3.6 Liter 2013 Chevy Traverse 3.6 Serpentine Belt Diagram
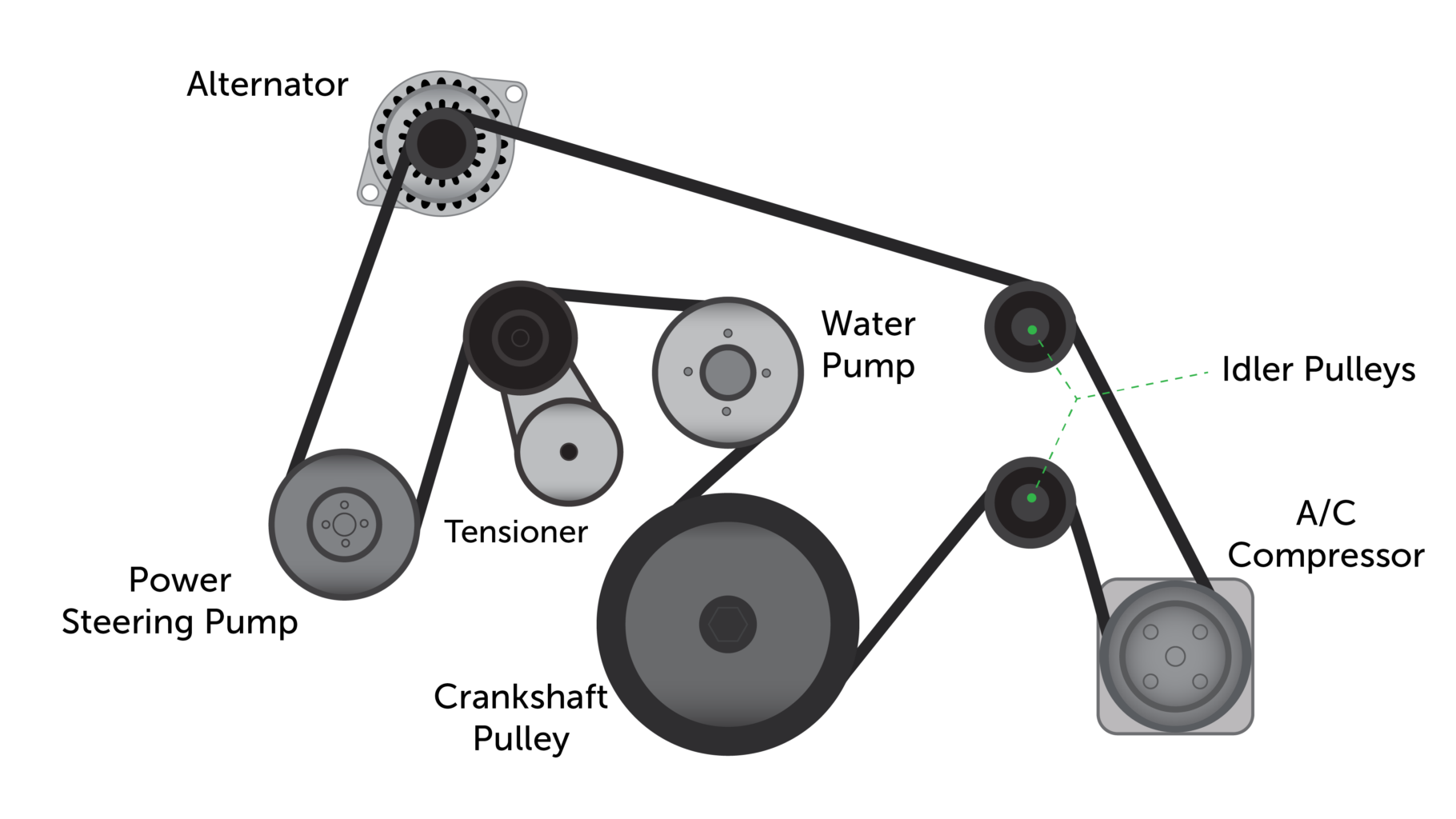
Alright, let's talk about the serpentine belt diagram for your 2013 Chevy Traverse with the 3.6L engine. Understanding this diagram is absolutely crucial if you're planning on tackling any repairs or maintenance related to your engine's accessory drive system. It's like a roadmap, guiding you through the maze of pulleys and components that keep your car running smoothly. We're going to dive deep, so grab your tools and let's get started.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
Why bother with a diagram? Well, several reasons. First, it's indispensable for proper belt routing. If the belt isn't routed correctly, your accessories – power steering pump, alternator, air conditioning compressor, and water pump – won't function correctly, or at all. This can lead to anything from a dead battery to overheating, or even loss of power steering. Second, it aids in identifying components. Sometimes it's hard to tell which pulley belongs to which accessory. The diagram clarifies this. Third, it's essential for troubleshooting. If you're experiencing belt squealing or accessory failure, the diagram can help you pinpoint the root cause. Finally, it empowers you to perform DIY maintenance, saving you money and giving you a better understanding of your vehicle. By understanding how everything's connected, you'll be more confident in performing belt replacements and other related tasks.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Let's break down the key components and some important specs for your 2013 Traverse 3.6L serpentine belt system.
Main Parts:
- Serpentine Belt: The heart of the system. It's a long, continuous belt that wraps around multiple pulleys, transferring rotational power from the crankshaft to the accessories.
- Crankshaft Pulley (Damper): Connected directly to the crankshaft, this pulley is the driving force for the entire system. It also dampens torsional vibrations from the engine.
- Alternator Pulley: Driven by the serpentine belt, the alternator generates electricity to power your car's electrical system and charge the battery.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: This pulley drives the power steering pump, providing hydraulic assistance to make steering easier.
- Air Conditioning Compressor Pulley: Powers the AC compressor, which circulates refrigerant to cool the cabin.
- Water Pump Pulley: This pulley drives the water pump, which circulates coolant through the engine to prevent overheating.
- Tensioner Pulley: A spring-loaded pulley that maintains the proper tension on the serpentine belt. This is crucial for preventing slippage and ensuring optimal performance.
- Idler Pulley: A smooth pulley that helps guide the belt and maintain the correct wrap angle around the other pulleys.
Key Specs:
While specific belt lengths can vary slightly depending on the manufacturer, a typical serpentine belt for the 2013 Chevy Traverse 3.6L is around 91-92 inches in length. Always double-check your vehicle's specific part number to ensure a proper fit. Also, the belt is typically a multi-rib (usually 6 ribs) design.
Symbols in the Diagram
The serpentine belt diagram isn't just a picture; it's a language. Let's decode it.
- Solid Lines: These represent the serpentine belt itself. The path of the line shows you how the belt is routed around the pulleys.
- Pulleys: Circles represent the pulleys. Often, the diagram will label each pulley with abbreviations like "ALT" for alternator, "P/S" for power steering, "A/C" for air conditioning, "W/P" for water pump, "CRANK" for crankshaft, "TEN" for tensioner, and "IDL" for idler.
- Arrows: Arrows indicate the direction of rotation for each pulley. This is important to visualize how the belt transfers power.
- Tensioner Symbol: The tensioner pulley is often depicted with a symbol that shows a spring or arm, indicating its ability to move and maintain belt tension.
- Colors (Less Common): Some diagrams might use different colors to highlight specific parts or sections of the belt path. For example, a section showing the path around the water pump might be highlighted in blue.
How It Works
Here's the gist of how the serpentine belt system functions on your Traverse:
- The engine's crankshaft rotates.
- The crankshaft pulley, connected to the crankshaft, spins.
- The serpentine belt, wrapped tightly around the crankshaft pulley and all other accessory pulleys, is driven by the crankshaft pulley's rotation.
- As the serpentine belt moves, it causes all the accessory pulleys (alternator, power steering pump, AC compressor, water pump) to rotate.
- Each accessory then performs its function: the alternator generates electricity, the power steering pump provides steering assistance, the AC compressor cools the cabin, and the water pump circulates coolant.
- The tensioner pulley maintains the proper tension on the belt, preventing slippage and ensuring that all accessories are driven effectively.
- The idler pulley guides the belt, ensuring the right wrap angle around crucial components.
The key to the entire system is maintaining the correct belt tension. If the belt is too loose, it will slip, causing accessories to malfunction. If it's too tight, it can put excessive strain on the bearings of the accessories, leading to premature failure.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Okay, your belt's squealing like a banshee, or your AC isn't blowing cold. Let's use the diagram to troubleshoot.
- Squealing Belt: A common symptom is a squealing noise, especially when the engine is first started or when the AC is turned on. The diagram helps you visually inspect the belt's path. Look for signs of wear, cracks, or glazing (a shiny, smooth surface). Check the tensioner to see if it's moving freely and maintaining proper tension. If the tensioner is weak or the belt is worn, replace them. Sometimes squealing can also indicate a failing pulley bearing.
- Accessory Failure: If your alternator isn't charging, power steering is weak, or AC isn't cold, consult the diagram to verify that the belt is properly routed and that the associated pulley is turning when the engine is running. If the pulley isn't turning, the belt might be broken or severely slipped. If the pulley is turning but the accessory isn't functioning, the accessory itself is likely the problem.
- Belt Slippage: Look for signs of belt dust near the pulleys. This is a sign that the belt is slipping. Again, check the belt tension and the condition of the belt and pulleys. Misalignment of the pulleys can also cause slippage.
- Visual Inspection: Before even starting the engine, use the diagram to visually inspect the belt for damage. Look for cracks, fraying, missing chunks, or any other signs of wear. Also, check the pulleys for any damage or signs of bearing failure (wobbling or excessive play).
Safety Considerations
Working on the serpentine belt system can be dangerous if you're not careful.
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on any electrical components, including the alternator. This will prevent accidental shorts or electrical shocks.
- Engine Must Be Off and Cool: Never work on the serpentine belt system while the engine is running or hot. The belt and pulleys can cause serious injury if they come into contact with your hands or clothing.
- Moving Parts: Be extremely cautious around the moving parts of the engine, especially the serpentine belt and pulleys. Keep your hands and clothing clear of these parts when the engine is running.
- Tensioner Spring: The tensioner pulley is spring-loaded and can snap back with considerable force. Use the correct tools and techniques to release the tension on the belt safely.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from flying debris.
Remember, if you're not comfortable performing these repairs yourself, it's always best to consult a qualified mechanic.
And there you have it! You now have a solid understanding of the 3.6L 2013 Chevy Traverse serpentine belt system. We've covered the purpose of the diagram, key components, troubleshooting tips, and safety considerations. Now you can confidently tackle serpentine belt maintenance and repairs on your Traverse. Remember to always double-check your work and consult your vehicle's repair manual for specific instructions and torque specifications.
We have the full resolution diagram available for download. This will allow you to zoom in and get a closer look at all the details we've discussed. Happy wrenching!
