2021 Nissan Rogue Fuse Box Diagram
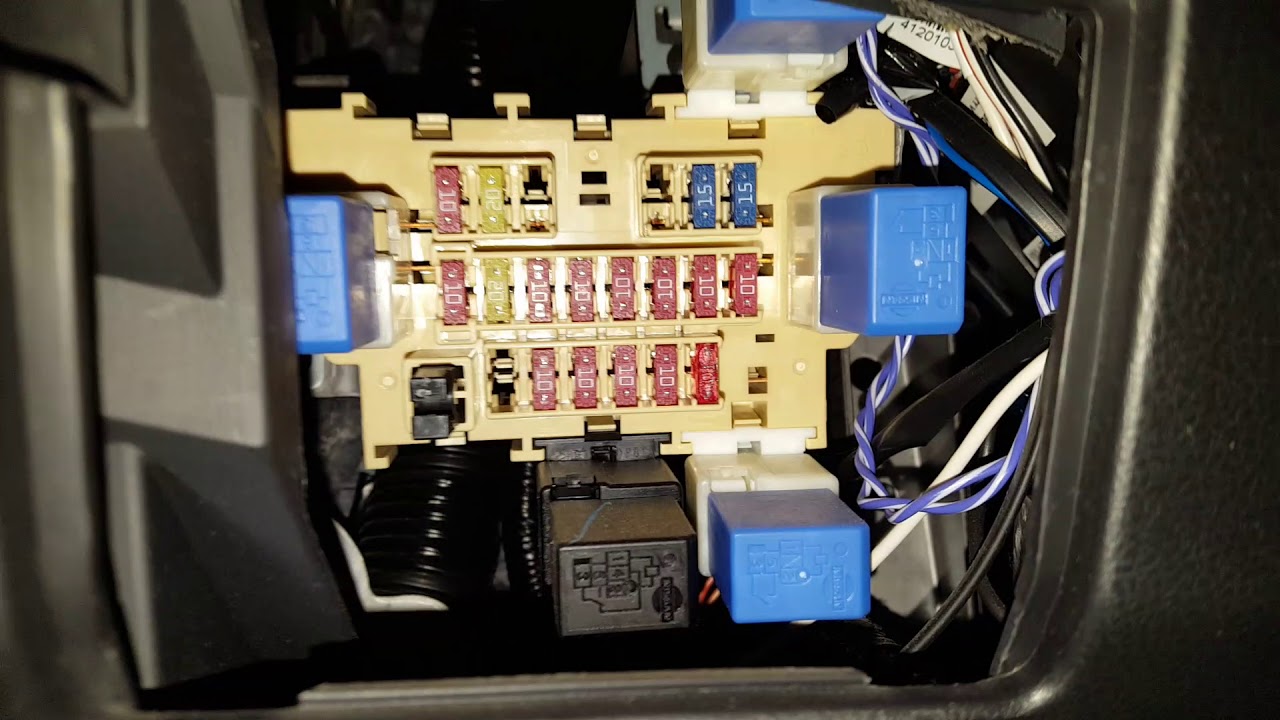
The 2021 Nissan Rogue represents a significant redesign for the popular SUV, and understanding its electrical system is crucial for both routine maintenance and more involved modifications. The fuse box diagram is your roadmap to navigating this system, allowing you to diagnose and resolve electrical issues efficiently. This article provides a detailed breakdown of the 2021 Rogue's fuse box, covering its purpose, components, symbology, and practical applications. We'll also address essential safety precautions to ensure you work safely.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram serves several vital purposes:
- Troubleshooting: Quickly identify which fuse corresponds to a malfunctioning component (e.g., headlights, radio, power windows).
- Preventive Maintenance: Inspect fuses regularly for signs of damage or corrosion.
- Modification: Safely tap into the electrical system for aftermarket accessory installation (e.g., adding a dashcam or auxiliary lighting).
- Learning: Gain a deeper understanding of your vehicle's electrical architecture.
Without a diagram, diagnosing electrical problems becomes a tedious and potentially damaging process of trial and error. Having this information readily available saves time, money, and frustration.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2021 Nissan Rogue generally has two primary fuse box locations:
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Located in the engine bay, usually near the battery. This box houses fuses and relays for critical systems like the engine control unit (ECU), anti-lock braking system (ABS), headlights, and cooling fans. It's designed to withstand higher temperatures and exposure to the elements.
- Interior Fuse Box (Instrument Panel Fuse Box): Typically located under the dashboard, either on the driver's side or passenger's side. This box protects circuits for interior accessories like the radio, power windows, door locks, interior lighting, and the climate control system.
Within each fuse box, you'll find:
- Fuses: These are sacrificial devices designed to protect electrical circuits from overcurrent. Each fuse has a specific amp rating, indicated by a number printed on the fuse and/or its color. When the current exceeds the fuse's rating, the internal filament melts, breaking the circuit and preventing damage to the protected component.
- Relays: These are electrically operated switches that control high-current circuits using a low-current signal. Relays are commonly used to control headlights, starter motors, and other high-power devices.
- Fuse Puller: A small plastic tool used to safely remove and install fuses without damaging them.
Important Specification: Pay close attention to the ampere (A) rating of each fuse. Replacing a blown fuse with one of a higher rating can overload the circuit and cause serious damage, potentially leading to a fire.
Understanding the Symbols
The fuse box diagram uses a variety of symbols to represent different components and their functions. Here's a breakdown of common symbols:
- Lines: Solid lines indicate a direct connection between components. Dashed lines might indicate a ground connection or a less critical connection.
- Colors: The color of the fuse corresponds to its amperage rating. Common colors and their corresponding ratings include:
- Yellow: 20A
- Blue: 15A
- Red: 10A
- Brown: 7.5A
- Orange: 5A
- Icons: Icons represent the component protected by the fuse. Examples include:
- Headlight icon: Headlights
- Radio icon: Audio system
- Window icon: Power windows
- Fan icon: Cooling fan
The diagram will also include text labels indicating the specific function of each fuse or relay. Careful study of the diagram is essential for accurate identification.
How It Works: Electrical Flow and Protection
The electrical system of the 2021 Rogue works by providing a closed circuit between the battery and the various electrical components. When a circuit is complete, electricity flows from the battery, through the component, and back to the battery. The fuse is placed in this circuit as a safety device.
Here's how it works in practice:
- The battery provides the source of electrical power.
- The power flows through the wiring harness to the fuse box.
- Each fuse protects a specific circuit.
- If a short circuit or overload occurs in a component (e.g., a faulty power window motor), the current draw increases dramatically.
- The increased current causes the fuse filament to melt, breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity.
- This prevents the overloaded circuit from damaging other components or causing a fire.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
When troubleshooting electrical issues, start with the fuse box. Here are some basic steps:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which component is not working.
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse corresponding to the malfunctioning component in the fuse box diagram.
- Inspect the Fuse: Use a fuse puller to remove the fuse. Visually inspect it for a broken filament. A blown fuse will have a visible gap in the wire inside the glass or plastic casing.
- Test the Fuse: Use a multimeter to test the fuse for continuity. Set the multimeter to the continuity setting (usually indicated by a sound wave symbol). Touch the probes to both ends of the fuse. If the multimeter beeps or shows a reading of 0 ohms, the fuse is good. If it shows no reading, the fuse is blown.
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Never use a fuse with a higher rating.
- Test the Component: After replacing the fuse, test the component to see if it is now working.
- If the Fuse Blows Again: If the new fuse blows immediately or shortly after replacement, there is a more serious problem in the circuit, such as a short circuit. Further diagnosis and repair by a qualified technician are recommended.
Safety Precautions
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous. Take the following precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent accidental short circuits.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools designed for automotive electrical work.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Protect your eyes from sparks or debris.
- Avoid Working in Wet Conditions: Water can conduct electricity and increase the risk of electric shock.
- Be Aware of High-Current Components: The starter motor, alternator, and battery are high-current components that can deliver a dangerous shock. Avoid touching these components while the engine is running or the battery is connected.
Special Note: The airbag system is a particularly sensitive and potentially dangerous component. If you need to work near the airbag system, consult a qualified technician to ensure it is properly disabled before proceeding.
We have a detailed fuse box diagram file available for download. This diagram provides a comprehensive overview of the 2021 Nissan Rogue's fuse locations, amperage ratings, and corresponding components. This resource will be invaluable for your DIY maintenance and troubleshooting efforts.
