3.6 Liter 2011 Chevy Traverse 3.6 Serpentine Belt Diagram
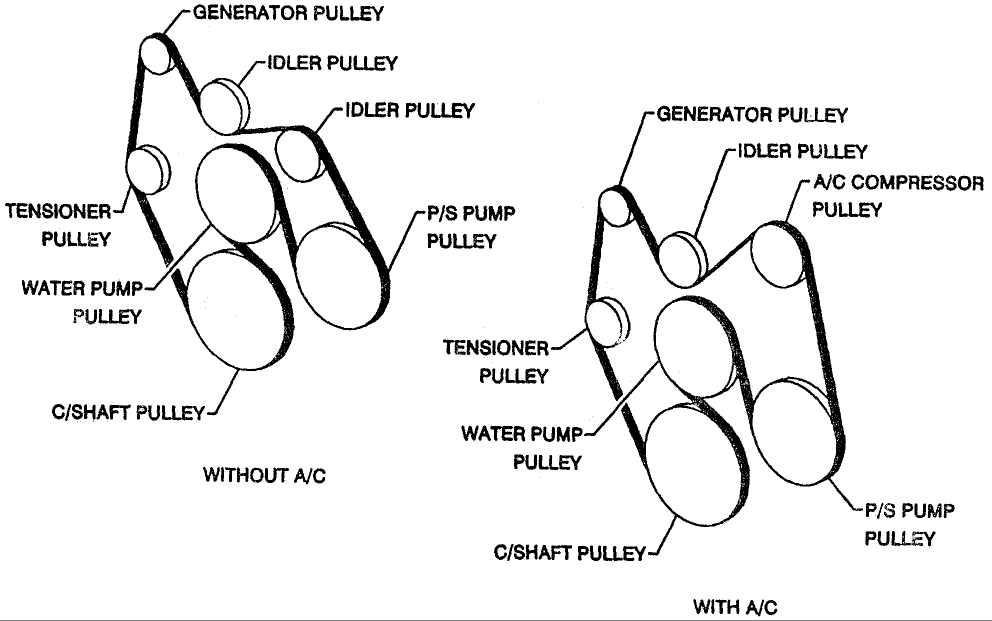
Alright, let's dive into the serpentine belt system on your 2011 Chevy Traverse with the 3.6L engine. Understanding this system is crucial for preventative maintenance, diagnosing issues, and even performing some repairs yourself. This article will walk you through the serpentine belt diagram, explaining its components, how it functions, and some real-world troubleshooting tips. We've got the diagram file available for download, which you'll find a link to at the end of this article.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
Why is a serpentine belt diagram so important? Well, the serpentine belt is responsible for powering several critical engine components. A failure of this belt can lead to a breakdown, leaving you stranded. The diagram allows you to:
- Identify components: Know exactly what each pulley and accessory is.
- Route the belt correctly: Essential during belt replacement. An incorrectly routed belt won't function properly and can damage components.
- Troubleshoot issues: Identify potential sources of noise, slippage, or failure within the system.
- Perform preventative maintenance: Visually inspect components for wear and tear.
- Understand the system: Gain a deeper knowledge of how your engine operates.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 2011 Chevy Traverse 3.6L Serpentine Belt System
Let's get familiar with the key components of the serpentine belt system on your 2011 Chevy Traverse. The 3.6L engine uses a single, long belt (the serpentine belt) to drive the following:
- Crankshaft Pulley: This pulley is connected directly to the crankshaft and provides the initial power to drive the belt.
- Alternator: The alternator generates electrical power to recharge the battery and power the vehicle's electrical systems.
- Power Steering Pump: This pump provides hydraulic pressure to assist with steering.
- Air Conditioning Compressor: The A/C compressor circulates refrigerant throughout the air conditioning system.
- Water Pump: The water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine and radiator to regulate temperature. Crucially important for preventing overheating!
- Tensioner Pulley: This spring-loaded pulley maintains the correct tension on the serpentine belt. A faulty tensioner can cause belt slippage, noise, and premature wear.
- Idler Pulley(s): These pulleys provide a smooth path for the belt and help to maximize its contact with the driven accessories.
Belt Specs: While the exact length can vary slightly depending on the manufacturer, the correct belt for your 2011 Chevy Traverse 3.6L engine will typically be around 90-92 inches long. Consult your owner's manual or a parts catalog for the precise part number.
Understanding Symbols in the Serpentine Belt Diagram
Serpentine belt diagrams use various symbols to represent the different components and the belt's routing. Here's a breakdown:
- Solid Lines: The solid line represents the path of the serpentine belt itself. The thickness of the line doesn't necessarily indicate anything specific; it's usually for visual clarity.
- Circles: Circles represent the pulleys. These pulleys are connected to the various engine accessories.
- Arrows: Arrows indicate the direction of rotation for each pulley. This is important because it helps you understand how the belt transfers power from the crankshaft to the accessories. Note that some pulleys rotate in the same direction as the crankshaft, while others rotate in the opposite direction.
- Text Labels: Each pulley is labeled with its corresponding accessory (e.g., ALT for alternator, P/S for power steering).
- Tensioner Symbol: The tensioner pulley is often depicted with a symbol indicating its spring-loaded mechanism. This is sometimes represented with a coil symbol or a small arrow indicating the direction of tension.
- Ribbed vs. Smooth Pulleys: Ribbed pulleys engage with the ribbed side of the serpentine belt, while smooth pulleys engage with the back side of the belt. The diagram won't always explicitly show this, but you can infer it from the belt routing.
Colors are not usually used in most basic diagrams. However, sometimes color-coding can highlight a specific area (e.g., vacuum lines) for greater clarity.
How the Serpentine Belt System Works
The serpentine belt system works by transferring rotational energy from the engine's crankshaft to the various accessories. The crankshaft pulley, driven directly by the engine, turns the serpentine belt. The belt, in turn, wraps around the pulleys of the alternator, power steering pump, A/C compressor, water pump, and idler pulleys. As the crankshaft pulley rotates, it pulls the belt along, causing these accessories to rotate as well.
The tensioner pulley plays a vital role in maintaining the proper tension on the belt. Without adequate tension, the belt will slip, resulting in reduced performance from the accessories. Slippage can cause the alternator to undercharge the battery, the power steering to be difficult, the A/C to blow warm air, and the engine to overheat due to a non-functional water pump. Excessive tension, on the other hand, can place undue stress on the accessory bearings and cause premature failure.
Real-World Use and Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common issues you might encounter with the serpentine belt system and how the diagram can help with troubleshooting:
- Squealing Noise: A squealing noise, especially when the engine is first started or when the A/C is turned on, often indicates belt slippage. Check the belt tension, look for signs of wear or damage on the belt, and inspect the tensioner pulley for proper operation. Use the diagram to verify proper belt routing.
- Battery Not Charging: If the alternator isn't spinning properly due to belt slippage, the battery won't charge. The diagram will confirm the belt runs to your alternator.
- Loss of Power Steering: If the power steering pump isn't being driven properly, you'll experience hard steering, especially at low speeds. Refer to the diagram to verify belt runs to the power steering pump.
- Overheating: If the water pump isn't circulating coolant, the engine can overheat. Again, the diagram ensures the belt is routed correctly to the water pump.
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the belt for cracks, fraying, missing chunks, or a glazed appearance. Any of these signs indicate the belt needs to be replaced. Check the pulleys for signs of rust or corrosion, which can damage the belt.
When diagnosing a serpentine belt issue, it's also a good idea to check the alignment of the pulleys. Misaligned pulleys can cause the belt to wear unevenly and fail prematurely. A straight edge or laser alignment tool can be used to check the pulley alignment.
Safety Considerations
Working on the serpentine belt system involves certain risks. Here are some crucial safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, including the alternator, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical shock.
- Engine Off and Cool: Never work on the serpentine belt system with the engine running. Allow the engine to cool completely before starting any work.
- Keep Hands Clear: Keep your hands, clothing, and tools clear of the belt and pulleys when the engine is running or when manually rotating the crankshaft. The belt can pinch or pull loose clothing.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
- Beware of Spring Tension: The tensioner pulley is spring-loaded and can snap back with considerable force. Use the correct tools and techniques to release the tension safely. Improper handling of the tensioner can result in injury.
High-Risk Components: The tensioner pulley spring is arguably the riskiest component due to the potential for injury if not handled correctly. Always use the appropriate tool (usually a serpentine belt tool or a wrench) to relieve the tension on the belt before removing or installing it.
Remember, if you're uncomfortable working on the serpentine belt system yourself, it's always best to consult a qualified mechanic. They have the experience and tools to perform the job safely and correctly.
You can download the detailed serpentine belt diagram for your 2011 Chevy Traverse 3.6L engine here: [Insert Download Link Here - Hypothetical Link]. This diagram should give you the visual aid to better understand the concepts we've discussed. Good luck, and happy wrenching!
