2015 Mitsubishi Outlander Serpentine Belt Diagram
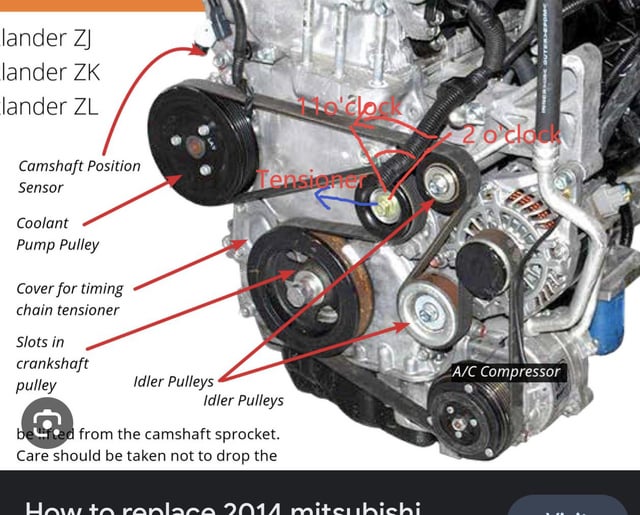
The serpentine belt on your 2015 Mitsubishi Outlander is a critical component, responsible for powering essential engine accessories. Understanding its routing and function is crucial for preventative maintenance, troubleshooting, and repairs. This article provides a detailed breakdown of the 2015 Outlander serpentine belt diagram, offering insights for the experienced DIYer.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
The serpentine belt diagram is your roadmap for understanding the belt's routing path. It's indispensable for several reasons:
- Correct Belt Installation: Ensures the belt is properly installed after replacement, preventing damage and premature wear. An incorrectly routed belt can slip, causing accessory failure and potential engine damage.
- Troubleshooting: Helps diagnose issues related to belt slippage, noise, or accessory malfunction. By visually inspecting the belt's path and tensioner, you can identify potential problems.
- Maintenance: Assists in visually inspecting the belt for wear and tear, cracks, or fraying. Early detection allows for timely replacement, avoiding costly breakdowns.
- Learning Engine Layout: Familiarizes you with the location and function of various engine components, promoting a better understanding of your vehicle's mechanics.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the Serpentine Belt System
The serpentine belt system on the 2015 Outlander consists of several key components, each playing a vital role in its operation:
- Serpentine Belt: The main drive belt, typically made of reinforced rubber, that transmits power from the crankshaft to the various accessories. The specific belt length and number of ribs are crucial for proper fitment. Check your owner's manual or a parts catalog for the correct specifications for your engine (2.4L or 3.0L).
- Crankshaft Pulley (Damper): Attached to the crankshaft, this pulley is the driving force behind the serpentine belt system. It's designed to dampen vibrations and provide a smooth power transfer.
- Alternator Pulley: Driven by the serpentine belt, the alternator generates electrical power to charge the battery and run the vehicle's electrical systems.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: The power steering pump provides hydraulic assistance for steering. Its pulley is driven by the serpentine belt.
- Air Conditioning Compressor Pulley: The A/C compressor circulates refrigerant in the air conditioning system. Its pulley is also driven by the serpentine belt.
- Tensioner Pulley: This spring-loaded pulley maintains proper tension on the serpentine belt, preventing slippage and ensuring optimal performance. There are generally two types of tensioners: automatic and manual. The 2015 Outlander uses an automatic tensioner.
- Idler Pulley: Some models may have an idler pulley, which helps guide the belt and maintain proper wrap around the other pulleys. It doesn't drive any specific accessory.
Understanding Serpentine Belt Diagram Symbols
Serpentine belt diagrams use specific symbols to represent different components and aspects of the belt's path. Here's a breakdown of common symbols:
- Solid Line: Represents the main path of the serpentine belt. Following the solid line will show you the correct routing of the belt around each pulley.
- Dashed Line: Sometimes used to indicate the belt's path behind other components or for clarity.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of belt rotation around each pulley.
- Component Icons: Small icons representing each component (e.g., alternator, A/C compressor, power steering pump) are often included to help identify their location on the engine.
- Pulley Diameter: While less common, some diagrams may indicate the diameter of each pulley. This information can be useful for identifying the correct replacement parts.
How the Serpentine Belt System Works
The serpentine belt system works on a simple principle: power transfer. The crankshaft, driven by the engine's combustion process, rotates the crankshaft pulley. The serpentine belt, wrapped around this pulley and the pulleys of various accessories, transfers this rotational energy to those accessories. The tensioner pulley maintains the correct belt tension, ensuring adequate grip and preventing slippage.
The order in which the belt wraps around the pulleys is critical. The diagram dictates this order, ensuring that each accessory receives the necessary power and that the belt doesn't rub against any engine components.
Real-World Use: Troubleshooting Tips
The serpentine belt diagram can be incredibly useful for troubleshooting common issues:
- Squealing Noise: A squealing noise often indicates a slipping serpentine belt. Check the belt for wear, cracks, or glazing. Also, inspect the tensioner pulley for proper function. A worn or weak tensioner may not be providing adequate tension.
- Accessory Malfunction: If an accessory (e.g., A/C compressor, power steering) stops working, check the serpentine belt. A broken belt will immediately disable all accessories. Also, check the belt routing to see if it's slipped off one of the pulleys.
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the serpentine belt for signs of wear and tear. Look for cracks, fraying, missing chunks, or glazing (a shiny, smooth surface). Replace the belt if any of these conditions are present.
- Belt Alignment: Use the diagram to verify that the belt is properly aligned on each pulley. Misalignment can cause premature wear and noise.
Safety Precautions
Working with the serpentine belt system can be dangerous if proper precautions are not taken:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on the serpentine belt system. This prevents accidental starting of the engine.
- Hot Engine: Allow the engine to cool completely before working on the serpentine belt. The exhaust manifold and other engine components can be extremely hot.
- Moving Parts: Never put your hands or tools near the serpentine belt while the engine is running. The belt can cause serious injury.
- Tensioner Release: When removing or installing the serpentine belt, use the correct tool to release the tension on the tensioner pulley. Follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully.
- Sharp Edges: Be aware of sharp edges on engine components. Wear gloves to protect your hands.
The tensioner pulley stores significant spring tension. Releasing it incorrectly can cause injury. Always use the correct tools and follow the service manual's procedure. Incorrect belt routing, even if seemingly minor, can lead to premature belt failure and damage to accessories. Double-check the diagram before starting the vehicle.
With a comprehensive understanding of the 2015 Mitsubishi Outlander's serpentine belt diagram, you're well-equipped to handle a variety of maintenance and repair tasks. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult the service manual for specific instructions and torque specifications.
We have the detailed 2015 Mitsubishi Outlander Serpentine Belt Diagram file available for download. This will provide you with a high-resolution image for easy reference during your work. Please contact us if you'd like the file.
