layout provides a broader understanding of your vehicle's electrical architecture.
Essentially, the diagram is your key to safely interacting with and modifying the electrical system of your 2020 Nissan Rogue. Without it, you risk damaging components or even causing a fire.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2020 Nissan Rogue, like most modern vehicles, utilizes multiple fuse boxes located in different areas. The most common locations are:
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: This box typically houses fuses and relays for critical engine components, such as the Electronic Control Module (ECM), fuel pump, ignition system, and cooling fans.
- Passenger Compartment Fuse Box: Usually located under the dashboard, often near the steering wheel or glove compartment, this box contains fuses for interior features like lights, power windows, power locks, the infotainment system, and the climate control system.
Each fuse box contains a variety of components:
- Fuses: These are the sacrificial elements designed to protect circuits from overcurrent. They come in various amperage ratings (measured in Amperes or "Amps"), indicated by a number printed on the fuse. Higher amperage fuses protect circuits that draw more current.
- Relays: These are electromechanical switches that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. For example, the headlight switch uses a relay to control the high-current headlights.
- Circuit Breakers: Some circuits may use circuit breakers instead of fuses. Circuit breakers are resettable devices that automatically interrupt the circuit when an overcurrent condition occurs.
- Connectors: These provide electrical connections to the fuse box and its components.
Understanding the location and function of each component is critical when interpreting the fuse box diagram.
Symbols: Lines, Colors, and Icons
Fuse box diagrams use a standardized set of symbols to represent different components and their functions. Here's a breakdown:
- Lines: Lines represent electrical wires or circuits. Thicker lines often indicate higher current capacity.
- Colors: Wire colors are often indicated on the diagram using abbreviations (e.g., BLK for black, RED for red, BLU for blue). These colors are crucial for identifying the correct wire when troubleshooting.
- Icons: Icons represent the specific component protected by a particular fuse. Some common icons include:
- Headlight Icon: Indicates the headlight circuit.
- Window Icon: Indicates the power window circuit.
- Radio Icon: Indicates the audio system circuit.
- Engine Icon: Indicates an engine-related circuit.
- Fan Icon: Indicates a cooling fan circuit.
- Amperage Rating: Each fuse location will have a number indicating its amperage rating. This is often displayed near the fuse symbol or in a legend accompanying the diagram. Never replace a fuse with one of a higher amperage rating, as this could damage the circuit.
The diagram will also include a legend that explains all the symbols and abbreviations used. Refer to this legend frequently to ensure proper interpretation.
How It Works
The fuse box functions as a central distribution point for electrical power throughout the vehicle. The battery provides the primary source of power, which is then distributed to various circuits via the fuse box. Each circuit is protected by a fuse (or circuit breaker) of the appropriate amperage rating.
When an overcurrent condition occurs (e.g., a short circuit), the fuse element melts, interrupting the flow of electricity and preventing damage to the circuit and connected components. This is the fuse's primary purpose – to protect the wiring and components connected to it.
Relays are used to control circuits that require a high current draw. A low-current signal from a switch (e.g., the headlight switch) activates the relay, which then closes a high-current circuit to power the component (e.g., the headlights).
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting tips using the fuse box diagram:
- Symptom: A specific component is not working (e.g., power windows are not functioning).
- Step 1: Consult the fuse box diagram to identify the fuse associated with the power windows.
- Step 2: Locate the correct fuse in the fuse box.
- Step 3: Visually inspect the fuse. A blown fuse will typically have a broken filament inside.
- Step 4: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating.
- Step 5: Test the component to see if it now functions correctly.
- Step 6: If the new fuse blows immediately, there is likely a short circuit in the wiring or the component itself. Further diagnosis is required.
- Symptom: Multiple components are not working.
- Step 1: Check the fuses for the affected components.
- Step 2: If multiple fuses are blown, suspect a more significant electrical problem, such as a short circuit or a faulty ground connection.
- Step 3: Consider checking the main fuses or fusible links located near the battery.
Always use the correct fuse puller tool to remove fuses. Attempting to remove them with pliers or other tools can damage the fuse box.
Safety: Highlight Risky Components
Working with the electrical system can be dangerous. Always observe the following safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical component, disconnect the negative (black) battery terminal to prevent accidental shorts and electrical shocks.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools to prevent electrical shocks.
- Never Replace a Fuse with a Higher Amperage Fuse: This can overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- Avoid Working in Wet Conditions: Water conducts electricity and increases the risk of electrical shock.
- Be Cautious Around Airbag Components: Airbags are electrically activated and can deploy unexpectedly if mishandled. Consult a professional if you need to work near airbag components.
- High-Voltage Components: Be aware of high-voltage components in the engine compartment, particularly those associated with the ignition system. These components can deliver a painful or even fatal shock.
Always exercise caution and consult a qualified technician if you are unsure about any aspect of the electrical system.
We have the complete 2020 Nissan Rogue Fuse Box Diagram available for download. It contains detailed illustrations and component locations to help you navigate your vehicle's electrical system safely and effectively.
