2018 Honda Accord Undercarriage Diagram
Understanding the undercarriage of your 2018 Honda Accord is crucial for everything from routine maintenance to complex repairs and modifications. This isn't just about knowing where the exhaust pipe is; it's about grasping the interplay of suspension components, braking systems, fuel lines, and more. A detailed undercarriage diagram is your roadmap to confidently diagnosing problems and tackling DIY projects. Let's dive in.
Purpose of the 2018 Honda Accord Undercarriage Diagram
Why bother with an undercarriage diagram? There are several compelling reasons:
- Repair and Maintenance: Identifying parts for replacement or repair becomes straightforward. Imagine trying to explain to a parts store clerk that you need a “thingy that connects to the other thingy near the wheel.” A diagram gives you the precise name and location.
- Troubleshooting: Hearing a clunking noise? Seeing a leak? The diagram helps you pinpoint the potential source, narrowing down your diagnostic efforts.
- Modifications: Planning to upgrade your suspension, exhaust, or add underbody protection? Knowing the layout ensures compatibility and avoids costly mistakes.
- General Understanding: Even if you don't plan on getting your hands dirty, understanding the undercarriage gives you a better appreciation for how your car works and can help you communicate more effectively with your mechanic.
- Accident Assessment: If your Accord has been involved in an accident, the diagram is invaluable for assessing potential structural damage and identifying compromised components.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2018 Honda Accord's undercarriage is a complex assembly. Here's a breakdown of the key components you'll find on the diagram:
- Suspension: This includes the front struts (MacPherson strut design in most models), rear multi-link suspension, coil springs, shock absorbers, stabilizer bars (also called sway bars), and various control arms. These work together to provide a smooth ride and stable handling.
- Braking System: You'll see brake calipers, brake rotors, brake lines (both rigid metal and flexible hoses), and potentially the ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) module. Note the routing of the brake lines – damage to these is critical.
- Exhaust System: This typically includes the exhaust manifold (connected to the engine), catalytic converter (crucial for emissions control), resonator, muffler, and exhaust pipes. Pay attention to the hangers that secure the exhaust system – broken hangers can lead to rattling and premature wear.
- Fuel System: You'll find fuel lines running from the fuel tank to the engine. These are often protected by heat shields. Never tamper with the fuel system without proper safety precautions.
- Drivetrain: For front-wheel-drive models, you'll see the transaxle, drive shafts, and CV joints (Constant Velocity joints). For all-wheel-drive models (if available in certain markets), you'll also see the rear differential, rear drive shaft, and rear axles.
- Steering System: The steering rack and tie rods are essential for steering. Look for any signs of leaks from the power steering system.
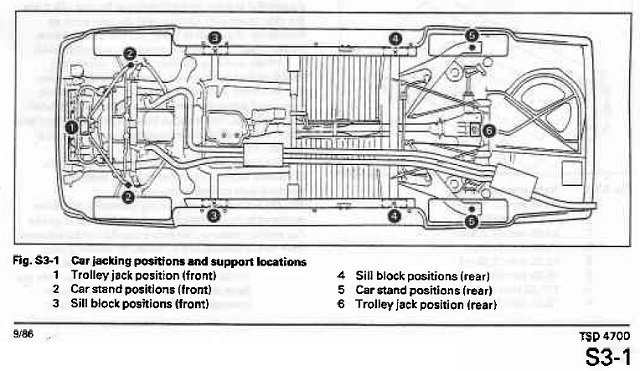
- Chassis and Frame: The frame rails provide the structural backbone of the vehicle. Damage to these rails can compromise the vehicle's safety. Also, note the location of jacking points and lift points.
- Heat Shields: These are strategically placed to protect components from excessive heat generated by the exhaust system. Missing or damaged heat shields can lead to overheating and potential damage to other components.
Symbols – Understanding the Diagram Language
Undercarriage diagrams aren't just pictures; they use a standardized set of symbols to convey information. Here's how to interpret them:
- Solid Lines: Typically represent rigid components like pipes, frame rails, and solid suspension members. Thicker lines often indicate larger or more structurally significant components.
- Dashed Lines: May indicate flexible components like hoses or wiring harnesses. They can also represent hidden components or the routing of a part behind another.
- Color Coding: While not universally standardized, some diagrams use colors to distinguish different systems. For example, fuel lines might be green, brake lines red, and exhaust components brown. Always refer to the diagram's legend for the specific color key.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of flow (e.g., fuel, exhaust).
- Callouts and Labels: Each component should be clearly labeled with its name or a code that corresponds to a parts list.
- Hatching/Crosshatching: Can indicate a specific material or surface treatment.
How It Works – The Interconnected Systems
The undercarriage isn't just a collection of individual parts; it's a complex network of interconnected systems. For example:
- Braking and Suspension: The suspension system's ability to maintain contact with the road surface directly impacts the effectiveness of the braking system. Worn suspension components can lead to longer stopping distances and reduced stability under braking.
- Exhaust and Fuel: The catalytic converter relies on precise temperature control to function properly. Heat shields and the overall exhaust system design play a crucial role in maintaining this temperature.
- Steering and Suspension: The steering system relies on the suspension to provide a stable platform for turning. Worn ball joints or tie rod ends can lead to vague steering and poor handling.
Understanding these interdependencies is crucial for effective troubleshooting. A problem in one area can often manifest as a symptom in another.
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how you can use the undercarriage diagram to diagnose common problems:
- Fluid Leaks: Identify the type of fluid (oil, coolant, brake fluid, etc.). Trace the leak back to its source using the diagram. Check for damaged hoses, loose fittings, or cracks in components.
- Suspension Noises: A clunking noise might indicate a worn ball joint, tie rod end, or sway bar link. The diagram helps you locate these components for inspection. Squeaking noises could be caused by dry bushings.
- Exhaust Rattles: Check the exhaust hangers for damage. The diagram shows the location of all the hangers. Also, inspect the exhaust pipes for cracks or holes.
- Brake Issues: If you're experiencing poor braking performance or unusual noises, use the diagram to inspect the brake lines for leaks or damage, and the calipers and rotors for wear.
Safety – Proceed with Caution
Working under a vehicle can be dangerous. Here are some crucial safety precautions:
- Always use jack stands: Never rely solely on a jack to support the vehicle. Use sturdy jack stands placed at designated jacking points.
- Wear safety glasses: Protect your eyes from debris.
- Disconnect the battery: This is especially important when working on the electrical system or near fuel lines.
- Be careful with fuel and brake lines: These systems are under pressure. Relieve the pressure before disconnecting any lines. Fuel is highly flammable!
- Work in a well-ventilated area: Exhaust fumes are toxic.
- Consult a repair manual: The undercarriage diagram is a visual aid, but it doesn't replace a detailed repair manual.
- Consider professional help: If you're uncomfortable with any aspect of the repair, don't hesitate to seek professional assistance.
The catalytic converter can get extremely hot. Avoid touching it, even long after the engine has been turned off. Brake fluid is corrosive and can damage paint. Clean up any spills immediately.
We have a high-resolution, downloadable 2018 Honda Accord undercarriage diagram available for your use. Having this file on hand will significantly aid you in your DIY repairs and modifications. Please contact us to request access to the file.
