2016 Toyota 4runner Fuse Box Diagram
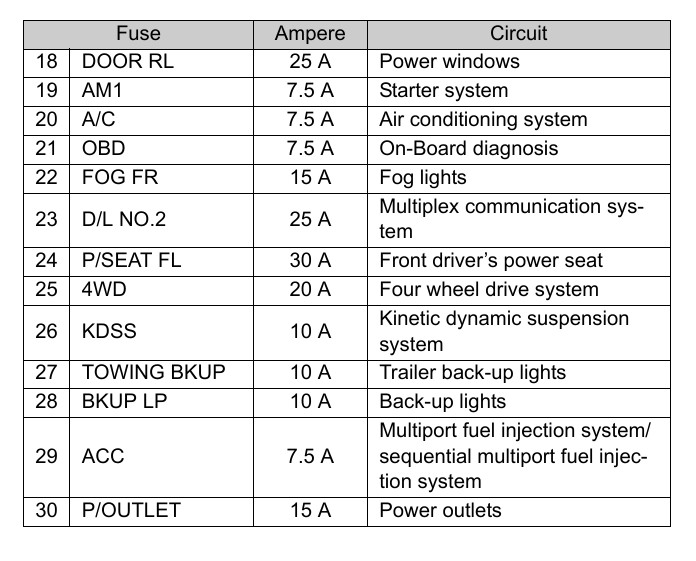
So, you're diving into the electrical system of your 2016 Toyota 4Runner, huh? Excellent choice. Understanding your vehicle's fuse box is crucial for everything from basic repairs to advanced modifications. This guide will walk you through the 2016 4Runner fuse box diagram, explaining what everything means, how it works, and how to use it safely. We're talking under-the-hood level knowledge here, but presented in a way that's approachable, even if you're not a certified mechanic. We also have a downloadable copy of the diagram available for you to save to your device for ease of reference later.
Why Bother with the Fuse Box Diagram?
Let's be honest, no one *wants* to deal with fuses. But when something electrical goes haywire, knowing your way around the fuse box can save you time, money, and a potential headache. The diagram is your roadmap. It’s essential for:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: A blown fuse is often the culprit behind a malfunctioning component. The diagram helps you quickly identify the correct fuse to check.
- Performing Repairs: Before replacing a faulty part, verify the fuse. It could be a simple (and cheap) fix.
- Adding Aftermarket Accessories: Planning to install a new sound system, lights, or other electronics? You'll need to tap into the electrical system, and the fuse box is the safest place to do it. Understanding the diagram prevents you from overloading circuits or causing shorts.
- General Vehicle Knowledge: Simply understanding how your car's electrical system is laid out increases your overall knowledge of vehicle maintenance and operation.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2016 4Runner has two main fuse box locations:
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Located under the hood, usually on the driver's side. This box houses fuses and relays for critical systems like the engine, headlights, and ABS.
- Instrument Panel Fuse Box: Found inside the cabin, often behind a small access panel near the driver's side dashboard. This box controls interior components like the radio, power windows, and climate control.
Each fuse box contains a collection of fuses and relays. Fuses are safety devices designed to protect circuits from overcurrent. They contain a thin wire that melts and breaks the circuit if the current exceeds a safe level. Relays are electrically operated switches that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. They are used to switch on components like the headlights, starter motor, and air conditioning compressor.
Decoding the Fuse Box Diagram: Symbols and Colors
The fuse box diagram isn't just a random collection of lines and boxes. It uses a standardized set of symbols to represent different components. Let's break down some common ones:
- Fuses: Represented by a simple line, sometimes with a break in the middle to indicate the fusible element. The amperage rating of the fuse is usually indicated next to the symbol (e.g., "10A" for a 10-amp fuse).
- Relays: Typically shown as a square or rectangle with internal circuitry. The diagram may indicate the relay's function (e.g., "Headlight Relay").
- Wiring: Solid lines represent wires connecting different components. Dashed lines may indicate grounds or shielded wiring.
- Grounds: Indicated by a symbol resembling an upside-down Christmas tree or a series of descending lines. Grounding is essential for completing the circuit and providing a return path for current.
Colors: While not always consistent across all diagrams, wire colors are often indicated with abbreviations (e.g., "BLU" for blue, "RED" for red, "BLK" for black). These colors correspond to the actual wire colors in your vehicle, helping you trace circuits and identify specific wires. Remember to verify the specific color coding used on your 2016 4Runner diagram, as slight variations are possible.
Icons: The diagram often uses icons to represent the components being protected by each fuse. These can include images of headlights, windows, radios, and other systems. This visual aid makes it easier to identify the correct fuse for a specific component.
How It Works: A Simplified Explanation
Imagine your car's electrical system as a series of interconnected circuits. Each circuit powers a specific component, like the headlights, radio, or power windows. The battery is the power source, providing the electrical energy needed to operate these components. The fuse box acts as a central distribution point, routing power from the battery to the various circuits. Each circuit has a fuse, which is a safety device that protects the circuit from overcurrent.
When a component malfunctions or experiences a short circuit, it can draw excessive current. This increased current flows through the fuse, causing the fusible element to heat up and melt. The melting of the fusible element breaks the circuit, preventing further current flow and protecting the wiring and components from damage. Think of it like a circuit breaker in your home – it trips to prevent an electrical fire.
Therefore, understanding the fuse box diagram allows you to quickly identify which fuse protects which circuit. If a component stops working, you can consult the diagram to locate the corresponding fuse, inspect it for damage, and replace it if necessary.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Okay, let's get practical. Here's how you can use the fuse box diagram to troubleshoot common electrical problems:
- Identify the Problem: What's not working? Headlights, radio, power windows, etc.
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse box diagram (either the one in your owner's manual or the downloadable one we provide). Find the fuse that corresponds to the malfunctioning component.
- Inspect the Fuse: Use a fuse puller (usually included in the fuse box) to remove the fuse. Examine the fusible element. A blown fuse will have a visible break or dark spot in the wire.
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can damage the circuit and potentially cause a fire.
- Test the Component: After replacing the fuse, test the component to see if it's working again. If the fuse blows again immediately, there's likely a more serious problem in the circuit (short circuit, faulty component) that requires further investigation.
Quick Tip: Keep a spare set of fuses in your glove compartment. You never know when you might need one!
Safety First!
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Always follow these safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on the fuse box, disconnect the negative (-) terminal of the battery. This prevents accidental shorts and shocks.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use tools with insulated handles to prevent electrical shock.
- Never Replace a Fuse with a Higher Amperage Fuse: As mentioned earlier, this can overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- If You're Unsure, Seek Professional Help: If you're not comfortable working on electrical systems, take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic.
- High-Current Circuits are Risky: Be especially careful around high-current circuits like the starter motor and alternator. These circuits can deliver a powerful shock.
Components like the fuel pump relay, ignition system fuses, and ABS system fuses control critical safety features. Mishandling these components could have serious consequences. If you're uncomfortable or unsure, leave it to a professional.
This guide provides a solid foundation for understanding your 2016 4Runner's fuse box. By using the diagram, you can troubleshoot electrical problems, perform repairs, and even add aftermarket accessories with confidence. And remember, we have a downloadable copy of the fuse box diagram readily available for your use, and safe and happy wrenching!
