3.5 Liter Chrysler 3.5 Engine Diagram
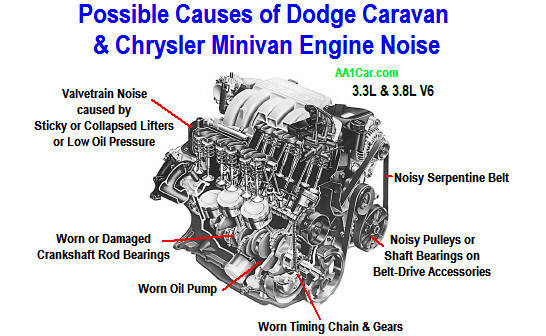
Welcome, gearheads! Today, we're diving deep into the 3.5 Liter Chrysler engine, a power plant found in a variety of Chrysler, Dodge, and Jeep vehicles. Specifically, we're going to break down a comprehensive diagram of this engine. This isn't just eye candy; understanding this diagram is crucial for anyone looking to perform anything from basic maintenance to complex repairs on their ride. We’ll cover the diagram's purpose, key components, how it all works together, troubleshooting tips, safety considerations, and even how to interpret those cryptic symbols and lines.
Purpose of the 3.5L Engine Diagram
So, why bother with a 3.5L engine diagram? Simply put, it's your roadmap for understanding, diagnosing, and working on your engine. Whether you're tackling a simple spark plug replacement, troubleshooting a misfire, or even considering a performance upgrade, the diagram is your invaluable guide. It provides a visual representation of the engine's components and their interconnections, allowing you to:
- Identify Components: Quickly locate and identify specific parts within the engine bay.
- Trace Circuits: Follow electrical and fluid pathways to diagnose issues.
- Understand Functionality: Visualize how different parts work together to create power.
- Plan Repairs: Strategize your repairs and ensure you have the right tools and parts.
- Learn Engine Mechanics: Enhance your overall understanding of how internal combustion engines operate.
This diagram empowers you to confidently approach repairs and modifications, saving you time, money, and potentially preventing costly mistakes. After all, wouldn't you rather understand what you're doing than fumble around in the dark?
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 3.5L Engine
Before we delve into the diagram itself, let's cover some essential specifications and main components of the 3.5L Chrysler engine. This engine is a 60-degree V6, meaning it has six cylinders arranged in two banks of three, forming a "V" shape. Key specifications typically include:
- Displacement: 3.5 Liters (214 cubic inches)
- Engine Configuration: V6
- Valvetrain: SOHC (Single Overhead Camshaft) or DOHC (Dual Overhead Camshaft) - depending on the specific year and model.
- Fuel Delivery: Sequential Port Fuel Injection (SFI)
- Horsepower: Varies depending on the model year and trim, but typically ranges from 210-250 horsepower.
- Torque: Similarly varies, but generally falls within the 230-250 lb-ft range.
Now, let’s highlight the core components you'll see prominently featured in the diagram:
- Cylinder Head(s): Houses the valves, camshaft(s), spark plugs, and fuel injectors.
- Cylinder Block: The main structural component containing the cylinders.
- Pistons: Move up and down within the cylinders, converting combustion energy into mechanical energy.
- Connecting Rods: Connect the pistons to the crankshaft.
- Crankshaft: Converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotary motion, which drives the transmission.
- Camshaft(s): Controls the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves.
- Intake Manifold: Distributes air to the cylinders.
- Exhaust Manifold(s): Collects exhaust gases from the cylinders.
- Fuel Injectors: Spray fuel into the intake ports or directly into the cylinders (depending on the design).
- Throttle Body: Controls the amount of air entering the engine.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant to regulate engine temperature.
- Oil Pump: Circulates oil to lubricate engine components.
- Timing Belt/Chain: Connects the crankshaft and camshaft(s), synchronizing their rotation.
Decoding the Diagram: Symbols, Lines, and Colors
Engine diagrams aren't always straightforward. Understanding the conventions used is key to deciphering the information they contain. Here's a breakdown of common symbols, lines, and colors you might encounter:
- Solid Lines: Typically represent mechanical connections or fluid lines carrying oil, coolant, or fuel. The thickness of the line may indicate the size or pressure of the line.
- Dashed Lines: Often represent vacuum lines or less critical connections.
- Dotted Lines: May indicate hidden components or internal passages within the engine.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of fluid or air flow.
- Color Coding: Can vary depending on the diagram, but commonly:
- Red: High-pressure oil lines.
- Blue: Coolant lines.
- Yellow: Fuel lines.
- Green: Vacuum lines.
- Symbols: Specific symbols represent different components like sensors (e.g., crank position sensor, camshaft position sensor), actuators (e.g., fuel injectors, throttle body), and electrical connectors. A key or legend will usually accompany the diagram to explain these symbols.
Pay close attention to the legend or key provided with the diagram. This is your Rosetta Stone for understanding the specific notation used in that particular illustration. Without the key, interpreting the diagram becomes significantly more challenging.
How the 3.5L Engine Works: A Simplified Overview
The 3.5L engine, like all internal combustion engines, operates on a four-stroke cycle: Intake, Compression, Combustion (Power), and Exhaust. Let's break it down:
- Intake: The piston moves down, creating a vacuum in the cylinder. The intake valve opens, allowing air (mixed with fuel in some designs) to enter the cylinder.
- Compression: The intake valve closes, and the piston moves up, compressing the air-fuel mixture. This increases the temperature and pressure inside the cylinder.
- Combustion (Power): The spark plug ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture, causing a rapid expansion of gases. This pushes the piston down, generating power.
- Exhaust: The exhaust valve opens, and the piston moves up, pushing the exhaust gases out of the cylinder and into the exhaust manifold.
The crankshaft translates this up-and-down motion into rotational motion, which is then transferred to the transmission and ultimately to the wheels, propelling the vehicle. The camshaft(s) precisely control the opening and closing of the valves, ensuring proper timing and efficient engine operation. Understanding this cycle is fundamental to understanding how the various components depicted in the diagram contribute to the overall function of the engine.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are a few examples of how you can use the 3.5L engine diagram for basic troubleshooting:
- Misfire Diagnosis: If you're experiencing a misfire, the diagram can help you locate the spark plugs, ignition coils, and fuel injectors for that cylinder. You can then test these components to determine the cause of the misfire.
- Coolant Leak: If you spot a coolant leak, the diagram will show you the routing of the coolant hoses and the location of the water pump, thermostat housing, and radiator. This will help you pinpoint the source of the leak.
- Vacuum Leak: A vacuum leak can cause a variety of problems, including rough idling and poor performance. The diagram will show you the routing of the vacuum lines, allowing you to inspect them for cracks or disconnections.
- Sensor Issues: Modern engines rely heavily on sensors. The diagram shows the location of sensors like the MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure), MAF (Mass Airflow), and crank/cam position sensors. Identifying the location is the first step toward testing the sensor to determine if it is failing.
Safety First: Highlighting Risky Components
Working on an engine can be dangerous if proper precautions aren't taken. Here are some key safety considerations when working with the 3.5L engine:
- Fuel System: Fuel lines are highly flammable. Always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on the fuel system. Relieve fuel pressure before disconnecting any fuel lines. Work in a well-ventilated area.
- Electrical System: Disconnect the negative battery cable before working on any electrical components. Be aware of high-voltage circuits, especially around the ignition system.
- Cooling System: The cooling system operates under pressure and at high temperatures. Never remove the radiator cap while the engine is hot. Allow the engine to cool down completely before working on the cooling system.
- Moving Parts: Never work on the engine while it is running unless absolutely necessary. If you must work on a running engine, be extremely careful to avoid getting your hands, clothing, or tools caught in moving parts.
- Exhaust System: The exhaust system gets extremely hot. Allow it to cool down completely before working on it.
Always consult the vehicle's service manual for specific safety precautions and procedures. Safety glasses, gloves, and appropriate clothing are essential when working on any engine.
With a 3.5L engine diagram and a solid understanding of these concepts, you're well-equipped to tackle a wide range of automotive tasks. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult the service manual for specific instructions.
We have a detailed 3.5L Chrysler engine diagram file available for you to download. This resource will further enhance your understanding and troubleshooting capabilities. Happy wrenching!
