97 Chevy 1500 1997 Chevy Silverado Fuse Box Diagram
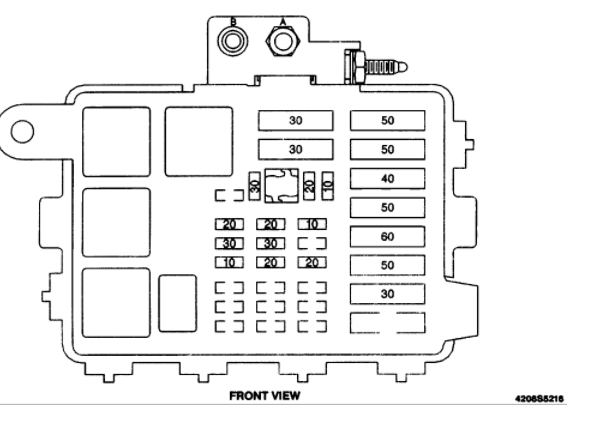
For the experienced DIYer tackling electrical repairs or modifications on their 1997 Chevy 1500 (also known as the '97 Chevy Silverado, part of the GMT400 platform), understanding the fuse box diagram is absolutely crucial. It's your roadmap to the electrical system, preventing costly mistakes and ensuring safety. Consider this your comprehensive guide to decoding that essential component.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram serves several vital purposes:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: When a circuit fails (e.g., a headlight stops working, the radio goes silent), the diagram helps pinpoint the blown fuse responsible. Instead of blindly replacing fuses, you can target the exact one associated with the malfunctioning component.
- Modifications and Upgrades: Adding accessories like aftermarket lights, amplifiers, or even a trailer brake controller requires tapping into the existing electrical system. The diagram allows you to identify appropriate circuits for drawing power or signaling, minimizing the risk of overloading circuits or damaging sensitive electronics.
- Preventing Electrical Fires: Incorrect fuse amperage can lead to overheating and potentially electrical fires. The diagram provides the correct fuse amperage ratings for each circuit, ensuring proper protection.
- Understanding the Electrical System: Beyond troubleshooting, the diagram offers a comprehensive overview of how different electrical components are interconnected. This knowledge is invaluable for diagnosing complex electrical issues.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the '97 Chevy 1500 Fuse Box
The 1997 Chevy 1500 (Silverado) typically has two main fuse box locations:
- Under-Hood Fuse Box: Located in the engine compartment, this box houses fuses and relays for critical systems like the engine control module (ECM), fuel pump, headlights, horn, and starting system. This is where higher amperage fuses are usually found.
- Interior Fuse Box: Typically located on the driver's side, often under the dashboard or behind a panel near the driver's footwell. This box protects circuits for interior components like the radio, power windows, power locks, instrument panel, and interior lighting.
Key Specs:
- Voltage: The '97 Silverado operates on a 12-volt DC electrical system.
- Fuse Types: Primarily uses blade-type fuses (also known as spade fuses) in various sizes (mini, ATO, maxi) based on the amperage rating. Some circuits may use circuit breakers which reset automatically or manually.
- Relays: Electromechanical switches that control high-current circuits using a low-current signal. They are frequently used for components like headlights, fuel pump, and starter motor.
- Grounding Points: Critical connection points where electrical circuits are connected to the vehicle's chassis, providing a return path for the current. Poor grounding can cause a wide range of electrical issues.
Decoding the Fuse Box Diagram: Symbols, Lines, Colors, and Icons
Understanding the symbols and conventions used in the fuse box diagram is essential for accurate interpretation:
- Fuses: Typically represented by a wavy line inside a rectangle. The amperage rating is usually indicated next to the symbol (e.g., "20A").
- Relays: Shown as a square or rectangle with pins indicating the coil and contact terminals.
- Circuit Breakers: May be depicted as a fuse symbol with a switch-like element.
- Wires: Solid lines represent wires. Different colors are often used to differentiate circuits. A wiring diagram will show wire colors more explicitly than a fuse box diagram.
- Grounds: Indicated by the ground symbol (often resembling a pitchfork or an inverted triangle).
- Abbreviations: The diagram uses abbreviations to identify components and circuits (e.g., "ECM" for Engine Control Module, "IGN" for Ignition).
- Component Icons: Small icons representing specific components (e.g., a light bulb for headlights, a speaker for the radio).
Important Notes on Wire Colors: While the fuse box diagram may not show wire colors precisely, it's worth noting common conventions: Red wires are typically for battery power (hot at all times), Orange wires are often for accessory power (switched on with the ignition), and Black wires are generally for ground.
How the Fuse Box Works: A Simplified Explanation
The fuse box acts as a central distribution point and protection mechanism for the vehicle's electrical circuits. Here's a simplified breakdown:
- Power Source: The battery provides the primary power source.
- Power Distribution: Power from the battery is routed to the fuse box.
- Circuit Protection: Each circuit is protected by a fuse or circuit breaker. If a circuit draws excessive current (due to a short circuit or overload), the fuse blows (the thin wire inside melts), breaking the circuit and preventing damage to components or wiring.
- Relay Control: In some cases, a low-current signal from a switch or the ECM activates a relay. The relay then closes a high-current circuit, powering the desired component.
Understanding the concept of "series" and "parallel" circuits is also helpful. Components connected in series share the same current, while components connected in parallel have the same voltage.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some troubleshooting tips using the fuse box diagram:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which component is not working.
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse or circuit breaker associated with the malfunctioning component in the fuse box diagram.
- Inspect the Fuse: Visually inspect the fuse. A blown fuse will have a broken filament (the thin wire inside). You can also use a multimeter to test for continuity (a continuous electrical path). A working fuse will show continuity (a reading of zero ohms or near zero ohms).
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a fuse of the EXACT same amperage rating. NEVER use a higher amperage fuse, as this can bypass the circuit protection and lead to damage or fire.
- Test the Circuit: After replacing the fuse, test the component to see if it now works. If the fuse blows again immediately, there is a short circuit or overload in the circuit that needs to be diagnosed and repaired.
- Check the Relay: If the fuse is good but the component still doesn't work, the relay might be faulty. You can try swapping the relay with a known good relay of the same type to see if that resolves the issue.
Example: Your headlights are not working. Consult the under-hood fuse box diagram. Locate the fuse labeled "Headlights" (or similar). Inspect the fuse. If blown, replace it with a new fuse of the correct amperage. If the fuse blows again immediately, there is likely a short circuit in the headlight wiring or within the headlight assembly itself.
Safety Precautions: Respecting the Electrical System
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Always observe these safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative (-) battery cable. This prevents accidental short circuits.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use tools with insulated handles to minimize the risk of electric shock.
- Never Bypass Fuses: Never bypass a fuse with a wire or other conductive material. This removes the circuit protection and can lead to serious damage or fire.
- Avoid Working in Wet Conditions: Water conducts electricity. Avoid working on electrical systems in wet or damp environments.
- High-Risk Components: Be particularly cautious when working with circuits related to the airbag system (SRS) or anti-lock braking system (ABS). Incorrect handling can trigger these systems, causing injury.
- Consult a Professional: If you are not comfortable working on electrical systems, consult a qualified mechanic.
Disclaimer: This information is for general guidance only. Always refer to the official service manual for your specific vehicle for accurate and detailed information.
You can download the full 1997 Chevy 1500 (Silverado) fuse box diagram file for detailed reference.
