Dodge Charger Trunk Fuse Box Diagram
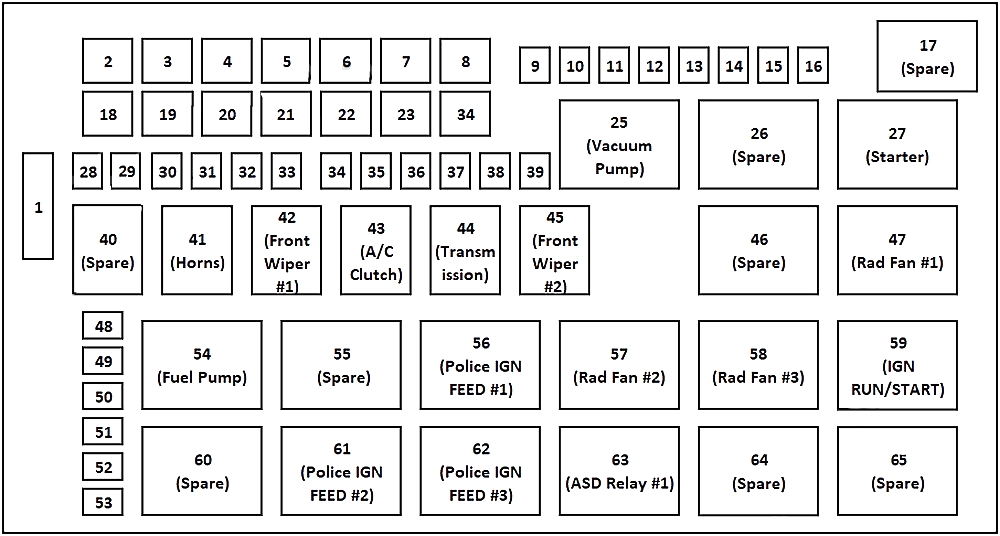
The Dodge Charger is a modern muscle car, and like any complex vehicle, it relies heavily on a well-organized electrical system. A critical component of this system is the trunk fuse box. Understanding its layout and function is invaluable for troubleshooting electrical issues, performing modifications, and generally maintaining your Charger. This article provides a detailed breakdown of the Dodge Charger trunk fuse box diagram, aimed at the intermediate car owner or DIY mechanic.
Purpose of the Trunk Fuse Box Diagram
The trunk fuse box diagram is your roadmap to the electrical circuits in the rear of your Dodge Charger. It's more than just a picture; it's a key that unlocks the mysteries behind electrical malfunctions. Knowing how to interpret this diagram allows you to:
- Diagnose Electrical Problems: Identify which fuse protects a specific circuit (e.g., rear lights, power trunk, amplifier).
- Perform Repairs: Locate and replace blown fuses or troubleshoot wiring issues with confidence.
- Install Aftermarket Accessories: Tap into existing circuits safely by knowing their amperage rating and function.
- Understand Vehicle Systems: Gain a deeper understanding of how the Charger's electrical components interact.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The trunk fuse box, also known as the Rear Power Distribution Center (RPDC), houses numerous fuses and relays, each protecting a specific circuit. Here's a breakdown of the key components:
- Fuses: These are sacrificial devices designed to protect circuits from overcurrent. They contain a thin wire that melts and breaks the circuit if the current exceeds its rated amperage.
- Relays: Electrically operated switches that control high-current circuits with a low-current signal. They're used for components like the fuel pump, starter motor, and various lighting systems.
- Wiring Harness: A bundle of wires that carries electrical signals and power throughout the vehicle. The diagram illustrates how these wires connect to the fuse box.
- Connectors: Plugs that provide a secure and reliable connection between the wiring harness and the fuse box.
Important Note: The specific layout and fuse/relay assignments can vary depending on the Dodge Charger model year, trim level, and optional equipment. Always consult the diagram specific to your vehicle.
Symbols: Understanding Lines, Colors, and Icons
The trunk fuse box diagram uses a standardized set of symbols to represent electrical components and connections. Deciphering these symbols is crucial for accurate interpretation.
- Lines: Solid lines typically represent wires, while dashed lines might indicate ground connections or signal paths. The thickness of the line can sometimes indicate the wire gauge (thicker lines for higher current).
- Colors: Each wire is assigned a color code (e.g., RED, BLU, GRN, YEL). These codes help you identify specific wires within the harness. The color code is usually printed directly on the wire insulation.
- Fuses: Fuses are usually depicted as a rectangle with a wavy line running through it. The amperage rating is typically printed next to the symbol.
- Relays: Relays are represented by a square or rectangle with internal symbols showing the coil and switch contacts. The diagram often includes a description of the relay's function (e.g., "Fuel Pump Relay").
- Grounds: Ground connections are often represented by a symbol resembling a tree or an upside-down triangle.
Example: A red line (RED) connecting a fuse symbol labeled "15A" to a relay symbol labeled "Fuel Pump Relay" indicates that a 15-amp fuse protects the circuit that powers the fuel pump relay.
How It Works: Circuit Protection and Control
The trunk fuse box acts as a central hub for distributing power and protecting electrical circuits in the rear of the vehicle. Here's how it works in principle:
- Power Input: The fuse box receives power directly from the battery, usually through a large-gauge cable.
- Fuse Protection: The incoming power is distributed to various circuits, each protected by a fuse. If a fault occurs in a circuit (e.g., a short circuit), the fuse blows, interrupting the current flow and preventing damage to components. The amperage rating of the fuse determines the maximum current it can handle before blowing. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating than specified can be dangerous, as it may not protect the circuit adequately.
- Relay Control: Relays are used to control high-current devices. A low-current signal from the engine control module (ECM) or another switch activates the relay, which then closes the circuit and allows power to flow to the device (e.g., fuel pump, lights).
- Grounding: All electrical circuits require a return path to the battery, known as the ground. The fuse box provides ground connections for various components.
Think of the fuse box as a miniature electrical distribution panel, similar to the one in your home. Each fuse represents a circuit breaker, and the relays act as remote-controlled switches.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting tips using the trunk fuse box diagram:
- Blown Fuse: If a component isn't working, the first step is to check its corresponding fuse in the trunk fuse box. Use the diagram to locate the correct fuse. A blown fuse will have a broken filament. Replace it with a fuse of the same amperage rating. If the new fuse blows immediately, there's likely a short circuit in the wiring or the component itself.
- Relay Problems: If a component isn't working and its fuse is good, the relay might be faulty. You can try swapping the relay with a known-good relay of the same type (if available) to see if that resolves the issue. Relays can also be tested with a multimeter.
- Wiring Issues: If you suspect a wiring problem, use the diagram to trace the wiring from the fuse box to the component. Look for damaged wires, loose connections, or corrosion. A multimeter can be used to check for continuity (a complete circuit) and voltage.
Example: The rear tail lights are not working. Consult the diagram, find the "Tail Light" fuse (usually a 10A or 15A fuse), and check its condition. If the fuse is blown, replace it. If the problem persists, inspect the wiring harness and connections to the tail lights, using the diagram as a guide.
Safety: Highlight Risky Components
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some important safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on the electrical system. This prevents accidental shorts and electrical shocks.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools designed for automotive electrical work.
- Avoid Water: Never work on the electrical system in wet conditions.
- High-Current Circuits: Be extremely careful when working with high-current circuits, such as the starter motor and alternator circuits. These circuits can deliver a powerful electrical shock.
- Do Not Bypass Fuses: Never bypass a fuse with a wire or any other conductive material. This eliminates the circuit protection and can lead to a fire or serious damage to the vehicle.
- Airbags: Be aware that some circuits in the trunk area may be related to the Supplemental Restraint System (SRS), including airbags. Disconnecting or tampering with these circuits can cause the airbags to deploy unexpectedly, resulting in serious injury. If you suspect an issue related to the SRS, consult a qualified technician.
Warning: The fuel pump relay and wiring related to the fuel system can be particularly hazardous. Always exercise extreme caution when working on these components, as fuel leaks can cause fires and explosions. If you smell gasoline, stop working immediately and ventilate the area.
Understanding the Dodge Charger trunk fuse box diagram is a valuable skill for any car owner or DIY mechanic. It empowers you to diagnose and repair electrical problems, install aftermarket accessories, and gain a deeper understanding of your vehicle's electrical system. Remember to always consult the specific diagram for your vehicle and follow proper safety precautions.
We have a high-resolution, downloadable version of the Dodge Charger Trunk Fuse Box Diagram available for you. This diagram details specific fuse locations, amperage ratings, and circuit information tailored to various Charger model years. Contact us for access to this valuable resource and take your understanding of your car's electrical system to the next level.
