2015 Jeep Grand Cherokee 3.6 Serpentine Belt Diagram
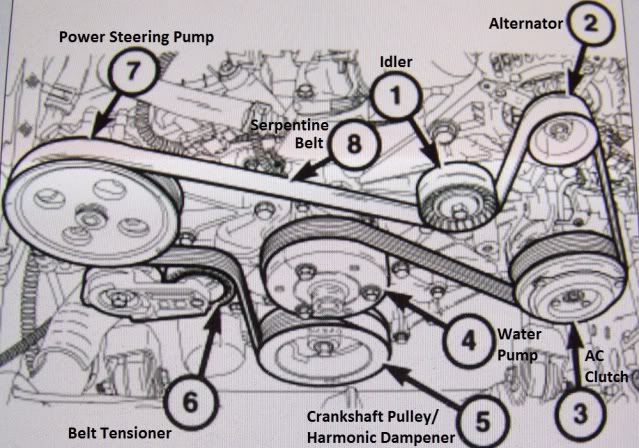
Alright, let's dive into the serpentine belt system on the 2015 Jeep Grand Cherokee with the 3.6L Pentastar engine. This guide is designed to help you understand the belt routing, diagnose problems, and tackle basic repairs yourself. We'll break down the diagram, explain what everything means, and give you some real-world tips. Knowing this system inside and out is crucial, whether you're doing routine maintenance, troubleshooting a squealing belt, or replacing a faulty component.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
The serpentine belt diagram is your roadmap for the entire accessory drive system. It's not just a pretty picture; it's essential for several reasons:
- Correct Belt Routing: The most obvious use. The serpentine belt weaves its way around multiple pulleys in a specific pattern. An incorrect routing can cause component failure, belt damage, and overall poor engine performance.
- Troubleshooting: The diagram helps you identify which component is driven by which part of the belt. This is invaluable when diagnosing issues like a non-functioning AC compressor or power steering pump.
- Maintenance and Replacement: Knowing the belt path allows you to inspect the belt for wear, cracks, or damage. It also guides you through the replacement process, ensuring the new belt is properly installed and tensioned.
- Component Identification: The diagram labels each pulley and its associated component (alternator, water pump, etc.), making it easier to understand the system's layout.
Key Specs and Main Parts (2015 Jeep Grand Cherokee 3.6L)
Before we dissect the diagram, let's define the key components and their purpose in the 2015 Jeep Grand Cherokee 3.6L Pentastar engine's serpentine belt system:
- Crankshaft Pulley (Harmonic Balancer): Located at the bottom of the engine, this pulley is directly connected to the crankshaft and provides the rotational power to drive the entire system. It also incorporates a harmonic balancer to dampen torsional vibrations from the engine.
- Alternator Pulley: The alternator generates electrical power to recharge the battery and power the vehicle's electrical systems.
- Water Pump Pulley: The water pump circulates coolant through the engine to prevent overheating.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: The power steering pump provides hydraulic assistance to make steering easier.
- Air Conditioning (AC) Compressor Pulley: The AC compressor circulates refrigerant in the air conditioning system.
- Idler Pulley(s): Smooth pulleys used to guide the belt around other components and maintain proper belt wrap. 'Wrap' refers to the amount of contact the belt has with each pulley, ensuring sufficient grip.
- Tensioner Pulley: This spring-loaded pulley automatically maintains the correct tension on the serpentine belt. Maintaining proper tension is critical for efficient operation and preventing belt slippage.
- Serpentine Belt: The heart of the system, this long, continuous belt transmits power from the crankshaft pulley to all the other components.
The OEM belt for the 2015 Grand Cherokee 3.6L is typically a multi-ribbed belt, and its specific length and rib count are critical for proper function. Consult your vehicle's owner's manual or parts catalog for the exact specifications. Using the wrong belt size can lead to improper tension, component damage, or even belt failure.
Symbols and Diagram Conventions
Understanding the symbols used in the serpentine belt diagram is key to interpreting it correctly. Here's a breakdown:
- Solid Lines: Represent the path of the serpentine belt. The thickness of the line can sometimes indicate the belt's width, but this isn't always consistent.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of belt rotation around each pulley. Pay close attention to these arrows, as they clarify the belt's travel.
- Pulleys: Shown as circles with labels indicating the component they drive (e.g., ALT for alternator, P/S for power steering).
- Tensioner: Usually depicted with a spring or a small arrow indicating the direction of tension. The tensioner is critical for maintaining proper belt tension.
- Component Labels: Abbreviations like ALT, P/S, AC, WP clearly identify each component driven by the belt.
- Routing Marks: Some diagrams may include small marks or notches to help align the belt during installation.
How It Works: The Serpentine System in Action
The serpentine belt system is a relatively simple but efficient way to power multiple engine accessories with a single belt. Here's how it works:
- The engine's crankshaft rotates, turning the crankshaft pulley.
- The serpentine belt, wrapped tightly around the crankshaft pulley, receives this rotational force.
- The belt then transfers this force to all the other pulleys in the system: alternator, water pump, power steering pump, and AC compressor.
- Each pulley, in turn, drives its respective component, enabling it to perform its function.
- The tensioner pulley maintains constant tension on the belt, preventing slippage and ensuring efficient power transfer. The tensioner's spring mechanism automatically adjusts for belt stretch and wear.
- Idler pulleys guide the belt along its path, ensuring proper alignment and preventing interference with other engine components.
Real-World Use and Troubleshooting
Here's how to use the serpentine belt diagram for troubleshooting common issues:
- Squealing Belt: A squealing belt often indicates slippage, which can be caused by a worn belt, a loose tensioner, or a contaminated pulley. Inspect the belt for cracks, glazing, or missing ribs. Check the tensioner for proper operation. If the pulleys are contaminated with oil or coolant, clean them thoroughly. Refer to the diagram to make sure that the belt is routed correctly.
- No Power Steering: If your power steering isn't working, check the diagram to confirm that the power steering pump is driven by the serpentine belt. Inspect the belt and pulley for damage. A broken or slipping belt will prevent the pump from operating.
- Overheating: The water pump is driven by the serpentine belt. If the belt is broken or slipping, the water pump won't circulate coolant effectively, leading to overheating. Check the belt and tensioner immediately.
- No AC: Similar to the power steering issue, a malfunctioning AC system could be caused by a broken or slipping belt preventing the AC compressor from operating. Use the diagram to verify the belt routing and inspect the belt and pulley for damage.
- Battery Not Charging: The alternator is responsible for charging the battery. If the serpentine belt is not properly driving the alternator, the battery won't charge. Refer to the diagram to verify belt routing.
If you suspect a problem with the serpentine belt system, always start by visually inspecting the belt, pulleys, and tensioner. Compare the actual belt routing to the diagram to ensure it's correct. Use a belt tension gauge to verify that the tension is within the manufacturer's specifications. Never work on the serpentine belt system with the engine running!
Safety Precautions
Working on the serpentine belt system can be dangerous if you're not careful. Here are some important safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on any electrical components. This prevents accidental shorts and potential injury.
- Hot Engine: Never work on the serpentine belt system when the engine is hot. Allow the engine to cool down completely before starting any work.
- Moving Parts: Never, ever put your hands or tools near the serpentine belt or pulleys while the engine is running. These components can cause serious injury.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
- Gloves: Wear gloves to protect your hands from dirt, grease, and sharp edges.
The tensioner pulley stores significant spring force. Use the correct tool (usually a socket and breaker bar) to relieve the tension before removing or installing the belt. Releasing the tensioner incorrectly can cause injury.
Remember, if you're not comfortable performing these repairs yourself, it's always best to consult a qualified mechanic.
And lastly, for your convenience, we have a PDF file containing the specific serpentine belt diagram for your 2015 Jeep Grand Cherokee 3.6L. You can download it for easy reference.
