6 Pin Ignition Switch Wiring Diagram
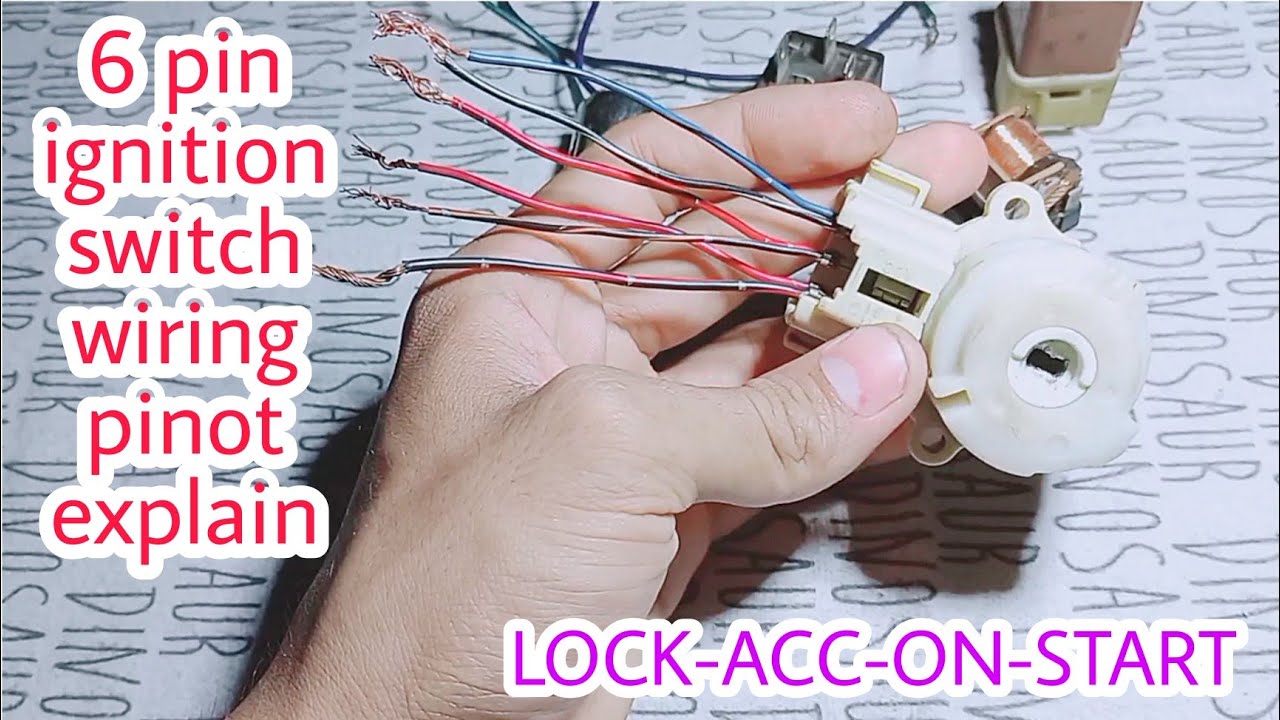
Understanding your vehicle's ignition switch is crucial for diagnosing starting problems, performing electrical modifications, or even just deepening your automotive knowledge. The 6-pin ignition switch is a common type, and deciphering its wiring diagram can seem daunting at first. But with a clear explanation, you'll be able to confidently trace circuits and troubleshoot issues. This article aims to provide that clarity, equipping you with the knowledge to understand and utilize a 6-pin ignition switch wiring diagram effectively.
Purpose of Understanding the 6-Pin Ignition Switch Wiring Diagram
Why bother learning about this diagram? Several reasons come to mind:
- Troubleshooting Starting Issues: A common symptom of a faulty ignition switch is a no-start condition. The diagram helps you isolate the problem to the switch itself or to connected components like the starter solenoid or fuel pump relay.
- Performing Electrical Repairs: Damaged wires leading to or from the switch can be repaired by referencing the diagram, ensuring you reconnect the wires to the correct terminals.
- Installing Aftermarket Accessories: Adding devices like remote starters, alarm systems, or even custom lighting often requires tapping into the ignition circuit. The diagram shows you where to find the appropriate wires for accessory power, ignition-switched power, and starter engagement.
- General Automotive Learning: Even if you're not actively working on your car, understanding the ignition system is a valuable skill for any enthusiast. It provides insight into the fundamental workings of a vehicle's electrical system.
Key Specs and Main Parts of a 6-Pin Ignition Switch
The 6-pin ignition switch, as the name suggests, has six terminals or pins. Each pin serves a specific purpose, and their arrangement can vary slightly depending on the vehicle manufacturer. However, the core functions are generally consistent. Here's a breakdown of the common terminals and their roles:
- Battery (B or BAT): This pin connects directly to the vehicle's battery, providing the main power source for the ignition system. It's typically a heavy-gauge wire carrying a substantial current.
- Ignition (IG or IGN): This pin supplies power to various engine control components, such as the ECU (Engine Control Unit), ignition coil, and fuel injectors, when the ignition key is in the "ON" or "RUN" position.
- Accessory (ACC): This pin provides power to non-essential accessories like the radio, power windows, and climate control system when the key is in the "ACC" or "ON" position. It typically deactivates during the "START" position to conserve power for starting.
- Starter (ST or START): This pin activates the starter solenoid, which in turn engages the starter motor to crank the engine. It only receives power when the key is in the "START" position.
- Ground (GND): While less common on all 6-pin switches, some designs include a ground terminal. This provides a direct ground path for the switch itself or internal circuitry.
- Second Ignition (IG2): Some vehicles use a second ignition terminal (IG2) to supply power to additional engine management components during the cranking phase. This ensures these components receive adequate power during the voltage drop experienced while the starter motor is engaged.
Symbols, Lines, Colors, and Icons in a Wiring Diagram
Wiring diagrams use standardized symbols and conventions to represent electrical components and their connections. Understanding these symbols is crucial for interpreting the diagram correctly.
- Lines: Solid lines represent wires. Thicker lines typically indicate wires carrying higher current. Dashed lines may indicate shielded wires or wires that are part of a specific harness.
- Colors: Wires are color-coded to aid in identification. Common colors include red (battery), black (ground), blue, green, yellow, and white. The specific color coding will vary depending on the vehicle manufacturer. A legend on the diagram will define what each color represents.
- Symbols:
- Battery: Represented by a symbol resembling a series of alternating long and short lines.
- Switch: Represented by a break in the line with a toggle or lever symbol to indicate the switch's position. Multiple positions (e.g., ACC, ON, START) will be shown with separate lines connected to the switch symbol.
- Resistor: Represented by a zig-zag line.
- Diode: Represented by a triangle pointing to a vertical line.
- Relay: Represented by a coil symbol (the relay's electromagnet) and a switch symbol (the relay's contacts).
- Ground: Represented by a series of decreasing horizontal lines.
- Numbers and Letters: These identify specific wires, terminals, and components. They often correspond to labels on the physical components in the vehicle.
How the 6-Pin Ignition Switch Works
The ignition switch acts as a central control point for the vehicle's electrical system. By turning the key to different positions, you activate different circuits.
The BAT terminal is always connected to the battery, providing a constant source of power.
When you turn the key to the ACC position, the switch connects the BAT terminal to the ACC terminal, powering the accessories. Turning the key further to the ON position connects the BAT terminal to both the ACC and IGN terminals, powering both the accessories and the engine management system. Finally, turning the key to the START position connects the BAT terminal to the START terminal, energizing the starter solenoid. Importantly, in the START position, the ACC terminal *may* be temporarily disconnected to provide maximum power to the starter motor. The IG2 terminal, if present, also becomes active in the START position to maintain power to vital engine components during cranking.
Releasing the key from the START position allows it to spring back to the ON position, maintaining power to the engine and accessories.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting tips when working with a 6-pin ignition switch:
- No Start, No Crank: If the engine doesn't crank at all, check the BAT terminal for voltage. Then, check the START terminal for voltage when the key is in the START position. No voltage on the START terminal indicates a faulty switch or a wiring problem between the switch and the starter solenoid.
- No Start, Cranks But Doesn't Fire: If the engine cranks but doesn't start, check the IGN terminal for voltage when the key is in the ON position. No voltage on the IGN terminal indicates a problem with the switch or the wiring leading to the engine management system.
- Accessories Don't Work: If the accessories don't work when the key is in the ACC or ON position, check the ACC terminal for voltage. No voltage indicates a problem with the switch or the wiring leading to the accessory circuit.
- Using a Multimeter: A multimeter is essential for diagnosing ignition switch problems. Use it to check for voltage at each terminal with the key in the appropriate position. Also, use it to check for continuity between the BAT terminal and each of the other terminals when the key is in the corresponding position.
Remember to consult your vehicle's specific wiring diagram for accurate pin assignments and wire colors. Generic diagrams provide a general understanding, but the specific configuration can vary.
Safety Considerations
Working with automotive electrical systems involves inherent risks. Here are some safety precautions to keep in mind:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical component, disconnect the negative (black) terminal of the battery to prevent accidental shorts or shocks.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: When working with fuel or flammable materials, ensure adequate ventilation to prevent the buildup of explosive fumes.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Protect your eyes from sparks, debris, and corrosive fluids.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools designed for automotive electrical work. Avoid using tools with damaged insulation.
- Be Careful with Airbags: Airbags are sensitive to electrical signals. Avoid probing or disconnecting wires near airbag components unless you are specifically trained to do so. Accidental airbag deployment can cause serious injury.
- High Current Circuits: The circuits connected to the ignition switch, particularly the battery and starter circuits, carry high current. Be extremely careful when working with these circuits to avoid burns or electrical shock.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only. Always consult a qualified mechanic for complex automotive repairs. We are not responsible for any damages or injuries resulting from the use of this information.
We understand that having a visual aid can be incredibly beneficial. We have the file containing a detailed 6-pin ignition switch wiring diagram ready for you to download. This diagram complements the information provided in this article, making it easier for you to understand the intricacies of the ignition switch wiring and confidently tackle any related troubleshooting or repair tasks.
