2016 Nissan Maxima Fuse Box Diagram
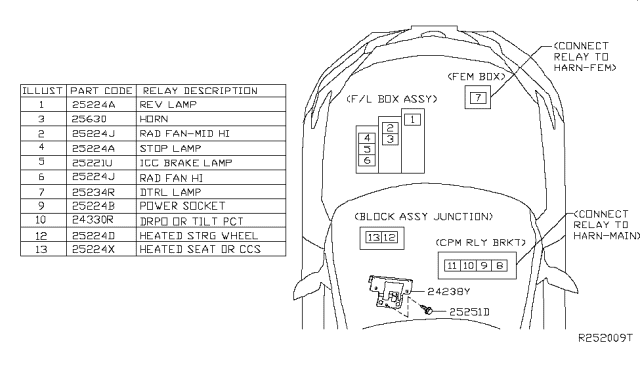
Okay, let's dive into the 2016 Nissan Maxima fuse box diagram. For any intermediate car enthusiast, DIY mechanic, or even someone just looking to better understand their vehicle, this diagram is an invaluable resource. We're going to cover everything you need to know to effectively use it, from understanding the symbols to real-world troubleshooting. And the best part? We've got the diagram available for download, so you can reference it directly as we go.
Purpose: Why You Need This Diagram
Why is this diagram so important? Well, think of your car's electrical system as a complex network of circuits. Fuses are like tiny circuit breakers, designed to protect these circuits from overloads. When a circuit draws too much current – perhaps due to a short circuit, a faulty component, or even just an unexpected surge – the fuse blows, interrupting the current flow and preventing damage to more expensive and critical components.
The fuse box diagram is essentially a roadmap to this electrical system. It allows you to quickly identify which fuse protects which circuit. This is crucial for:
- Troubleshooting electrical problems: If a specific component, like your radio or headlights, stops working, the diagram can help you pinpoint the likely culprit – a blown fuse.
- Performing repairs and modifications: When adding aftermarket accessories like a new amplifier or auxiliary lights, you'll need to tap into the existing electrical system safely. The diagram shows you which circuits are available and how to properly protect them.
- Understanding your vehicle's systems: Even if you're not actively troubleshooting or modifying anything, the diagram provides a valuable overview of how your car's electrical components are interconnected.
Without the diagram, you're essentially guessing, which can lead to wasted time, further damage, and potentially dangerous electrical issues. It's the difference between educated diagnosis and blind trial and error.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2016 Nissan Maxima typically has two main fuse box locations:
- Inside the Cabin (Instrument Panel): This fuse box is usually located on the driver's side, often behind a small access panel on the dashboard or near the footwell. It typically houses fuses for interior components like the radio, power windows, climate control, and instrument panel.
- Under the Hood (Engine Compartment): This fuse box is situated within the engine bay, usually near the battery. It contains fuses for critical engine-related systems such as the engine control unit (ECU), fuel pump, ignition system, headlights, and other high-current components.
Within each fuse box, you'll find:
- Fuses: These are the protective devices we've already discussed. They come in various amperage ratings (e.g., 5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 30A), each designed to handle a specific amount of current.
- Relays: These are electromechanical switches that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. For example, a low-current signal from the headlight switch activates a relay, which then allows a high-current circuit to power the headlights.
- Fuse Puller: A small plastic tool used to safely remove and install fuses.
- Fuse Box Cover: The cover that protects the fuses and usually contains a simplified diagram of the fuse layout. However, always refer to the detailed diagram for accuracy.
Symbols: Understanding the Language of the Diagram
The fuse box diagram uses a variety of symbols and abbreviations to represent different components and circuits. Understanding these symbols is key to interpreting the diagram correctly.
- Lines: Lines represent electrical circuits. Thicker lines generally indicate circuits carrying higher current.
- Rectangles: Rectangles typically represent fuses or relays. The number inside or next to the rectangle indicates the fuse's amperage rating or the relay's function.
- Circles: Circles can represent various components, depending on the surrounding symbols. They might indicate sensors, switches, or other electrical devices.
- Icons: Small icons often represent the specific component protected by a fuse. For example, a headlight icon indicates the headlight circuit, a radio icon indicates the radio circuit, and so on. These icons can vary, so it's important to consult the diagram's legend.
- Abbreviations: Common abbreviations include:
- ECU: Engine Control Unit (the car's computer)
- ABS: Anti-lock Braking System
- IGN: Ignition
- ACC: Accessory
- HTR: Heater
- PWR: Power
- Colors: Colors may be used to distinguish different circuits or voltage levels. However, color-coding on the diagram may not always match the actual wire colors in your car, so use caution.
The key is to always refer to the diagram's legend or key, which will provide a detailed explanation of all the symbols used. Every manufacturer has slight variations in symbols, so don’t assume; verify.
How It Works: Tracing a Circuit
Let's say your 2016 Maxima's cigarette lighter (or auxiliary power outlet) isn't working. Here's how you'd use the fuse box diagram to troubleshoot:
- Locate the Fuse Box Diagram: Consult the owner's manual or search online for the specific diagram for the 2016 Nissan Maxima. (Remember, we have it available for download!)
- Identify the Fuse: Look for the fuse labeled "CIG LTR" or "AUX PWR" or something similar in the cabin fuse box diagram. Note its amperage rating (e.g., 15A).
- Locate the Fuse in the Fuse Box: Using the diagram as a guide, physically locate the corresponding fuse in the fuse box. The diagram shows you its position relative to other fuses.
- Inspect the Fuse: Carefully remove the fuse using the fuse puller. Examine the filament inside the fuse. If the filament is broken or blackened, the fuse is blown and needs to be replaced.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Never use a fuse with a higher amperage rating, as this could overload the circuit and cause damage.
- Test the Circuit: After replacing the fuse, test the cigarette lighter to see if it's working again. If it still doesn't work, there may be a problem with the wiring or the cigarette lighter socket itself.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some practical tips for using the fuse box diagram to troubleshoot electrical issues:
- Start with the Obvious: Before diving into the fuse box, check the simplest things first. Is the component switched on? Is the connection secure?
- Visual Inspection: Always visually inspect the fuses for signs of damage (broken filament, blackened glass) before testing them with a multimeter.
- Use a Multimeter: A multimeter can be used to test the continuity of a fuse (i.e., whether it's allowing current to flow). If the multimeter shows no continuity, the fuse is blown.
- Document Your Work: Keep a record of the fuses you've checked and the results of your testing. This can be helpful if you need to troubleshoot the problem further.
- Consult the Owner's Manual: The owner's manual often provides additional information about the fuse box layout and the function of specific fuses.
- Test after each change: Verify you solve the problem before moving on.
Safety: Handle with Care!
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous, so always take the following precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical system, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent accidental short circuits.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use tools with insulated handles to protect yourself from electric shock.
- Never Bypass a Fuse: Never bypass a fuse by using a wire or a piece of metal. This can overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- Replace Fuses with the Correct Amperage: Always replace a blown fuse with a fuse of the same amperage rating. Using a higher amperage fuse can damage the circuit.
- Be Aware of High-Current Components: Components like the starter motor and alternator draw very high currents. Be extremely careful when working around these components.
High-current circuits like the ABS and airbag systems are particularly risky. If you're not comfortable working on these systems, it's best to leave them to a qualified mechanic. Mishandling these circuits could lead to serious injury.
By understanding the fuse box diagram and following these safety precautions, you can safely and effectively troubleshoot electrical problems in your 2016 Nissan Maxima. We've covered the basics, but remember, the most important tool you have is knowledge. So, study the diagram, understand the symbols, and approach each problem methodically.
Ready to get started? Download the 2016 Nissan Maxima Fuse Box Diagram here.
