Distributor Wiring Diagram Chevy 350
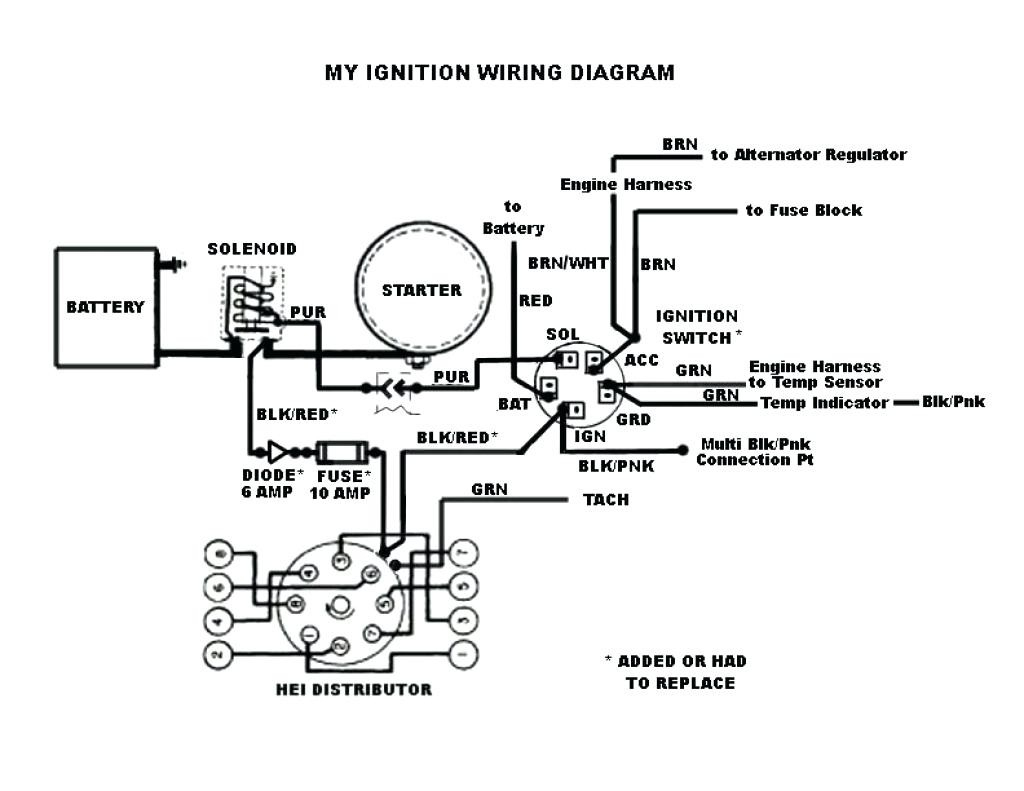
Understanding the distributor wiring diagram for a Chevy 350 engine is crucial for various reasons, ranging from simple repairs and maintenance to more complex modifications and performance upgrades. Whether you're replacing a faulty distributor, diagnosing ignition problems, or simply deepening your understanding of your engine's inner workings, this guide will provide the necessary knowledge to confidently tackle the wiring.
Why This Diagram Matters
Having access to and understanding the distributor wiring diagram is essential for several scenarios:
- Troubleshooting Ignition Problems: When your engine isn't starting or running properly, the distributor and its associated wiring are prime suspects. A wiring diagram allows you to systematically check connections, identify shorts or opens, and verify the integrity of the circuit.
- Distributor Replacement or Upgrade: Whether you're replacing a worn-out distributor with an identical unit or upgrading to a more performance-oriented model (such as an HEI distributor), understanding the wiring is critical for a successful installation.
- Engine Swaps and Modifications: If you're transplanting a Chevy 350 into a different vehicle or modifying the existing electrical system, you'll need to know how the distributor wiring integrates with the overall system.
- Learning Engine Fundamentals: Studying the wiring diagram offers valuable insights into the fundamental principles of ignition timing and the role of each component in the combustion process.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Before diving into the diagram, let's review the key components and specifications relevant to the Chevy 350 distributor wiring:
Main Parts:
- Distributor Body: Houses the internal components and provides a mounting point on the engine.
- Distributor Cap: Distributes the high-voltage spark to the correct spark plug at the correct time.
- Rotor: Spins inside the distributor cap, directing the high-voltage spark to the terminals.
- Pick-up Coil (or Magnetic Pick-up): Generates a signal that tells the ignition module when to fire the spark plugs. In older points-style distributors, this is replaced by the points and condenser.
- Ignition Module: Amplifies the signal from the pick-up coil and controls the flow of current to the ignition coil. (Often integrated into the distributor on HEI systems.)
- Vacuum Advance Unit: Advances the ignition timing based on engine vacuum, improving fuel economy and performance at part-throttle.
- Mechanical Advance: Advances the ignition timing based on engine speed (RPM). This is accomplished using weights and springs inside the distributor.
- Ignition Coil: Steps up the voltage from the battery to the high voltage needed to jump the spark plug gap.
- Wiring Harness: Connects the distributor to the rest of the vehicle's electrical system.
Key Specs:
- Voltage: The system operates primarily on 12V DC.
- Firing Order: The Chevy 350's firing order is typically 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2. This is critical for correctly connecting the spark plug wires to the distributor cap.
- Distributor Rotation: The distributor rotor rotates clockwise. This is important for understanding the relative positions of the spark plug terminals on the distributor cap.
Understanding the Symbols
Wiring diagrams use a standardized set of symbols to represent electrical components and connections. Here's a breakdown of the common symbols you'll encounter in a Chevy 350 distributor wiring diagram:
- Solid Lines: Represent wires. The thickness of the line doesn't necessarily indicate wire gauge (thickness).
- Dashed Lines: May represent shielding or grounding paths.
- Circles: Often used to represent connectors or terminals.
- Resistors: Represented by a zig-zag line. These limit current flow.
- Capacitors: Represented by two parallel lines. These store electrical energy.
- Ground Symbol: Looks like an upside-down tree. Indicates a connection to the vehicle's chassis ground.
- Battery Symbol: Represents the battery. It typically shows a long and a short line parallel to each other, with + and - signs.
- Connectors: Are shown as circles, squares, or other geometric shapes with wires leading into them. Sometimes a number is listed next to the connector which represents the pin number.
Colors:
Wire colors are standardized to make identification easier. Common colors include:
- Red: Typically indicates a power wire (12V+).
- Black: Typically indicates a ground wire.
- Brown: Often used for distributor signals.
- White: May be used for various signals or ground connections.
- Other Colors: Blue, green, yellow, etc., are used for various other circuits. The diagram will always specify the function of each color-coded wire.
How It Works
The Chevy 350 distributor is a critical component of the ignition system. Here's a simplified explanation of how it works:
- Power Supply: The ignition system receives power from the battery, typically through the ignition switch.
- Ignition Coil Charging: The ignition coil is energized. The primary winding of the coil builds up a magnetic field.
- Signal Generation: As the engine turns, the distributor shaft rotates. The pick-up coil (or points) inside the distributor generates a signal.
- Switching: This signal tells the ignition module when to trigger. The ignition module interrupts the current flow to the primary winding of the ignition coil.
- Voltage Step-Up: When the current to the primary coil is interrupted, the magnetic field collapses and a very high voltage is induced in the secondary winding of the coil (often 20,000 - 40,000 volts).
- Distribution: The high-voltage spark is sent to the distributor cap. The rotor, which is synchronized with the engine's timing, directs the spark to the correct spark plug.
- Combustion: The spark jumps the gap at the spark plug, igniting the air-fuel mixture in the cylinder.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
A distributor wiring diagram can be invaluable when troubleshooting ignition problems. Here are some basic troubleshooting tips:
- No Spark: If you're not getting any spark at the spark plugs, start by checking the basics: are all the wires connected? Is the ignition coil receiving power? Use a multimeter to check for voltage at the appropriate terminals.
- Intermittent Spark: Intermittent spark can be caused by loose connections, corroded terminals, or a failing pick-up coil. Carefully inspect the wiring harness and connectors for any signs of damage.
- Poor Performance: If the engine is running poorly (misfiring, lack of power), check the spark plug wires to make sure they are connected to the correct terminals on the distributor cap (following the firing order). Also verify the ignition timing.
- Using a Multimeter: A multimeter is your best friend for diagnosing electrical problems. Learn how to use it to check for voltage, continuity (a complete circuit), and resistance.
Safety Considerations
Working on the ignition system can be dangerous. Here are some important safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on the ignition system. This will prevent accidental shocks and damage to electronic components.
- High Voltage: The ignition system generates extremely high voltage. Avoid touching any of the components while the engine is running or the ignition is turned on.
- Fuel Vapors: Be careful around fuel vapors. Work in a well-ventilated area and avoid sparks or open flames.
- Capacitors Capacitors store electrical energy even after the power has been disconnected. Be careful when handling capacitors, and discharge them properly before working on them.
The ignition coil in particular can deliver a dangerous shock, so always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on this area of the vehicle.
We have a detailed Chevy 350 Distributor Wiring Diagram available for download. This diagram will provide a visual representation of the wiring layout, making it easier to understand the connections and troubleshoot problems.
