2015 Nissan Altima 2.5 Belt Diagram
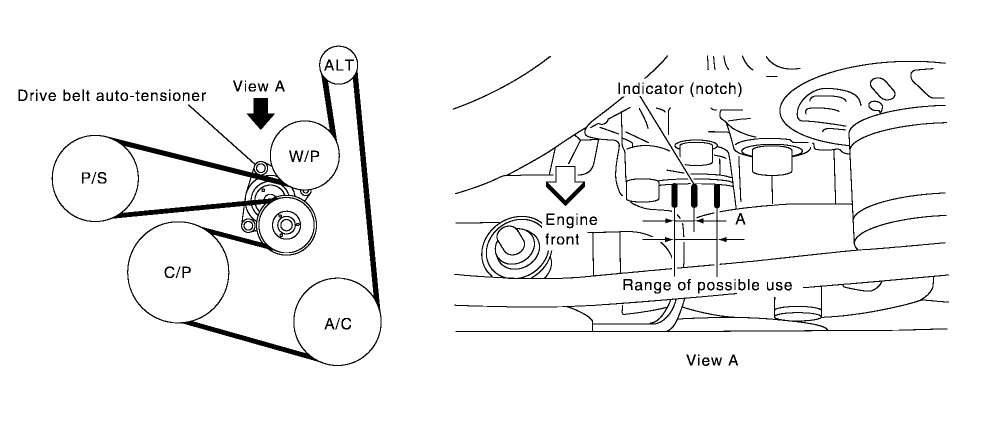
Understanding the serpentine belt system on your 2015 Nissan Altima 2.5L is crucial for maintenance, repairs, and even some performance modifications. This article delves into the belt diagram, explaining its purpose, key components, how the system functions, and how to use the diagram for troubleshooting. Knowing your way around this system can save you money and prevent breakdowns. We’ll equip you with the knowledge to tackle common issues and even identify potential problems before they escalate.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
The serpentine belt diagram serves as a visual roadmap for the entire belt system. Its main purpose is to illustrate the routing of the serpentine belt around various engine components. This is especially useful when:
- Replacing the belt: Ensuring the new belt is routed correctly is critical. Incorrect routing can lead to component failure, belt slippage, and reduced engine performance.
- Troubleshooting: Identifying which component is driven by a specific section of the belt helps in diagnosing problems like a squealing noise or a non-functioning AC.
- Maintenance: Visual inspection of the belt and pulleys is much easier with a clear understanding of their arrangement.
- Education: Understanding the system is the first step to keeping your Altima running smoothly. It helps you comprehend how the different components interact.
Think of it as the operating manual for your belt system. Attempting to work on the system without this knowledge is akin to doing a complex surgery without an anatomy chart – risky and likely to end badly!
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2015 Nissan Altima 2.5L engine uses a single serpentine belt to drive multiple accessories. Here’s a breakdown of the critical components:
- Crankshaft Pulley: The main driving force, connected directly to the engine's crankshaft. This pulley is the origin of the serpentine belt’s motion.
- Alternator Pulley: Drives the alternator, which charges the battery and powers the electrical system.
- Air Conditioning (AC) Compressor Pulley: Drives the AC compressor, responsible for cooling the cabin.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: Drives the power steering pump, providing hydraulic assistance for steering.
- Idler Pulley(s): Smooth, unpowered pulleys that guide the belt and maintain proper tension. These are crucial for routing the belt correctly and preventing excessive wear.
- Tensioner Pulley: A spring-loaded pulley that automatically maintains the correct tension on the belt. This is a very important part of the system.
Key Specs: While the belt length varies slightly depending on manufacturer, the 2015 Altima 2.5 usually uses a serpentine belt around 86-87 inches in length. Always refer to the manufacturer's specifications or use the part number of your old belt to ensure correct replacement. Using the wrong belt can damage your engine or the other components.
Symbols and Diagram Interpretation
The belt diagram isn’t just a picture; it's a standardized representation of the system using symbols:
- Solid Lines: Represent the serpentine belt itself. The thickness of the line can sometimes indicate the belt's width, but this is not always consistent.
- Circles/Ovals: Represent pulleys. The size of the circle often corresponds to the actual pulley size, which can be helpful in identification.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of rotation for each pulley. Pay close attention to these arrows when routing the belt.
- Text Labels: Clearly identify each component (e.g., "ALT" for alternator, "AC" for AC compressor, "PS" for power steering).
- Tensioner Symbol: The tensioner pulley is typically shown with a spring symbol or a curved arrow indicating the direction it moves to apply tension.
Understanding these symbols allows you to quickly interpret the diagram and follow the correct belt routing path.
How the Serpentine Belt System Works
The serpentine belt system is relatively simple in concept. The engine's crankshaft rotates, turning the crankshaft pulley. This pulley, in turn, drives the serpentine belt, which loops around all the other accessory pulleys. The belt’s frictional grip on each pulley transfers the rotational force, causing each accessory to function.
The tensioner pulley plays a crucial role in maintaining the necessary grip. It constantly applies pressure to the belt, compensating for stretching or wear and ensuring the belt remains tight against all the pulleys. Without proper tension, the belt will slip, leading to reduced performance of the driven accessories (e.g., weak AC, poor power steering, low battery charge).
Essentially, the serpentine belt acts as the lifeline, powering several vital systems in your vehicle.
Real-World Use and Basic Troubleshooting
The serpentine belt diagram becomes invaluable during troubleshooting. Here are a few scenarios:
- Squealing Noise: A squealing noise, especially upon starting the engine, often indicates a slipping belt. Check the belt for cracks, glazing, or wear. Also, inspect the tensioner pulley for proper operation. If the tensioner arm is bouncing excessively, the tensioner may need replacement.
- Weak AC: If the AC is not cooling effectively, and you've ruled out other causes, check the belt routing to the AC compressor. A slipping belt may not be providing sufficient power to the compressor.
- Charging Problems: If the battery is not charging correctly, verify the belt routing to the alternator. A loose or damaged belt can prevent the alternator from generating sufficient power.
- Power Steering Issues: If the steering feels heavy or difficult, especially at low speeds, check the belt routing to the power steering pump. A slipping belt can reduce the hydraulic assistance, making steering more challenging.
Troubleshooting Tips:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the belt for cracks, fraying, or missing chunks. These are signs of imminent failure.
- Tensioner Check: Ensure the tensioner pulley is moving freely and maintaining consistent tension on the belt.
- Pulley Alignment: Check that all pulleys are properly aligned. Misalignment can cause premature belt wear and noise.
Safety Considerations
Working on the serpentine belt system involves inherent risks. Never work on the system with the engine running. The rotating components can cause serious injury.
- Disconnect the Battery: Before starting any work, disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent accidental starting of the engine.
- Hot Surfaces: Be aware that engine components, especially the exhaust manifold, can be extremely hot. Allow the engine to cool completely before working on the system.
- Proper Tools: Use the correct tools for the job. A serpentine belt tool is essential for releasing the tension on the tensioner pulley.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
The tensioner pulley stores significant spring force. When releasing the tension, ensure you have a firm grip on the tensioner tool to prevent it from snapping back violently. This is very important for avoiding injury.
We have a printable PDF version of the 2015 Nissan Altima 2.5L Serpentine Belt Diagram available for download. Having a hard copy can be incredibly useful when working in the garage.
