3.5 L 2006 Chevy Impala 3.5 Serpentine Belt Diagram
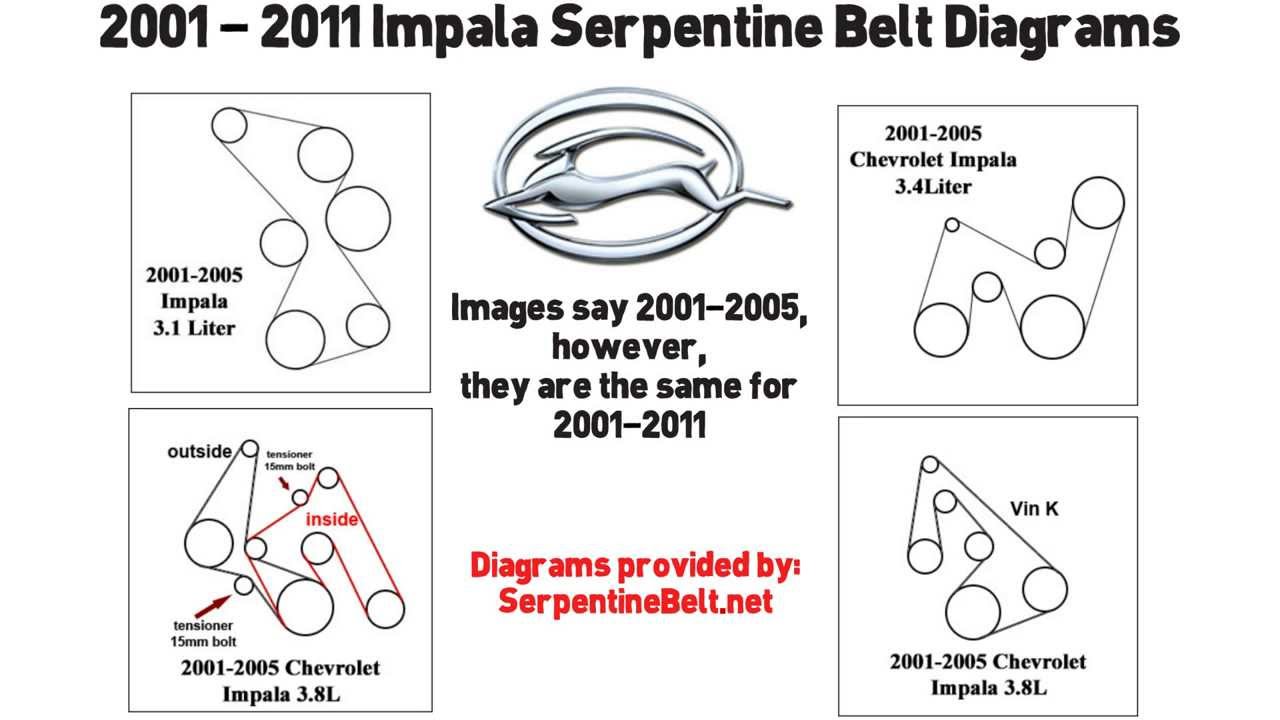
Alright, let's talk about the serpentine belt system on your 2006 Chevy Impala with the 3.5L engine. Understanding this system and, crucially, having access to a reliable serpentine belt diagram is essential whether you're planning to replace a worn belt, diagnosing a squealing noise, or simply wanting to familiarize yourself with your engine's layout. This article will break down everything you need to know, from the purpose of the diagram to practical troubleshooting tips.
Why a Serpentine Belt Diagram Matters
The serpentine belt diagram is essentially a roadmap for your engine's accessory drive system. It visually illustrates the routing of the serpentine belt around the various pulleys connected to engine-driven accessories. This is vital for a few key reasons:
- Correct Belt Installation: The most obvious reason. A mistake in the belt routing can prevent accessories from functioning correctly, leading to overheating (water pump not working), loss of power steering, or even a dead battery (alternator not charging).
- Troubleshooting: A diagram helps you identify which accessory a specific pulley belongs to. This aids in diagnosing problems like accessory bearing noise or accessory failure.
- Preventative Maintenance: Knowing the belt routing allows you to visually inspect the belt's condition along its entire length, catching potential problems early.
- Parts Identification: The diagram helps you identify the locations of various pulleys and tensioners, making ordering replacement parts easier.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 2006 Chevy Impala 3.5L Serpentine System
The 2006 Chevy Impala with the 3.5L engine (specifically, the LX9 engine) uses a single serpentine belt to drive the following accessories:
- Crankshaft Pulley (Harmonic Balancer): The main pulley driven directly by the engine. It provides rotational power to the entire system.
- Alternator: Supplies electrical power to the vehicle and charges the battery.
- Power Steering Pump: Provides hydraulic pressure for power-assisted steering.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant through the engine to prevent overheating.
- Air Conditioning Compressor: Compresses refrigerant for the air conditioning system.
- Idler Pulley(s): Smooth pulleys that provide additional belt routing and tension. These don't drive any accessories.
- Automatic Belt Tensioner: A spring-loaded device that maintains the correct tension on the serpentine belt. This is crucial for proper system operation.
Key Specs: The belt length is specific to this engine and accessory configuration. While exact lengths can vary slightly based on manufacturer, expect something around the 90-inch mark (e.g., 90.5 inches, but verify with the correct part number). Always use the correct belt specified for your vehicle, identified by the year, make, model, and engine. Using the wrong length can cause slipping or damage to the accessories.
Serpentine Belt Diagram Symbols and What They Mean
A good serpentine belt diagram will use a variety of symbols to convey information. Here's a breakdown of common conventions:
- Solid Lines: Represent the serpentine belt itself. The path of the line shows the belt's routing.
- Circles: Represent pulleys. The size may indicate the relative size of the pulley.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of rotation of each pulley. This is helpful for visualizing how the belt drives each accessory.
- Shading/Color Coding: Some diagrams may use shading or color coding to differentiate between different types of pulleys (e.g., driven pulleys vs. idler pulleys).
- Tensioner Symbol: The automatic belt tensioner is usually represented by a pulley with a curved arrow indicating the direction it pivots to maintain tension. You'll often see a spring symbol incorporated into the tensioner representation.
- Component Labels: Each pulley will be labeled with its corresponding accessory (e.g., "ALT" for alternator, "P/S" for power steering, "A/C" for air conditioning).
Pay close attention to the arrows indicating the belt direction around each pulley. The diagram shows how the grooved side of the belt interacts with the grooved pulleys, and the smooth side interacts with the smooth idler pulleys. Getting this wrong will prevent the system from working.
How the Serpentine Belt System Works
The crankshaft pulley, driven by the engine's rotation, is the heart of the serpentine belt system. As the crankshaft turns, it rotates the serpentine belt. The belt, in turn, drives all the accessories connected to the other pulleys in the system. The automatic belt tensioner ensures that the belt maintains proper tension at all times. As the belt stretches over time, the tensioner automatically adjusts to maintain the correct tension, preventing slippage and ensuring optimal accessory performance. A malfunctioning tensioner is a common cause of serpentine belt squeal and premature belt wear. The system is a carefully balanced loop, and the health of each component impacts the entire system's performance.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are a few common problems related to the serpentine belt system and how a diagram can help with troubleshooting:
- Squealing Noise: A squealing noise, especially when the engine is first started or under heavy load (e.g., turning the steering wheel at low speeds with A/C on), often indicates a slipping belt. Use the diagram to inspect the belt for cracks, fraying, or glazing. Also, check the tensioner for proper operation. If the tensioner is weak, it may not be providing enough tension, causing the belt to slip.
- Accessory Failure: If an accessory stops working (e.g., no power steering), use the diagram to verify that the belt is properly routed around the accessory's pulley. If the belt is properly routed and the pulley is turning, the accessory itself may be faulty. If the pulley is not turning, the belt may be broken or slipping excessively at that pulley.
- Belt Wear: Regularly inspect the serpentine belt for signs of wear, such as cracks, fraying, or missing chunks. Use the diagram to examine the belt's entire length, paying close attention to areas where it bends sharply around pulleys.
- Belt Comes Off: This can indicate a worn belt, a faulty tensioner, or a misaligned pulley. Use the diagram to check the belt routing and to inspect the tensioner and pulleys for damage or misalignment. A misaligned pulley will cause the belt to walk off over time.
Safety Considerations
Working on the serpentine belt system can be dangerous if proper precautions are not taken. Here are a few key safety points:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on the serpentine belt system to prevent accidental electrical shock or damage to electrical components.
- Hot Engine: Never work on the serpentine belt system when the engine is hot. Allow the engine to cool completely before starting any work.
- Moving Parts: Be extremely careful when working near the serpentine belt while the engine is running. The belt and pulleys are rotating at high speeds and can cause serious injury if you get your fingers or clothing caught in them. Never reach into a running engine compartment.
- Tensioner Spring: The automatic belt tensioner is under spring tension. Use the appropriate tool (usually a serpentine belt tool) to relieve the tension on the belt before removing it. Releasing the tension without the proper tool can be dangerous.
The alternator and A/C compressor contain electrical components and refrigerant, respectively. Handle these components with care and consult a qualified technician if you suspect a problem with either.
With the information above, and access to a diagram, you should be able to safely replace and manage most issues that involve the serpentine belt system on your 2006 Chevy Impala with a 3.5L.
We have a downloadable, high-resolution serpentine belt diagram available. It provides a clear and detailed visual representation of the belt routing for your specific vehicle. This diagram can be an invaluable resource for any DIY mechanic or car owner looking to perform maintenance or repairs on their serpentine belt system.
