2018 Nissan Maxima Fuse Box Diagram
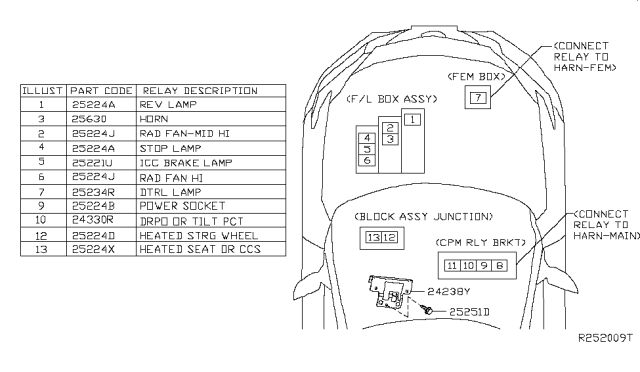
The fuse box in your 2018 Nissan Maxima is a critical component, acting as the central protection point for your vehicle's electrical system. Understanding its layout and function is essential for both routine maintenance and troubleshooting electrical issues. This article will provide a detailed breakdown of the 2018 Maxima's fuse box diagram, empowering you to diagnose problems, perform repairs, and even safely add aftermarket accessories. We're aiming for clarity, so while we'll use technical terms, we'll ensure you understand what they mean.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
Why bother understanding your fuse box diagram? Simply put, it's your roadmap to electrical troubleshooting. Without it, diagnosing a blown fuse is a guessing game. With it, you can quickly identify the circuit affected and pinpoint the potential source of the problem. Here’s why it’s crucial:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Issues: Identifying blown fuses is the first step in solving electrical problems. The diagram tells you exactly which fuse corresponds to which component.
- Performing Repairs: Knowing the fuse layout is vital when replacing a faulty component or repairing damaged wiring. You need to ensure you're not inadvertently affecting other circuits.
- Adding Aftermarket Accessories: If you're installing a new stereo, lighting, or other electronic device, you'll need to tap into the vehicle's electrical system safely. The fuse box diagram helps you identify suitable circuits and choose appropriate fuse ratings.
- Preventing Further Damage: Replacing a blown fuse with one of the correct amperage is crucial. Using a higher amperage fuse can bypass the intended protection and potentially damage components or even cause a fire.
- General Understanding: It deepens your understanding of your car's electrical system, allowing you to perform more maintenance tasks and communicate more effectively with mechanics if professional help is needed.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2018 Nissan Maxima typically has two primary fuse box locations:
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Located near the engine, this box houses fuses and relays for critical systems like the engine control unit (ECU), anti-lock braking system (ABS), headlights, and cooling fan. This box is usually the larger of the two and contains higher amperage fuses.
- Interior Fuse Box: Usually found under the dashboard (typically on the driver's side, but sometimes on the passenger side), this box protects circuits related to interior functions such as the power windows, power locks, radio, and interior lighting.
Key Components:
- Fuses: These are sacrificial devices designed to protect circuits from overcurrent. They contain a thin wire that melts and breaks the circuit when the current exceeds a specific rating (measured in amperes or amps).
- Relays: These are electrically operated switches that control higher-current circuits using a low-current signal. They are used to activate components that require a lot of power, such as headlights, starters, and fuel pumps. A relay has coil, and set of contacts that are either normally open(NO) or normally closed(NC). Applying voltage to the coil causes the contacts to switch.
- Fuse Puller: A small plastic tool designed to easily remove fuses from the fuse box. Using pliers can damage the fuses and the fuse box.
- Test Light or Multimeter: Used to test for voltage and continuity in a circuit. This is essential for verifying that a fuse is blown and for troubleshooting the cause of the blown fuse.
- Fuse Box Cover: The cover protects the fuses and relays from the elements and usually contains a diagram indicating the function of each fuse.
Understanding Fuse Box Symbols
Fuse box diagrams utilize various symbols to represent different components and functions. These symbols can vary slightly between manufacturers, but some common ones include:
- Lines: Solid lines indicate a direct electrical connection. Dotted lines may indicate a connection through a switch or relay.
- Colors: While not always present *on* the fuse box itself, some diagrams may use colors to differentiate between different circuits or voltage levels. For example, red might indicate a constant 12V power source, while blue might indicate a switched power source.
- Icons: These are the most important elements. Common icons include:
- Headlight Icon: Indicates a fuse or relay related to the headlight system.
- Radio Icon: Represents the radio or audio system.
- Window Icon: Corresponds to the power window system.
- Lock Icon: Relates to the power door locks.
- Engine Icon: Indicates a fuse or relay related to the engine control system.
- ABS Icon: Represents the anti-lock braking system.
- Fan Icon: Pertains to the cooling fan system.
Pay close attention to the amperage rating printed on each fuse. This is usually indicated by a number followed by the letter "A" (e.g., 10A, 15A, 20A). It's crucially important to replace a blown fuse with one of the *exact same* amperage rating. Using a higher amperage fuse can allow excessive current to flow, potentially damaging components and creating a fire hazard.
How It Works
The fuse box acts as a central distribution and protection point for the vehicle's electrical system. Power from the battery is routed through the fuse box, where it's distributed to various circuits. Each circuit is protected by a fuse of the appropriate amperage rating. When a fault occurs in a circuit (e.g., a short circuit), the current flow increases dramatically. This excessive current causes the fuse's filament to melt, breaking the circuit and preventing damage to the connected components. The relay, on the other hand, uses a low amperage circuit as an actuator to energize another circuit of higher amps. Think of it as using a tiny bit of energy to control a big power source.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here’s a basic troubleshooting scenario using your knowledge of the fuse box:
- Symptom: Your car radio suddenly stops working.
- Step 1: Consult the fuse box diagram (both engine compartment and interior).
- Step 2: Identify the fuse labeled "Radio" or "Audio System." Note its amperage rating.
- Step 3: Locate the fuse in the appropriate fuse box.
- Step 4: Use a fuse puller to remove the fuse.
- Step 5: Inspect the fuse. If the filament inside is broken or blackened, the fuse is blown. You can also use a multimeter set to continuity to check. A good fuse will have continuity(Beep).
- Step 6: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the *exact same* amperage rating.
- Step 7: Test the radio. If it works, you've solved the problem. If the fuse blows again immediately, there's likely a short circuit in the radio wiring or the radio itself, and further diagnosis is needed.
Important: If a fuse blows repeatedly, do *not* simply replace it with a higher amperage fuse. This is a sign of a more serious electrical problem that needs to be investigated. Consult a qualified mechanic or automotive electrician to diagnose and repair the underlying issue.
Safety Considerations
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some safety precautions to follow:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical system, disconnect the negative (black) terminal of the battery. This will prevent accidental short circuits and electric shock.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use tools with insulated handles to minimize the risk of electric shock.
- Never Replace a Fuse with a Higher Amperage Fuse: This can bypass the intended protection and potentially damage components or cause a fire.
- Avoid Working in Wet Conditions: Water can conduct electricity, increasing the risk of electric shock.
- Consult a Professional: If you're unsure about any aspect of electrical repair, consult a qualified mechanic or automotive electrician. Working around the ABS or ECU can be particularly risky, as improper handling can damage these sensitive components.
High-Risk Components: Be particularly cautious when working near the ECU (Engine Control Unit), ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) module, and airbag system. These components are sensitive to voltage fluctuations and can be damaged by improper handling. Airbag systems can also be dangerous if triggered accidentally.
We have a complete 2018 Nissan Maxima fuse box diagram available for download. This diagram provides a detailed layout of both the engine compartment and interior fuse boxes, along with descriptions of each fuse and relay. Having access to this resource will greatly simplify your troubleshooting and repair efforts. Please download the file, and happy fixing!
