2024 Chevy Colorado Fuse Box Diagram
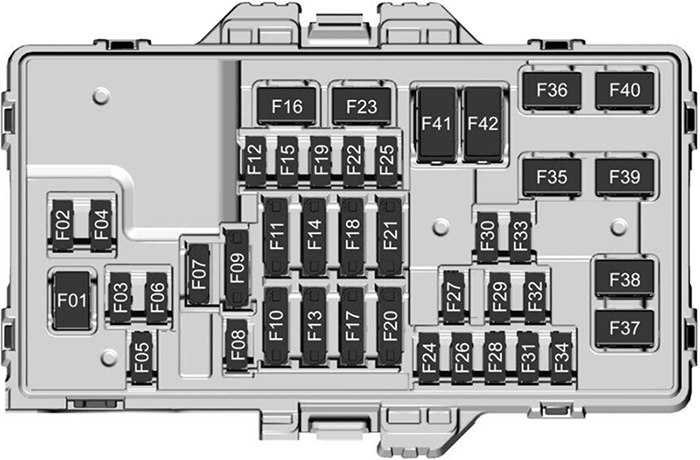
For the experienced DIY mechanic or the avid car modifier, understanding the fuse box is crucial for troubleshooting electrical issues, performing upgrades, or simply gaining a deeper understanding of your vehicle. This article dives deep into the 2024 Chevy Colorado's fuse box diagram, offering a comprehensive guide to its purpose, components, and practical application. We'll break down the complexities, offering insights that will empower you to confidently tackle electrical projects on your truck. This will give you the skills to identify the correct fuse, understand its amperage, and diagnose related problems, ultimately saving you time and money on potentially costly repairs.
Why This Diagram Matters
The fuse box diagram is more than just a pretty picture; it's your key to diagnosing and resolving electrical problems in your 2024 Chevy Colorado. Here's why it's so important:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Issues: When an electrical component stops working (e.g., headlights, radio, power windows), the fuse box is the first place to check. The diagram helps you identify the fuse associated with that component.
- Performing Modifications: If you're adding accessories like aftermarket lights, a winch, or a sound system, you'll need to tap into the electrical system. The diagram shows you where to safely and properly connect these accessories, preventing overloads and potential damage.
- Understanding Your Vehicle's Electrical System: The diagram provides a bird's-eye view of how your Colorado's electrical system is wired, allowing you to learn how different circuits are protected and interconnected. This is invaluable for advanced diagnostics and repairs.
- Preventative Maintenance: Regularly inspecting fuses can reveal potential problems before they become major headaches. A blown fuse often indicates an underlying issue that needs attention.
- Avoiding Costly Repairs: Being able to diagnose and replace a blown fuse yourself can save you a significant amount of money compared to taking your truck to a mechanic.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2024 Chevy Colorado likely has multiple fuse boxes. Expect to find at least one located in the engine compartment and another inside the cab, often under the dashboard or in the side panel. Each fuse box contains a collection of fuses, relays, and possibly circuit breakers. Let's break down the key components:
- Fuses: These are the sacrificial components designed to protect circuits from overcurrent. Each fuse has a specific amperage rating (e.g., 5A, 10A, 20A, 30A), indicating the maximum current it can handle before blowing. Different amperage ratings are designated by color, which will be explained below.
- Relays: These are electrically operated switches that control high-current circuits using a low-current signal. They're used to power components like headlights, starters, and fuel pumps. A faulty relay can prevent a component from functioning even if the fuse is good.
- Circuit Breakers: Some circuits might be protected by circuit breakers instead of fuses. Circuit breakers are resettable, meaning they trip and cut off the current when overloaded but can be reset manually once the overload is removed.
- Fuse Box Housing: This protects the fuses and relays from the elements and provides a organized way to access them. Usually made of plastic.
- Fuse Puller: A small plastic tool often included in the fuse box. This is used to safely remove fuses without damaging them or your fingers.
Understanding Fuse Box Symbols
Fuse box diagrams use a variety of symbols, colors, and lines to represent different components and their functions. Deciphering these symbols is essential for understanding the diagram. Here's a breakdown:
- Fuses: Fuses are typically represented by a rectangular box. The amperage rating is often printed directly on the fuse and indicated on the diagram. Different fuses are labeled with different numbers corresponding to what the fuse protects.
- Relays: Relays are generally represented by a square or rectangular shape with internal symbols indicating the coil and contacts.
- Lines: Lines indicate the wiring connections between different components. Thicker lines might represent higher-current circuits.
- Colors: Fuse colors are standardized to indicate their amperage rating. Here are some common examples:
- Yellow: 20 Amp
- Blue: 15 Amp
- Red: 10 Amp
- Brown: 7.5 Amp
- Orange: 5 Amp
- Clear/White: 25 Amp
- Icons: Icons are used to represent the components protected by each fuse. Common icons include headlights, turn signals, radio, power windows, and more. Consult the legend or key included with the diagram to understand the meaning of each icon. For example, an icon of a steering wheel may represent the power steering.
How It Works
The fuse box acts as a central distribution point for electrical power throughout your Colorado. Power from the battery flows through the ignition switch and various control modules, then distributed to different components via the fuse box. Each circuit is protected by a fuse with a specific amperage rating. If the current in a circuit exceeds the fuse's rating, the fuse's internal filament melts (blows), breaking the circuit and preventing damage to the protected component. This prevents potential shorts that can lead to fires.
Relays, on the other hand, are used to control high-current circuits with a low-current signal from a switch or control module. For example, when you turn on your headlights, the headlight switch sends a small electrical signal to the headlight relay. The relay then closes, allowing high-current power from the battery to flow to the headlights, turning them on.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how to use the fuse box diagram to troubleshoot common electrical problems:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which component is not working (e.g., headlights, radio, power windows).
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse box diagram (often found in the owner's manual or on a sticker inside the fuse box cover). Find the fuse that corresponds to the non-functional component.
- Inspect the Fuse: Use the fuse puller to remove the fuse. Visually inspect the fuse. If the filament inside the fuse is broken or blackened, the fuse is blown.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can damage the circuit and potentially cause a fire.
- Test the Component: Turn on the component to see if it now works. If it does, the problem was a blown fuse. If the fuse blows again immediately, there's likely a short circuit in the wiring or a faulty component.
- If the Fuse is Good, Check the Relay: If the fuse is good, the problem might be a faulty relay. Consult the fuse box diagram to locate the relay associated with the non-functional component. Swap the relay with a known-good relay (if possible) to see if that resolves the issue.
Safety First: Risky Components
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Always take the following precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative (-) terminal of the battery to prevent electrical shocks and short circuits.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use insulated tools to prevent electrical shocks.
- Never Replace a Fuse with a Higher Amperage Rating: Doing so can overload the circuit and potentially cause a fire.
- Work in a Well-Lit Area: Ensure you have adequate lighting to see what you're doing.
- Consult a Professional: If you're not comfortable working on electrical systems, consult a qualified mechanic. Working on advanced circuits like the ECU (Engine Control Unit) can be very risky.
- Be Aware of Airbags: Disconnecting and reconnecting certain electrical components can inadvertently trigger airbags. Always consult the service manual for proper procedures when working near airbag components.
Understanding your 2024 Chevy Colorado's fuse box is a great way to perform basic maintenance, and troubleshoot basic issues. When you are ready to work on your truck make sure that you have the correct diagram on hand.
