2017 Mitsubishi Outlander Serpentine Belt Diagram
Hey gearheads! Today, we're diving deep into the serpentine belt system of a 2017 Mitsubishi Outlander. Understanding this system is crucial for any DIY mechanic, whether you're tackling routine maintenance or troubleshooting a pesky issue. We'll cover everything from the diagram's layout to practical real-world applications. And the best part? We've got the actual diagram ready for you to download, making your life even easier!
Why Bother with the Serpentine Belt Diagram?
Let's face it, staring at a tangled mess of belts and pulleys under the hood can be intimidating. The serpentine belt diagram is your roadmap to sanity. It provides a visual representation of how the belt is routed around various engine components. Knowing this route is essential for:
- Correct Belt Installation: Installing the belt incorrectly can damage the belt, the accessories it drives, or even the engine itself.
- Troubleshooting: A diagram helps you identify which component is causing a problem (e.g., a squealing noise might be from a failing idler pulley).
- General Maintenance: Familiarizing yourself with the belt's path allows for easier inspection for wear and tear.
- Part Replacement: If you need to replace a component like the alternator or power steering pump, the diagram shows how the belt interacts with it.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the Serpentine Belt System
The 2017 Outlander, depending on the engine (usually a 2.4L inline-4 or a 3.0L V6), will have a slightly different serpentine belt arrangement. However, the fundamental components remain the same:
- Serpentine Belt: This is the single, continuous belt that drives multiple engine accessories. Its length and rib count are specific to the engine type. Crucially, using the wrong belt size can lead to system malfunction.
- Crankshaft Pulley (or Harmonic Balancer): This pulley is connected directly to the crankshaft and provides the rotational power to drive the belt.
- Alternator Pulley: The alternator generates electrical power for the car's systems and charges the battery.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: The power steering pump provides hydraulic assistance to make steering easier.
- Air Conditioning Compressor Pulley: The A/C compressor circulates refrigerant to cool the cabin.
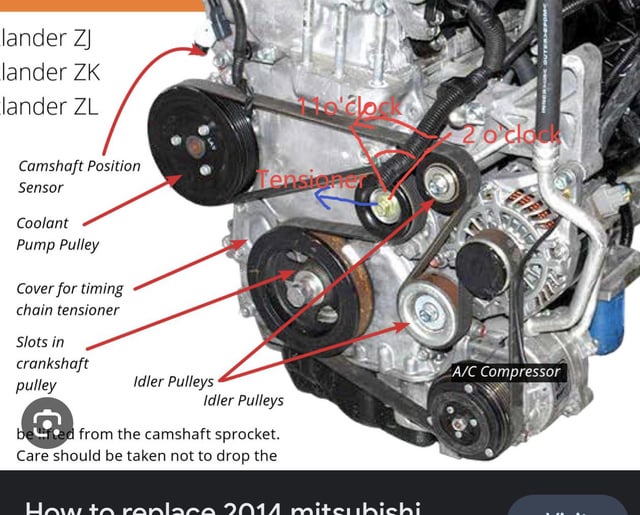
- Idler Pulleys: These pulleys are smooth and used to guide the belt along the correct path, often changing the belt's direction.
- Tensioner Pulley: This pulley, usually spring-loaded, maintains the correct tension on the serpentine belt. Maintaining proper tension is critical for efficient operation and belt longevity. A failing tensioner can cause belt slippage and component damage.
Engine Specifics
While the components are similar, their placement and the overall belt routing will differ between the 2.4L and 3.0L engines. Always refer to the specific diagram for *your* engine type. The diagram will often show the belt length and routing specific to that engine.
Decoding the Serpentine Belt Diagram: Symbols and Conventions
Understanding the symbols on the diagram is key to interpreting it correctly.
- Solid Lines: These represent the path of the serpentine belt itself. The thickness of the line might vary on some diagrams, but generally, it simply indicates the belt's path.
- Pulleys: Pulleys are usually depicted as circles. The diagram might label them with abbreviations (e.g., ALT for Alternator, P/S for Power Steering, A/C for Air Conditioning).
- Arrows: Arrows on the belt path indicate the direction of belt rotation. This is crucial for ensuring correct belt installation.
- Tensioner Location: The tensioner is often represented with a special symbol, sometimes showing the spring mechanism. It's usually clearly labeled.
- Text Labels: The diagram will include text labels identifying each component and providing other relevant information (e.g., torque specifications for the tensioner bolt).
How the Serpentine Belt System Works
The serpentine belt system is a relatively simple, yet crucial, part of the engine. The crankshaft, driven by the engine's combustion, turns the crankshaft pulley. This pulley then drives the serpentine belt, which in turn spins the pulleys of the various accessories (alternator, power steering pump, A/C compressor).
The tensioner plays a vital role by maintaining constant tension on the belt. As the belt stretches over time (which it will), the tensioner automatically compensates, ensuring that the accessories continue to be driven effectively. Without proper tension, the belt will slip, leading to reduced performance from the accessories (e.g., weak power steering, poor A/C cooling, low battery charging).
Real-World Use: Troubleshooting with the Diagram
Here are a few common problems and how the diagram can help:
- Squealing Noise: A squealing noise often indicates a slipping belt. Use the diagram to check the belt's routing and condition. Inspect the tensioner to ensure it's providing adequate tension. Look for signs of glazing (a shiny, hard surface) on the belt, which indicates slippage.
- Accessory Failure: If the alternator, power steering pump, or A/C compressor isn't working correctly, the diagram helps you trace the belt's path to that component. A broken or frayed belt could be the culprit.
- Belt Jumping Off: This is a serious issue. It often indicates a misaligned pulley or a failing tensioner. The diagram will help you identify the correct pulley alignment.
- Routine Inspection: Use the diagram as a visual aid when inspecting the belt for cracks, fraying, or missing chunks. Replace the belt if you find any significant damage.
Quick Troubleshooting Tips:
Tip 1: Always inspect the pulleys for damage (e.g., bent flanges, cracks). A damaged pulley can quickly destroy a new belt.
Tip 2: If replacing the belt, consider replacing the tensioner and idler pulleys as well. These components wear out over time and can contribute to belt failure.
Tip 3: Before removing the old belt, take a picture or draw a diagram of its routing. This will help you avoid mistakes when installing the new belt.
Safety First! Precautions Around the Serpentine Belt
Working around the serpentine belt system can be dangerous. Here's why:
- Moving Parts: The engine must be OFF and cool before working on the serpentine belt. Even a brief touch while the engine is running can cause serious injury.
- Hot Components: The engine components, especially the exhaust manifold, can be extremely hot. Allow the engine to cool completely before working on the belt.
- Tensioner Spring: The tensioner is spring-loaded and can snap back forcefully if not handled correctly. Use the appropriate tools (usually a wrench or socket) to relieve the tension.
- Eye Protection: Always wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
- Battery Disconnect: Consider disconnecting the negative battery terminal before working on the system. This will prevent accidental starting of the engine.
Always consult your owner's manual or a qualified mechanic if you're unsure about any procedure.
Ready to Download the Diagram?
You've made it this far, and now for the good stuff! We have the serpentine belt diagram for the 2017 Mitsubishi Outlander (both 2.4L and 3.0L engine versions). Simply click the link [link to downloadable file] to download a PDF version. This will allow you to zoom in, print it out, and take it right to your garage. Good luck, and happy wrenching!
