4 Door Power Window Wiring Diagram
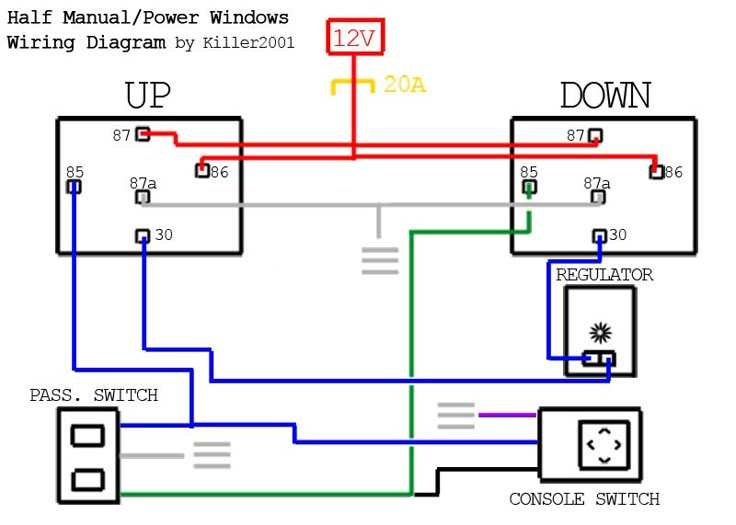
Alright, let's dive into the fascinating world of 4-door power window wiring diagrams. This isn't just about blindly swapping fuses; understanding how your power windows are wired is crucial for effective troubleshooting, DIY repairs, and even custom modifications. Think of it as unlocking another level of automotive knowledge. We're going to break down the intricacies, making even the seemingly complex aspects understandable. And, to make things even better, we have a downloadable, detailed diagram that accompanies this guide, giving you a visual reference as we go. We'll mention that again at the end.
Purpose: Why Bother with Wiring Diagrams?
Why should you even care about a wiring diagram? Several reasons, actually:
- Repairing Faulty Windows: The most common reason. A window that won't roll up or down is a major inconvenience (and security risk). A diagram helps you pinpoint the source of the problem, whether it's a bad motor, a broken wire, or a faulty switch.
- Diagnosing Electrical Issues: Power window problems are often symptoms of broader electrical issues. Understanding the circuit can help you trace the problem back to its root cause.
- Performing Custom Installations: Want to add aftermarket power windows to a classic car? Or upgrade your existing system? A wiring diagram is essential for safe and proper installation.
- Learning Automotive Electrical Systems: Even if you don't have a specific problem, studying a power window wiring diagram is a great way to improve your general understanding of automotive electrical systems.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Before we jump into the diagram itself, let's identify the key components and their functions:
- Battery: The heart of the system, providing the necessary DC voltage (typically 12V) to power the windows.
- Fuse/Circuit Breaker: A safety device that protects the circuit from overloads. A blown fuse or tripped circuit breaker indicates a problem in the system.
- Power Window Switch (Master and Individual): These are the controls you use to operate the windows. The master switch, usually located on the driver's door, controls all windows, while individual switches are located on each door.
- Window Motor: An electric motor that drives the window regulator mechanism, moving the window up and down.
- Window Regulator: The mechanical linkage that translates the motor's rotational motion into linear motion to raise and lower the window.
- Wiring Harness: A bundle of wires that connects all the components.
- Relays (Optional): Some systems use relays to handle the high current required by the window motors. Relays act as remote-controlled switches, allowing a low-current signal from the switch to control a high-current circuit to the motor.
- Ground Connections: Every electrical circuit needs a good ground connection to complete the circuit. Poor ground connections are a common cause of power window problems.
Symbols: Deciphering the Wiring Diagram
A wiring diagram is essentially a roadmap of the electrical circuit. Understanding the symbols is critical. Here's a breakdown of common symbols:
- Lines: Represent wires. The thickness of the line often indicates the wire gauge (thickness), which determines its current-carrying capacity.
- Colors: Each wire is assigned a color code to help you identify it in the wiring harness. Standard color codes vary by manufacturer, but common colors include red (power), black (ground), blue, green, yellow, and white. The diagram will typically include a color key.
- Circles: Often represent connection points or splices in the wiring.
- Squares/Rectangles: Typically represent components like switches, relays, and fuses. The specific symbol inside the square/rectangle will indicate the type of component.
- Resistor Symbol (Zigzag line): Indicates a resistor, which limits the flow of current.
- Ground Symbol (Stacked lines or inverted triangle): Indicates a ground connection.
- Motor Symbol: A circle with an "M" inside.
- Diode Symbol (Triangle pointing to a line): A semiconductor device that allows current to flow in only one direction.
Important: Always refer to the diagram's legend or key for specific symbol definitions, as they can vary slightly depending on the source.
How It Works: The Flow of Electricity
Let's trace the flow of electricity through a typical 4-door power window system:
- Power Source: Power flows from the battery, through a fuse or circuit breaker, to the power window circuit.
- Master Switch (Driver's Door): When you press the master switch to raise or lower a window, you're essentially closing a circuit. This sends a signal to the appropriate window motor, either directly or through a relay.
- Individual Door Switches: Each door also has its own switch, allowing passengers to control their respective windows. These switches typically bypass the master switch for the specific window they control.
- Window Motor Activation: When the switch is activated, it sends power to the window motor. The motor's direction of rotation (and thus the window's direction of movement) is determined by the polarity of the voltage applied to it. Reversing the polarity reverses the motor's direction. This polarity reversal is typically handled by the window switch itself.
- Ground Connection: The motor needs a ground connection to complete the circuit.
Important concept: The switch doesn't just "send power." It *completes* a circuit. The power is already there, waiting for a closed path to flow through.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting
Okay, your window's stuck. What do you do? Here are some basic troubleshooting steps using the wiring diagram:
- Check the Fuse: The first and simplest step. Use a multimeter to check for continuity across the fuse. A blown fuse indicates a short circuit somewhere in the system. Replace the fuse with the correct amperage rating. If it blows again immediately, you have a serious problem that needs further investigation.
- Test the Switch: Use a multimeter to check if the switch is functioning correctly. Disconnect the switch and use the multimeter to check for continuity between the terminals when the switch is in the "up" and "down" positions. If there's no continuity, the switch is likely faulty.
- Inspect the Wiring: Visually inspect the wiring harness for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, broken connectors, or corrosion. Pay close attention to areas where the wires pass through the door jamb, as this is a common point of failure. Use the wiring diagram to trace the wires and identify any potential breaks or shorts.
- Test the Motor: If you suspect the motor is faulty, you can test it directly by applying 12V power and ground to its terminals. If the motor doesn't run, it's likely bad. *Be cautious when doing this* – ensure the window is not in a position where it could crush anything if it suddenly moves.
- Check Ground Connections: A poor ground connection can cause all sorts of electrical problems. Locate the ground connections for the power window circuit (the wiring diagram will show you where they are) and make sure they are clean and tight.
Important: Always disconnect the battery before working on electrical components to prevent accidental shorts.
Safety: Risky Components
While power windows aren't inherently dangerous, there are a few components that can pose a risk:
- Battery: The battery stores a significant amount of energy and can deliver a powerful shock if short-circuited. Always disconnect the battery before working on electrical components.
- Window Motor: The window motor can generate a lot of force, especially if the window regulator is jammed. Keep fingers and other body parts clear of the window mechanism while testing or repairing the motor.
- Wiring Harness: Damaged or frayed wires can create a shock hazard. Wear gloves when handling wiring harnesses, especially if they are wet or damaged.
- High Amperage Circuits: Power window circuits can carry high currents. Working on these circuits without proper knowledge and precautions can lead to electrical shock or burns.
Always consult a qualified technician if you're unsure about any aspect of the repair or troubleshooting process.
By understanding your 4-door power window wiring diagram, you're not just fixing a window; you're gaining valuable knowledge about your car's electrical system. Take your time, be methodical, and always prioritize safety. And remember, we have that detailed wiring diagram file ready for you to download. It provides a visual aid that complements this guide, making the process even easier to understand and follow. Happy wrenching!
