2018 Chevy Silverado 2500 Hd Nox Sensor Locations Diagram
Alright, let's dive into the NOx sensor locations on a 2018 Chevy Silverado 2500 HD. This information is crucial whether you're diagnosing a pesky check engine light, planning a modification, or just deepening your understanding of your truck's emissions system. Knowing where these sensors are and how they function can save you a ton of time and money on repairs.
Why You Need a NOx Sensor Location Diagram
First off, why bother with a diagram at all? Several reasons:
- Troubleshooting: A common cause of a check engine light on these trucks is a faulty NOx sensor. The trouble code will only tell you there's a problem, not where the problem is. The diagram pinpoints the sensor location, saving you the headache of aimlessly searching.
- Repair and Replacement: Replacing a NOx sensor isn't rocket science, but you need to find it first! The diagram guides you directly to the sensor, simplifying the removal and installation process.
- Understanding Your Vehicle: For those of us who like to understand how our vehicles operate, the diagram provides a visual representation of the NOx sensor's role within the exhaust system.
- Aftermarket Modifications: Planning on modifying your exhaust system? Knowing the location of the NOx sensors is critical to avoid damaging them during modifications and ensuring your modifications don't negatively impact the sensor readings.
Key Specs and Main Parts
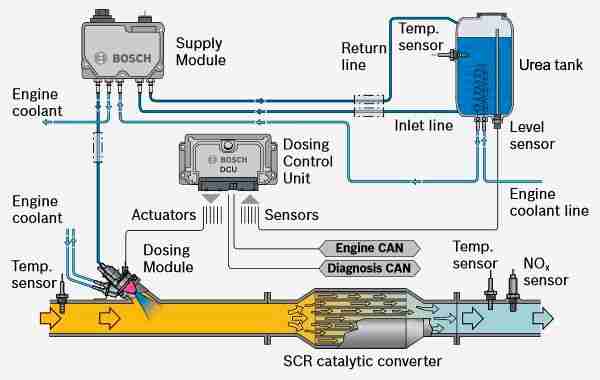
The 2018 Chevy Silverado 2500 HD with the Duramax diesel engine (L5P) typically utilizes two NOx sensors. These sensors are crucial components of the Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) system, which reduces harmful nitrogen oxides (NOx) emissions from the exhaust. Let's break down the key specs and parts:
- Upstream NOx Sensor (NOx Sensor 1): Located *before* the SCR catalyst. It measures the NOx concentration in the exhaust gas entering the catalyst.
- Downstream NOx Sensor (NOx Sensor 2): Located *after* the SCR catalyst. It measures the NOx concentration in the exhaust gas exiting the catalyst. This allows the engine control module (ECM) to determine the efficiency of the SCR system.
- SCR Catalyst: The heart of the NOx reduction system. This component uses a chemical reaction to convert NOx into harmless nitrogen and water. The NOx sensors monitor the effectiveness of this catalyst.
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) Injector: Sprays DEF into the exhaust stream upstream of the SCR catalyst. The DEF reacts with the NOx in the presence of the catalyst to reduce NOx emissions.
- ECM (Engine Control Module): The "brain" of the operation. The ECM receives signals from the NOx sensors and uses this information to control the DEF injection rate and other engine parameters.
- Sensor Connectors: These connectors link the NOx sensors to the vehicle's wiring harness, transmitting data to the ECM.
While not directly part of the sensor itself, understanding the interaction with these components is essential for effective troubleshooting.
Understanding the Diagram: Symbols, Lines, and Colors
A good diagram uses standard automotive symbols to represent different components. Here's a breakdown of what you might encounter:
- NOx Sensor Symbol: Typically represented by a box or rectangle with the letters "NOx" inside. Sometimes, it might resemble a simplified sensor shape.
- Exhaust Pipe: Usually depicted as solid lines, often with arrows indicating the direction of exhaust flow.
- Wiring Harness: Represented by dashed or dotted lines connecting the sensors to the ECM or other components.
- Connectors: Shown as small circles or squares at the ends of wiring harness lines, indicating the physical connection points.
- Colors: Color-coding varies, but common practices include using different colors to distinguish between different wiring circuits or sensor types. The legend in the diagram would define these.
- Abbreviations: Look for abbreviations like "Upstream," "Downstream," "SCR," "ECM," and "DEF."
Key Takeaway: Always refer to the diagram's legend or key to understand the specific symbols and color codes used. No two diagrams are exactly alike.
How It Works: The NOx Sensor's Role
Let's delve into how the NOx sensors work within the SCR system. NOx sensors are essentially specialized oxygen sensors that can also detect the presence of nitrogen oxides. Here's a simplified explanation:
- Exhaust Gas Analysis: The upstream NOx sensor analyzes the exhaust gas coming directly from the engine. It measures the concentration of NOx present in the exhaust.
- Data Transmission: The sensor sends this data to the ECM as an electrical signal.
- DEF Injection Control: The ECM uses the upstream NOx sensor data to determine the optimal amount of DEF to inject into the exhaust stream.
- SCR Catalyst Reaction: The DEF reacts with the NOx in the presence of the SCR catalyst, converting the NOx into nitrogen and water.
- Downstream Monitoring: The downstream NOx sensor monitors the exhaust gas exiting the SCR catalyst. It measures the remaining NOx concentration.
- Efficiency Assessment: The ECM compares the readings from the upstream and downstream sensors to determine the efficiency of the SCR system. If the downstream sensor detects a high NOx concentration, it indicates that the SCR system is not functioning properly.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): If the ECM detects a problem with the NOx sensors or the SCR system, it will set a DTC, triggering the check engine light.
The entire system forms a closed-loop feedback mechanism, ensuring that NOx emissions are minimized.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
So, you've got a check engine light and suspect a NOx sensor issue. Here are some basic troubleshooting steps:
- Scan for DTCs: Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). Common codes related to NOx sensors include P2200-P2203 (NOx Sensor Circuit) and P20EE (SCR NOx Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold).
- Visually Inspect the Sensors: Locate the sensors using the diagram. Check for any visible damage, such as cracked housings, damaged wiring, or corroded connectors.
- Check the Connectors: Ensure the connectors are securely attached to the sensors and that there is no corrosion or damage to the connector pins.
- Test Sensor Resistance: Using a multimeter, you can check the resistance of the NOx sensor. Refer to the vehicle's service manual for the correct resistance values. Important: Disconnect the sensor from the wiring harness before testing resistance.
- Check Wiring Harness Continuity: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the wiring harness between the sensor and the ECM. Look for any open circuits or shorts to ground.
- Consult a Professional: If you're unsure about any of these steps, consult a qualified mechanic. Working with electrical systems can be dangerous.
Safety First!
Working on exhaust systems involves certain risks. Here are a few safety precautions to keep in mind:
- Hot Exhaust: Never work on the exhaust system immediately after the engine has been running. Allow the system to cool down completely to avoid burns.
- Electrical Hazards: Disconnect the negative battery cable before working on any electrical components, including the NOx sensors. This will prevent accidental shorts or shocks.
- Protective Gear: Wear safety glasses, gloves, and appropriate clothing to protect yourself from hot surfaces, sharp edges, and potential chemical exposure.
- DEF Fluid: Diesel Exhaust Fluid is corrosive. Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Wear gloves and eye protection when handling DEF.
Remember: If you're not comfortable working on your vehicle, it's always best to consult a qualified mechanic. Your safety is paramount!
Armed with this knowledge and the diagram, you'll be well-equipped to diagnose and repair NOx sensor-related issues on your 2018 Chevy Silverado 2500 HD. Good luck!
