3.5 L 2009 Chevy Impala 3.5 Serpentine Belt Diagram
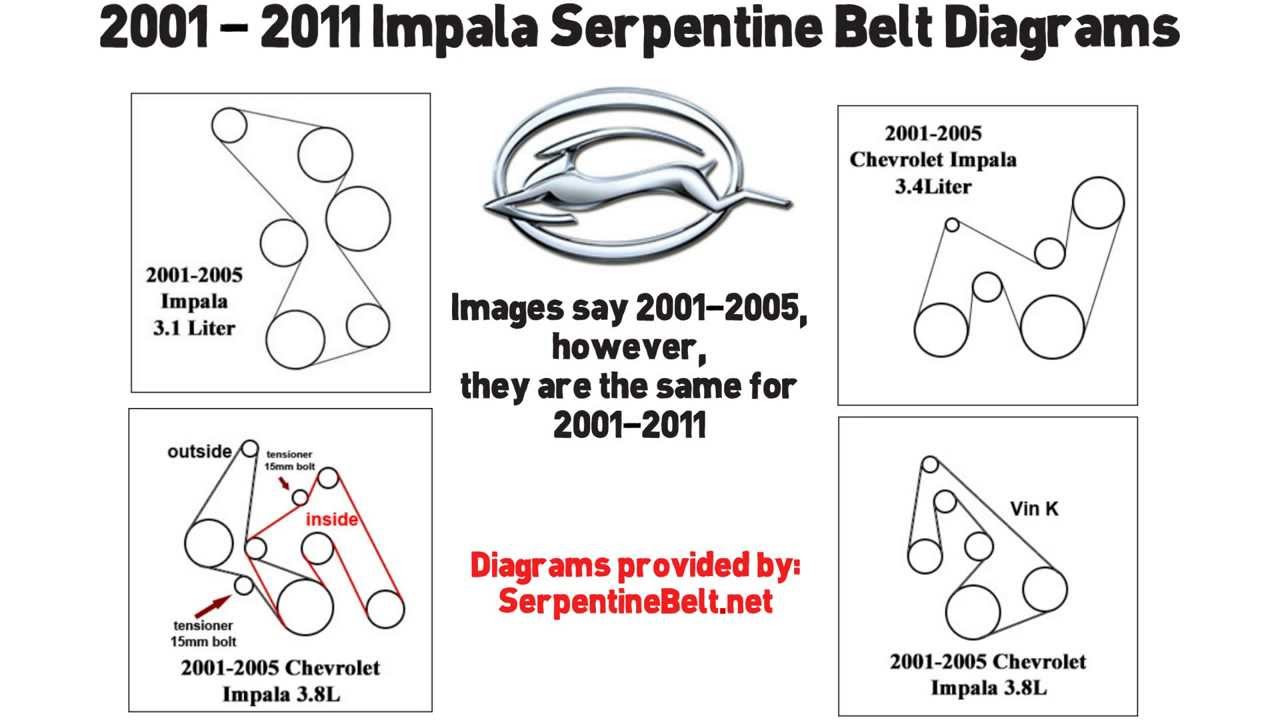
Alright, let's dive into the serpentine belt system for the 2009 Chevy Impala with the 3.5L engine. Understanding this setup is crucial whether you're tackling routine maintenance, troubleshooting a squealing noise, or just expanding your automotive knowledge. This guide provides a detailed breakdown of the serpentine belt diagram, its components, and practical tips for working with it.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
The serpentine belt diagram is your roadmap for navigating the belt system. It's invaluable for several reasons:
- Belt Replacement: It shows you the exact path the belt must follow to ensure correct installation. Incorrect routing can damage components and lead to system failure.
- Troubleshooting: If you're experiencing issues like a dead battery (alternator not charging), loss of power steering, or overheating (water pump not functioning), the diagram helps you pinpoint which component might be affected by a faulty belt or pulley.
- Component Replacement: When replacing components like the alternator, power steering pump, or idler pulley, the diagram provides visual confirmation of their location and relationship to the belt.
- General Maintenance: Familiarizing yourself with the system allows for quick visual inspections to identify potential problems before they escalate.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2009 Chevy Impala with the 3.5L V6 uses a single serpentine belt to drive multiple engine accessories. Key components involved include:
- Crankshaft Pulley (or Damper): Located at the bottom of the engine, this pulley is directly connected to the crankshaft and provides the rotational power for the entire system.
- Alternator: Charges the battery and provides electrical power to the vehicle's systems.
- Power Steering Pump: Provides hydraulic pressure to assist steering.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant through the engine to regulate temperature.
- Air Conditioning Compressor: Compresses refrigerant for the air conditioning system.
- Tensioner Pulley: An spring-loaded pulley that applies constant tension to the belt, preventing slippage. This is *crucially* important for proper system function.
- Idler Pulley (Sometimes): A smooth pulley that guides the belt and helps maintain the correct wrap angle on other pulleys. The 2009 Impala 3.5L *may* or *may not* have an idler pulley. The diagram will confirm this.
Symbols and Diagram Conventions
Understanding the symbols on the serpentine belt diagram is essential for accurate interpretation:
- Solid Lines: Represent the path of the serpentine belt itself. Follow these lines carefully when routing the belt.
- Pulleys: Shown as circles. Some may have internal features that indicate their function (e.g., grooves for a ribbed belt).
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of rotation for each pulley. Knowing the rotation direction is critical, especially when inspecting for proper belt tracking.
- Tensioner Icon: Typically a symbol indicating a spring or a mechanism for applying tension. Pay close attention to the tensioner's location and adjustment process.
Colors aren't generally standardized on serpentine belt diagrams. However, if present, they *might* differentiate between the smooth side and the ribbed side of the belt. The ribbed side always engages with pulleys that have grooves.
How It Works
The serpentine belt system operates based on a simple principle: transferring rotational power from the engine's crankshaft to various accessories.
- The crankshaft pulley, driven by the engine, rotates the serpentine belt.
- The belt wraps around each accessory pulley (alternator, power steering pump, water pump, A/C compressor), causing them to rotate.
- The tensioner pulley maintains constant tension on the belt, ensuring good contact with each pulley and preventing slippage. This constant tension is *vital* for efficient operation. A loose belt will cause squealing and reduce the performance of the driven components.
- The correct routing of the belt is essential to ensure that each component rotates in the correct direction.
Real-World Use and Basic Troubleshooting
Here are some common issues and troubleshooting tips:
- Squealing Noise: This is often the first sign of a problem. It can be caused by a loose belt, a worn belt, a glazed belt (shiny appearance), or a failing pulley bearing.
- Check Belt Tension: Ensure the tensioner is functioning correctly. If the belt is loose, the tensioner may need replacement.
- Inspect Belt Condition: Look for cracks, fraying, missing ribs, or glazing. Replace the belt if any of these conditions are present.
- Check Pulley Bearings: Spin each pulley by hand (with the engine off and the belt removed) to check for roughness or play. Replace any pulleys with bad bearings.
- Dead Battery: If the alternator isn't being driven effectively due to a slipping belt, the battery won't charge properly.
- Overheating: A slipping belt can prevent the water pump from circulating coolant effectively, leading to overheating.
- Loss of Power Steering: A slipping belt can reduce the assist from the power steering pump, making steering difficult.
- A/C Not Working: The A/C compressor may not function if the belt is slipping or broken.
When diagnosing issues, always visually inspect the entire belt path and each component for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. A straight edge can be useful for checking pulley alignment.
Safety Considerations
Working with the serpentine belt system involves potential hazards. Here are some important safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Negative Battery Terminal: Before working on any part of the electrical system, disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent accidental shorts.
- Work on a Cold Engine: Allow the engine to cool completely before working on the belt system to avoid burns.
- Keep Hands and Clothing Clear: Never work on the serpentine belt system while the engine is running. Keep your hands and clothing away from moving parts.
- Proper Tools: Use the correct tools for the job, including a serpentine belt tool for removing and installing the belt.
- Tensioner Safety: The tensioner is spring-loaded and can snap back forcefully. Use caution when releasing and engaging the tensioner.
- Fan Clearance: Be extremely careful around the engine cooling fan. Ensure it cannot start while you are working. If necessary, disconnect the fan motor connector.
Remember, the tensioner stores significant spring energy. Improper handling can result in injury. Always use the correct tool and follow the manufacturer's instructions for releasing and engaging the tensioner.
In Conclusion: This detailed guide provides the knowledge you need to understand and work on the serpentine belt system of your 2009 Chevy Impala 3.5L. By understanding the diagram, components, and troubleshooting steps, you can confidently tackle maintenance and repairs, saving time and money.
We have the detailed serpentine belt diagram file available. You can download it [link to diagram download]. Keep it handy for future reference during your repairs and maintenance!
