2021 Nissan Sentra Fuse Box Diagram
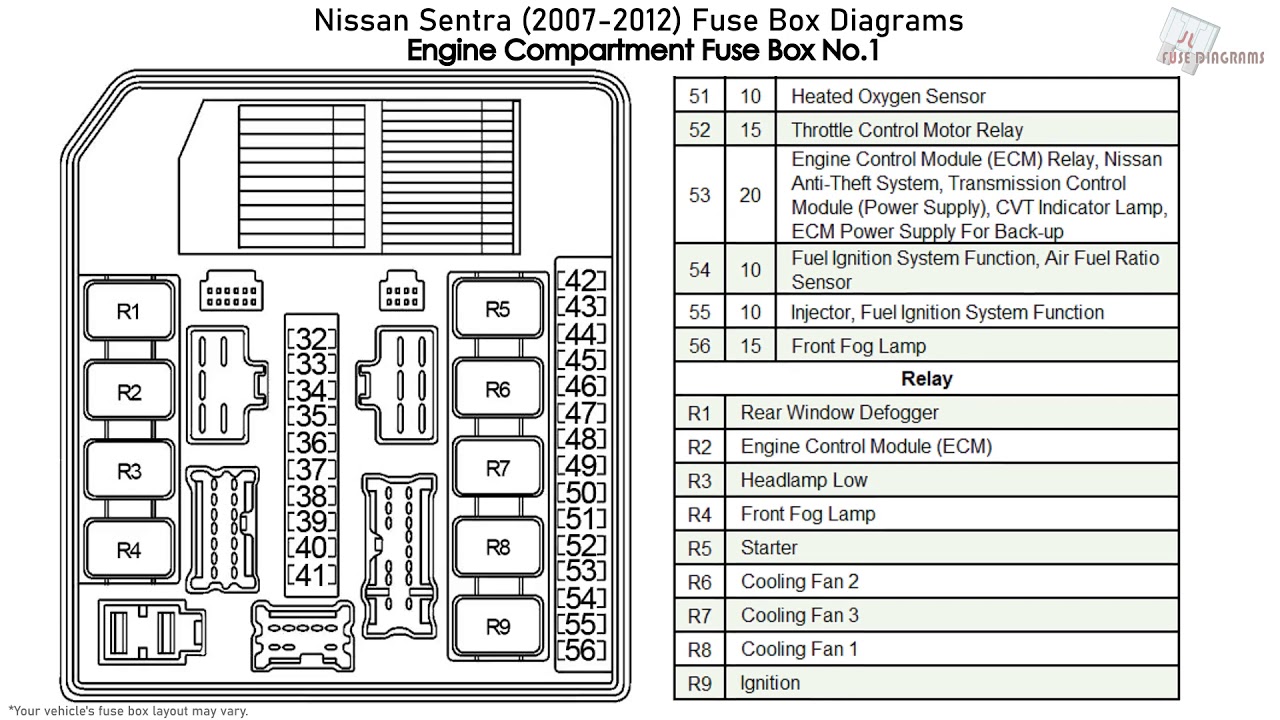
The 2021 Nissan Sentra, like any modern vehicle, relies on a complex electrical system to operate. Protecting this system from overloads and short circuits are fuses, housed within fuse boxes. Understanding the 2021 Nissan Sentra fuse box diagram is crucial for DIY repairs, modifications, and even just routine maintenance. This guide will walk you through the key aspects of this diagram, empowering you to diagnose and address electrical issues confidently.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram serves as a roadmap to your Sentra's electrical system. Its primary purpose is to identify the specific fuse responsible for a particular circuit. This is essential for several reasons:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: When a component stops working, the fuse diagram helps you pinpoint the potential culprit. Checking a blown fuse is often the first step in diagnosing electrical faults.
- Replacing Blown Fuses: Incorrectly replacing a fuse with one of a higher amperage rating can cause serious damage to your vehicle's wiring and components. The diagram ensures you use the correct fuse for the circuit.
- Adding Aftermarket Accessories: If you're adding accessories like a new sound system or auxiliary lights, the fuse diagram helps you identify suitable power sources and fuse locations for safe and proper integration. It's important to understand circuit loading (the total current draw on a circuit) to avoid overloading existing fuses.
- General Understanding: Familiarizing yourself with the fuse box layout provides a better understanding of your car's electrical system, making you a more informed owner.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2021 Sentra typically has two fuse boxes: one located inside the cabin (usually under the dashboard) and another in the engine compartment. The engine compartment fuse box is often larger and handles higher-current circuits. The specific locations can vary slightly depending on the trim level, but are usually clearly indicated in the owner's manual.
Key Components:
- Fuse Box Housing: The plastic enclosure that houses the fuses, providing physical protection and organization.
- Fuses: Overcurrent protection devices containing a thin metal strip that melts and breaks the circuit when excessive current flows through it. They are rated in amperes (amps), indicating the maximum current they can handle.
- Relays: Electrically operated switches that control high-current circuits using a low-current signal. Relays are used for components like headlights, starter motors, and fuel pumps.
- Fuse Puller: A small plastic tool (often stored in the fuse box) used to safely remove fuses without damaging them.
- Diagram Label: A sticker or printed card affixed to the fuse box cover, detailing the function and amperage rating of each fuse and relay.
Symbols and Markings
Understanding the symbols and markings on the fuse box diagram is crucial for accurate interpretation. Here's a breakdown:
- Fuse Amperage Ratings: Fuses are color-coded and labeled with their amperage rating (e.g., 5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, 30A). Common color coding is:
- Gray: 2A
- Violet: 3A
- Pink: 4A
- Orange: 5A
- Brown: 7.5A
- Red: 10A
- Blue: 15A
- Yellow: 20A
- Clear: 25A
- Green: 30A
- Lines and Circuit Traces: The diagram uses lines to represent electrical circuits, showing which components are protected by each fuse.
- Icons and Symbols: Icons represent various electrical components, such as:
- Light Bulb: Indicates a lighting circuit (headlights, taillights, interior lights).
- Fan: Represents a cooling fan circuit.
- Horn: Indicates the horn circuit.
- Radio: Represents the audio system circuit.
- Windshield Wipers: Indicates the windshield wiper circuit.
- Various generic symbols may also be used for more complex components.
The diagram also includes descriptions of each fuse's function. It’s essential to consult your owner's manual for the definitive legend specific to your vehicle's trim and options.
How It Works
The fuse box acts as a central distribution and protection point for the vehicle's electrical system. Power from the battery is distributed to various circuits through the fuse box. Each circuit is protected by a fuse of the appropriate amperage rating. If a short circuit or overload occurs, the fuse's internal element melts, breaking the circuit and preventing damage to the wiring and connected components. Relays, controlled by low-current signals from the vehicle's computer or switches, allow the switching of high-current circuits without requiring heavy-duty wiring to the switches themselves. This protects the switches and improves overall system efficiency. Without fuses, a short circuit could easily lead to a fire.
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting
Here's how you can use the fuse box diagram to troubleshoot common electrical problems:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which component isn't working (e.g., the radio, headlights, power windows).
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse box diagram (usually on the inside of the fuse box cover or in your owner's manual).
- Locate the Corresponding Fuse: Find the fuse that corresponds to the malfunctioning component. Note its amperage rating.
- Inspect the Fuse: Use the fuse puller to remove the fuse. Examine it closely. A blown fuse will have a broken or melted filament inside.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating. Never use a higher amperage fuse.
- Test the Circuit: Turn on the component to see if it now works.
- If the Fuse Blows Again: If the new fuse blows immediately or shortly after, there's likely a short circuit in the wiring or a faulty component. This requires further investigation and may necessitate professional help.
Safety Precautions
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Always take the following precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative (-) battery terminal to prevent accidental shorts and electrical shocks.
- Use the Correct Fuse: Never replace a fuse with one of a higher amperage rating. This can overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- Avoid Working in Wet Conditions: Water conducts electricity. Never work on electrical components in wet or damp conditions.
- Be Aware of Airbag Circuits: Some fuse boxes contain fuses for the airbag system. Airbags can deploy unexpectedly if the system is tampered with incorrectly. If you suspect an issue with the airbag system, consult a qualified technician.
- Consult a Professional: If you're uncomfortable working with electrical systems or if you encounter complex problems, seek the assistance of a qualified mechanic.
Disclaimer
This information is for general guidance only and should not be considered a substitute for professional advice. Consult your vehicle's owner's manual and a qualified technician for specific instructions and safety procedures.
We have the 2021 Nissan Sentra fuse box diagram readily available for download. This comprehensive diagram will provide you with a detailed overview of your vehicle's electrical system, empowering you to confidently tackle a wide range of maintenance and repair tasks.
