3.6 Liter 2011 Buick Enclave Serpentine Belt Diagram
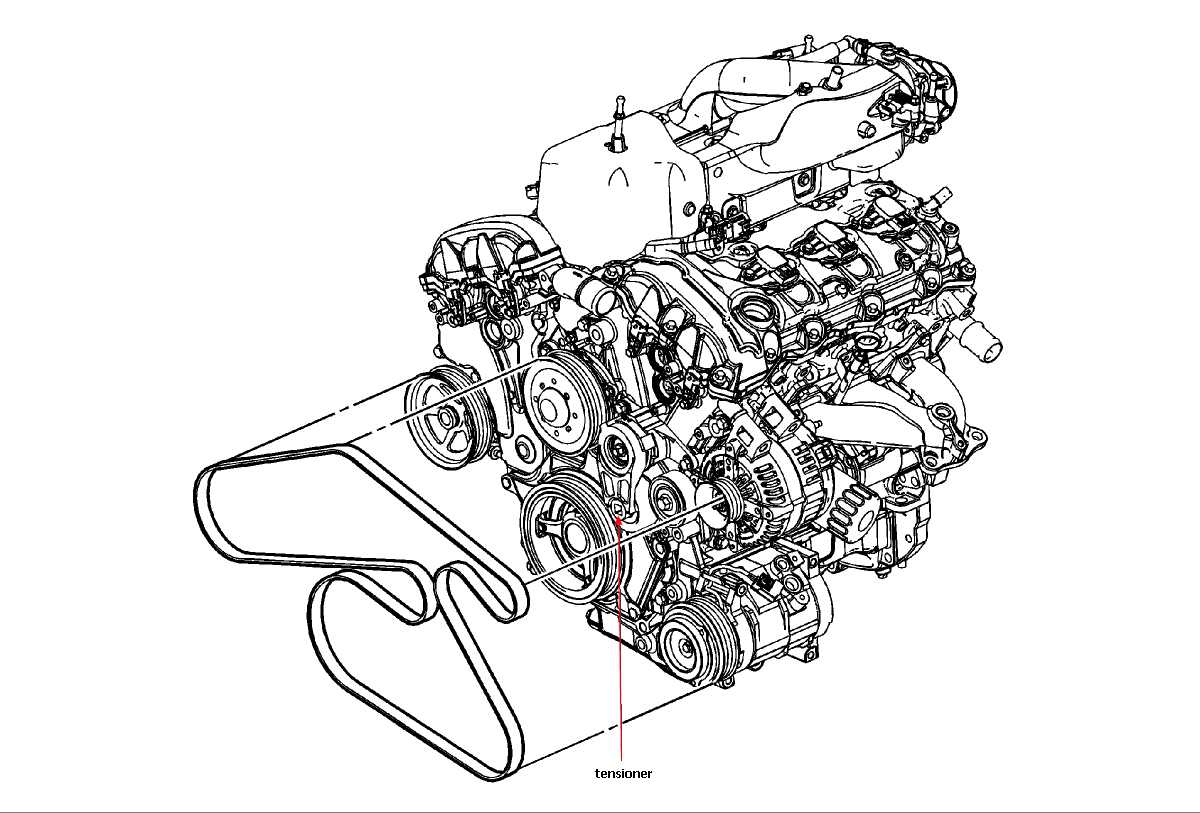
For the experienced DIYer tackling maintenance or repairs on a 2011 Buick Enclave with the 3.6-liter V6 engine (specifically the LLT engine), understanding the serpentine belt routing is absolutely critical. This article will provide a detailed explanation of the serpentine belt diagram, its components, and how it functions. We'll cover everything from the purpose of the diagram to real-world troubleshooting tips, all aimed at empowering you to confidently work on your Enclave.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
The serpentine belt, also known as the accessory drive belt, is a single, continuous belt that snakes around various engine components. It's responsible for powering several crucial systems, including:
- Alternator: Charges the battery and provides electrical power.
- Power Steering Pump: Assists in steering the vehicle.
- Air Conditioning Compressor: Cools the cabin air.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant to regulate engine temperature.
The serpentine belt diagram is a visual representation of the belt's specific routing around these components. Without it, correctly reinstalling a new or removed belt can be a frustrating and potentially damaging endeavor. Incorrect routing can lead to:
- Belt slippage: Reduced performance of the accessories, leading to dim headlights, difficult steering, or poor AC performance.
- Premature belt wear: The belt rubbing against components it shouldn't, shortening its lifespan.
- Component damage: If the belt isn't properly tensioned, it can damage the pulleys or even the accessories themselves.
- Complete system failure: If the belt breaks, none of the accessories will function.
The diagram is also useful for diagnosing belt-related issues, such as squealing or chirping noises, which can often be traced to misalignment or wear. Finally, studying the diagram enhances your understanding of the engine's accessory drive system, making you a more knowledgeable and capable DIY mechanic.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The 2011 Buick Enclave with the 3.6L LLT engine uses a serpentine belt that is typically around 90-95 inches in length. The exact length will be printed on the belt itself if you can read the old belt. Keep in mind that a worn belt may have stretched slightly, so don't rely *solely* on the old belt's length for replacement. Always consult the specific diagram for your vehicle and verify the part number of the replacement belt.
The main parts involved in the serpentine belt system are:
- Serpentine Belt: The rubber belt itself, typically made of a reinforced polymer compound.
- Crankshaft Pulley (Damper): Driven directly by the engine crankshaft. It's the starting point for the belt's rotation.
- Alternator Pulley: Connected to the alternator.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: Connected to the power steering pump.
- Air Conditioning Compressor Pulley: Connected to the AC compressor.
- Water Pump Pulley: Connected to the water pump.
- Tensioner Pulley: Spring-loaded pulley that maintains proper belt tension. This is crucial for the system's function.
- Idler Pulley: Smooth pulley used to guide the belt and maintain proper wrap angle around other pulleys. Not all engines have idler pulleys.
Understanding Pulleys
Pulleys are either smooth or grooved. The grooved side of the belt always engages a grooved pulley. A smooth pulley runs on the backside of the belt.
Symbols and Diagram Interpretation
Serpentine belt diagrams use a standard set of symbols to represent the belt and its components:
- Solid Line: Represents the main path of the serpentine belt.
- Dashed Line: May be used to indicate the belt's path behind other components or to represent the tensioner's movement.
- Circles: Represent pulleys.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of rotation for each pulley. These are very important for determining the correct belt routing.
- Labels: Abbreviations (ALT for alternator, P/S for power steering, A/C for air conditioning, W/P for water pump) identify each component.
- Tensioner Symbol: A special symbol, often resembling a spring, identifies the tensioner pulley. The direction of the arrow on the tensioner indicates which way to rotate the tensioner to relieve belt tension.
Some diagrams may use color-coding to highlight specific aspects of the system, but this is less common. The key is to carefully trace the solid line, noting the direction of rotation at each pulley, and ensuring that the belt follows the correct path according to the diagram.
How It Works
The engine's crankshaft rotates the crankshaft pulley. This, in turn, drives the serpentine belt. As the belt rotates, it drives each of the accessory pulleys (alternator, power steering pump, AC compressor, water pump). The tensioner pulley maintains constant pressure on the belt, preventing slippage and ensuring that all the accessories are driven efficiently.
The tensioner pulley is spring-loaded. When installing or removing the belt, you use a wrench (usually a socket wrench with a long handle) to rotate the tensioner arm against its spring pressure. This creates slack in the belt, allowing you to slip it off or onto the pulleys. Once the belt is properly routed, releasing the tensioner arm allows the spring to apply the correct tension to the belt.
Real-World Use: Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common problems related to the serpentine belt and how the diagram can help you troubleshoot:
- Squealing or Chirping Noise:
- Possible Causes: Slipping belt, worn belt, misaligned pulleys, glazed belt.
- Troubleshooting: Inspect the belt for cracks, fraying, or glazing. Check the pulley alignment using a straight edge. Ensure the tensioner is functioning correctly and providing adequate tension. Use the diagram to confirm belt routing is correct, because a small misroute is a common cause.
- Belt Slippage (Dim Headlights, Poor AC Performance):
- Possible Causes: Loose belt, worn belt, faulty tensioner, pulley damage.
- Troubleshooting: Check the belt tension. Replace the belt if it's worn or stretched. Inspect the tensioner for proper function. Look for damage or excessive wear on the pulleys.
- Belt Breakage:
- Possible Causes: Old belt, excessive wear, pulley misalignment, seized component.
- Troubleshooting: Replace the belt. Identify and address the underlying cause of the breakage (e.g., seized component).
Always refer to the serpentine belt diagram before replacing the belt. Take photos of the old belt's routing before removing it, as a backup. This can be a lifesaver if you get confused during reinstallation.
Safety Precautions
Working on the serpentine belt system can be risky if proper safety precautions aren't taken:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on any electrical components or near moving parts. This prevents accidental sparking and potential electrical shock.
- Engine Must Be Off and Cool: Never work on the serpentine belt system while the engine is running. Allow the engine to cool down completely before starting any work.
- Keep Hands and Clothing Clear: Keep your hands, fingers, and loose clothing away from the belt and pulleys while the engine is running or while rotating the crankshaft by hand.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
- Be Mindful of the Radiator Fan: The radiator fan can turn on automatically, even when the engine is off. Be extremely careful when working near the fan. Consider disconnecting the fan's electrical connector if possible.
The tensioner pulley stores a significant amount of spring energy. Always use the correct tool (usually a socket wrench with a long handle) and technique to release the tension gradually and safely. Never attempt to release the tensioner with makeshift tools or by forcing it.
Replacing a serpentine belt is within the skillset of many DIYers. The 2011 Buick Enclave's belt is reasonably accessible, but attention to detail and careful adherence to the routing diagram is critical for success.
To aid you in your project, we have a high-resolution serpentine belt diagram for the 2011 Buick Enclave with the 3.6L LLT engine available for download. This diagram includes all the necessary details for proper belt routing and component identification.
