Automatic Transmission Transmission Diagram Dodge Ram 1500
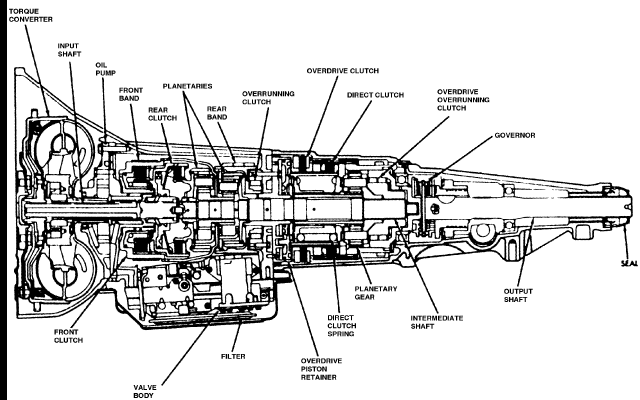
Understanding the inner workings of your Dodge Ram 1500's automatic transmission can be invaluable, whether you're tackling a minor repair, planning a performance upgrade, or simply expanding your automotive knowledge. A detailed transmission diagram serves as a roadmap, guiding you through the complex network of gears, valves, and hydraulic circuits. This article will break down a typical Dodge Ram 1500 automatic transmission diagram, explaining its components, symbols, and how it can be used for diagnostics and maintenance. We have the transmission diagram available for download at the end of this article.
Purpose of the Transmission Diagram
The transmission diagram is far more than just a pretty picture. Its primary purposes include:
- Troubleshooting: Pinpointing the source of a transmission problem by tracing hydraulic circuits or identifying faulty components.
- Repair: Guiding disassembly and reassembly during overhaul or component replacement.
- Modification: Understanding the impact of aftermarket parts or modifications on transmission performance.
- Education: Providing a visual aid for learning the principles of automatic transmission operation.
For experienced DIYers, having this diagram is like having a seasoned mechanic by your side, offering insight into the transmission's inner workings.
Key Specs and Main Parts (Example: 4L60E Transmission)
While specifics vary depending on the exact year and model of your Ram 1500, a common automatic transmission found in many models is the 4L60E. Therefore, we'll use this as our example, but the principles apply broadly.
Key Specs (4L60E):
- Type: 4-speed automatic, electronically controlled.
- Gear Ratios:
- 1st: 3.06:1
- 2nd: 1.63:1
- 3rd: 1.00:1
- 4th: 0.70:1
- Reverse: 2.29:1
- Torque Capacity: Varies depending on application, but generally suitable for light-duty trucks.
Main Parts:
- Torque Converter: The fluid coupling that connects the engine to the transmission, allowing the engine to keep running even when the vehicle is stopped. It contains the impeller (connected to the engine), turbine (connected to the transmission), and stator.
- Oil Pump: Provides hydraulic pressure to operate the transmission's clutches, bands, and valve body.
- Valve Body: The hydraulic control center, containing a complex network of valves that direct fluid flow to engage different gears.
- Clutch Packs: Multi-disc clutches that engage and disengage to select different gear ratios. These are critical for smooth shifting.
- Bands: Friction bands that apply to drums to hold them stationary, creating different gear ratios.
- Planetary Gear Sets: A series of gears that work together to provide multiple gear ratios. Commonly include a sun gear, planet gears, and a ring gear.
- Transmission Control Module (TCM): The electronic brain of the transmission, receiving inputs from various sensors and controlling the shift solenoids.
- Shift Solenoids: Electrically operated valves that control the flow of hydraulic fluid to the clutches and bands, enabling gear changes.
Understanding Diagram Symbols
A transmission diagram is a schematic representation of the transmission's hydraulic and mechanical systems. Understanding the symbols is crucial for interpreting the diagram correctly. Here's a breakdown of common symbols:
- Lines:
- Solid Lines: Represent hydraulic lines carrying fluid under pressure. The thickness of the line may indicate the volume or pressure.
- Dashed Lines: Often represent electrical wiring or vacuum lines.
- Circles: Can represent various components, depending on the context. They may indicate pressure sensors, accumulators (which smooth out shifts), or other control elements.
- Squares/Rectangles: Usually represent valves, solenoids, or switches.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of fluid flow.
- Color Coding: Many diagrams use color to distinguish different pressure circuits (e.g., main line pressure, converter pressure, lubrication pressure). The color key is usually found on the diagram itself. For example, red might indicate high pressure, green might be lubrication, and blue might be converter flow.
- Labels: Each component and circuit is typically labeled with a descriptive name or code. For example, "MLP" might stand for "Main Line Pressure."
Carefully review the legend or key provided with your specific diagram. Without it, interpretation can be difficult and misleading.
How It Works (Simplified)
The diagram depicts the flow of hydraulic fluid through the valve body and to the various clutches and bands. The TCM receives information from sensors such as vehicle speed, throttle position, and engine load. Based on this information, the TCM activates specific shift solenoids. These solenoids, in turn, control valves within the valve body, directing hydraulic fluid to engage or disengage clutches and bands. By selectively engaging these clutches and bands, the transmission changes gear ratios, providing the appropriate torque and speed for different driving conditions.
The torque converter acts as a fluid coupling between the engine and the transmission. It allows the engine to idle without stalling the vehicle. At higher speeds, it can also provide torque multiplication, enhancing acceleration. The stator within the torque converter improves efficiency by redirecting fluid flow back to the impeller.
The planetary gear sets are the heart of the gear-changing mechanism. By holding different elements of the planetary gear set stationary, different gear ratios are achieved. The clutches and bands are the actuators that control which elements are held.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
A transmission diagram can be extremely useful in diagnosing common problems. Here are a few examples:
- No Shift: If the transmission refuses to shift, the diagram can help you trace the hydraulic circuit for the affected gear. Check for blocked passages, faulty solenoids, or stuck valves. Use a multimeter to test the solenoid's electrical continuity and voltage.
- Slipping: If the transmission slips in a particular gear, the diagram can help you identify the corresponding clutch pack or band. Inspect the clutch plates for wear or damage.
- Harsh Shifting: A harsh shift can be caused by a malfunctioning accumulator or a problem in the valve body. The diagram can help you locate the accumulator and identify the valves that control shift quality.
- Fluid Leaks: The diagram can help you trace the source of a fluid leak by showing the location of seals and gaskets within the transmission.
Important: Always use a scan tool to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) before attempting any repairs. DTCs can provide valuable clues about the source of the problem.
Safety Considerations
Working on an automatic transmission can be hazardous. Here are some key safety precautions:
- High Pressure: The hydraulic system operates at high pressure. Always relieve pressure before disconnecting any lines or components.
- Hot Fluid: Transmission fluid can be extremely hot. Allow the transmission to cool down completely before working on it.
- Heavy Components: The transmission and torque converter are heavy. Use proper lifting equipment to avoid injury.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from flying debris or fluid.
- Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling harmful fumes.
The torque converter, in particular, should be handled with care. It contains a significant amount of fluid and can be quite heavy. Dropping it can cause serious damage and injury. Be mindful of the high pressure present in the hydraulic system, especially after the vehicle has been running.
Accessing the Diagram
By now, you should have a foundational understanding of your Dodge Ram 1500's automatic transmission diagram and how it relates to troubleshooting and general knowledge. For the full diagram, please download it here: [Link to Diagram - Placeholder, Replace with actual link]. This detailed diagram will provide all the specifics you need for your particular transmission model.
