2015 Hyundai Sonata 2.4 Belt Diagram
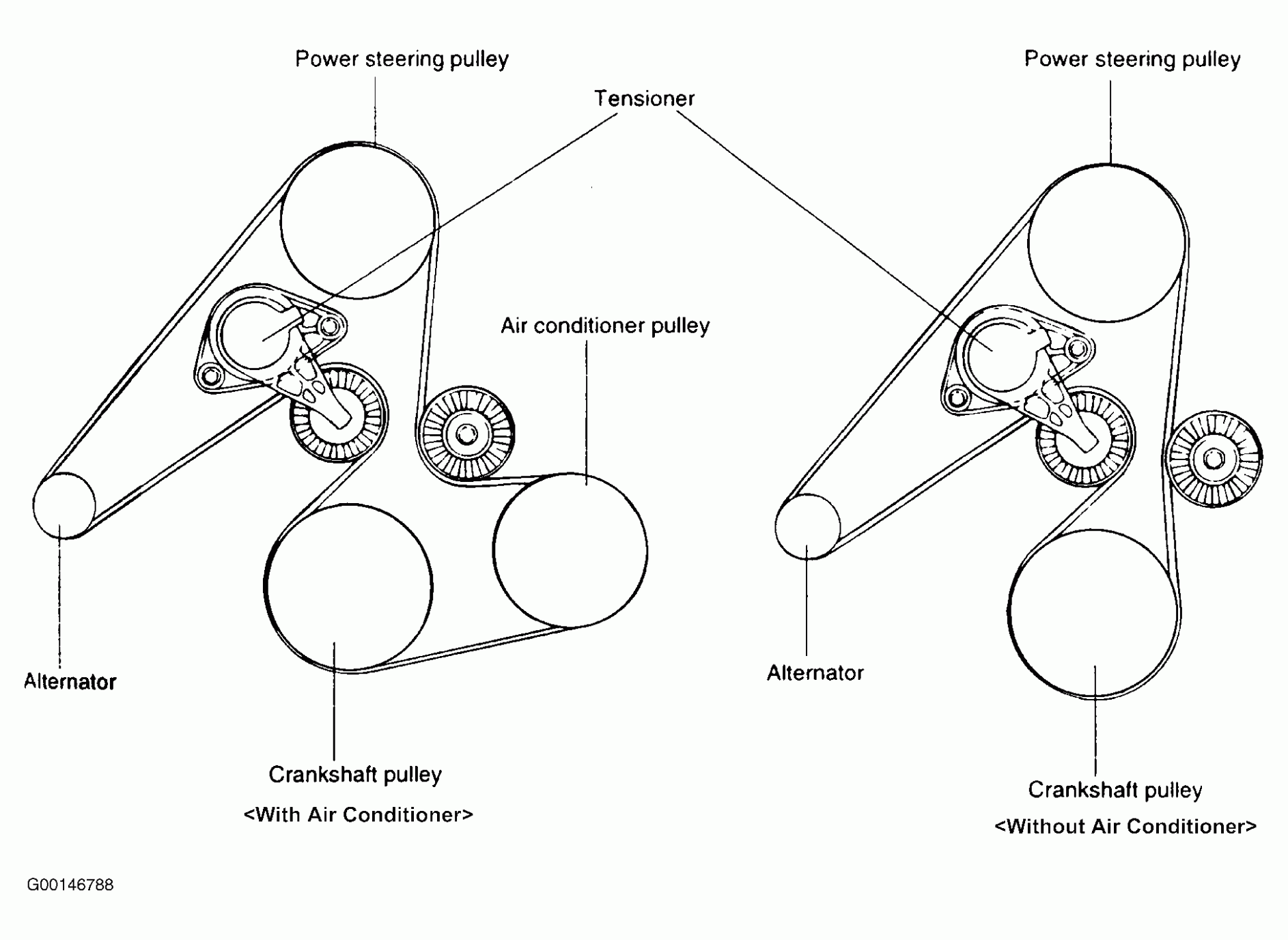
Alright, let's dive into the serpentine belt diagram for the 2015 Hyundai Sonata with the 2.4-liter engine. This is crucial information whether you're tackling routine maintenance, chasing down a pesky squeal, or just trying to understand how your engine's accessories are driven. Having a good understanding of the belt routing will save you time, frustration, and potentially prevent costly mistakes.
Purpose of the 2015 Hyundai Sonata 2.4 Serpentine Belt Diagram
Why bother with a belt diagram? Simple. It's your roadmap to properly routing the serpentine belt. The serpentine belt is a single, continuous belt that drives multiple engine accessories. Without the diagram, you're essentially guessing, and that can lead to:
- Incorrect Installation: Wrong routing means the belt won't properly engage the pulleys, leading to accessory malfunctions.
- Belt Slippage: Insufficient tension causes the belt to slip, reducing accessory performance and potentially damaging the belt itself.
- Component Damage: Incorrect routing can put undue stress on pulleys, leading to premature failure of components like the alternator, power steering pump, or AC compressor.
- Preventive Maintenance: The diagram helps you identify components that may be experiencing issues that are impacting the belt’s performance and may need to be addressed.
Furthermore, if you are a DIY mechanic or a modder who is trying to customize your Sonata, you will need a diagram that helps you trace your components and see the impact of other components on their performance.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2015 Sonata 2.4L engine uses a single serpentine belt to drive the following components:
- Crankshaft Pulley: The engine's main drive pulley, powered directly by the engine's rotation.
- Alternator: Generates electrical power for the car's systems and charges the battery.
- Power Steering Pump: Provides hydraulic assistance for steering.
- Air Conditioning (A/C) Compressor: Compresses refrigerant for the air conditioning system.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant through the engine to regulate temperature. The belt often (but not always) drives the water pump on this engine. A failing water pump can lead to serious overheating.
- Tensioner Pulley: An automatically adjusting spring-loaded pulley that maintains proper belt tension. This is critical for belt life and accessory performance.
- Idler Pulley: A smooth pulley that helps guide the belt and maintain proper wrap around other pulleys. Not all engines have idler pulleys.
Belt Length: While this varies slightly depending on aftermarket brands, the approximate belt length for the 2015 Sonata 2.4L is typically around 87-88 inches. Always verify the correct part number for your specific vehicle using your VIN or the original belt's part number.
Belt Type: Serpentine belts are typically made of a reinforced rubber compound. They have multiple V-shaped ribs that grip the pulleys. Look for cracks, fraying, or missing ribs, as these are signs of wear.
Understanding Diagram Symbols
Belt diagrams may seem confusing at first, but once you understand the symbols, they become clear. Here's a breakdown:
- Solid Lines: Indicate the path of the smooth side of the belt.
- Dashed Lines: (Less Common) Could indicate the path of the ribbed side of the belt or a section of the belt that is obscured in the diagram. Always refer to the diagram's legend for clarification.
- Circles: Represent the pulleys. Larger circles are usually the crankshaft pulley, while smaller circles represent other accessories and idler pulleys.
- Arrows: Show the direction of belt travel. Follow the arrows carefully to ensure proper routing.
- Tensioner Symbol: The tensioner pulley will often be represented by a specific symbol, often with a small arrow indicating the direction it pivots to apply tension. This is crucial for understanding how to relieve tension when replacing the belt.
- Component Labels: Each pulley is labeled with an abbreviation indicating the component it drives (e.g., ALT for alternator, P/S for power steering).
How It Works: The Serpentine Belt System
The serpentine belt system is a clever design that allows a single belt to power multiple accessories. The crankshaft pulley, driven by the engine, provides the rotational force. This force is then transferred to the other pulleys via the serpentine belt. The tensioner pulley maintains the correct belt tension, ensuring good grip and preventing slippage.
Here's the general process:
- The engine turns the crankshaft pulley.
- The crankshaft pulley drives the serpentine belt.
- The serpentine belt rotates the pulleys of the alternator, power steering pump, A/C compressor, and water pump.
- The tensioner pulley automatically adjusts to maintain the correct belt tension.
The water pump is essential for engine cooling and if it’s driven by the serpentine belt and it stops, it can cause catastrophic engine failure due to overheating. The air conditioning and power steering pumps are important for comfort and handling. The alternator keeps the battery charged and all the other systems of your vehicle running.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how you can use the serpentine belt diagram for troubleshooting:
- Squealing Noise: A common symptom of a loose or worn belt. Inspect the belt for cracks, glazing, or missing ribs. Check the tensioner pulley for proper operation. Refer to the diagram to ensure the belt is routed correctly.
- Accessory Malfunction: If your alternator isn't charging, your power steering isn't working, or your A/C isn't cooling, check the belt routing first. A misrouted or slipping belt can cause these issues.
- Belt Slippage in Wet Conditions: Old or worn belts are more prone to slipping when wet. Replace the belt with a new one.
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the belt for signs of wear and tear. Look for cracks, fraying, missing ribs, and glazing (a shiny, hardened surface).
Using the Diagram for Replacement: When replacing the serpentine belt, carefully note the routing before removing the old belt. Take a picture or sketch the path if needed. Use the diagram to confirm the correct routing when installing the new belt. Make sure the belt is properly seated on all pulleys before releasing the tensioner. After installation, start the engine and listen for any unusual noises. Re-check the belt tension after a short drive.
Safety Considerations
The serpentine belt system involves rotating parts and high tension. Always take the following precautions:
- Disconnect the Negative Battery Terminal: Before working on the serpentine belt system, disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent accidental starting of the engine.
- Engine Must be Cool: Allow the engine to cool completely before working on the belt. Exhaust manifolds can get extremely hot!
- Keep Hands Clear: Keep your hands and fingers clear of the belt and pulleys while the engine is running. Rotating parts can cause serious injury.
- Tensioner Safety: Be careful when releasing the tensioner. The spring-loaded mechanism can snap back quickly. Use the correct tool to relieve tension.
- High-Pressure A/C Lines: Be extremely careful around the A/C compressor and lines. These contain high-pressure refrigerant, which can cause severe frostbite if released. Never disconnect A/C lines unless you are a trained technician with the proper equipment.
The most risky components are the A/C compressor and lines, due to the high-pressure refrigerant, and the rotating components when the engine is running.
Armed with this knowledge and the proper diagram, you should be well-equipped to tackle most serpentine belt-related tasks on your 2015 Hyundai Sonata 2.4L. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult a professional mechanic if you're unsure about any procedure.
To help you further, we have the complete 2015 Hyundai Sonata 2.4 Serpentine Belt Diagram available for download. This detailed diagram provides a clear visual representation of the belt routing, making your maintenance and repair tasks much easier.
