Drive Belt Diagram For Exmark Lazer Z
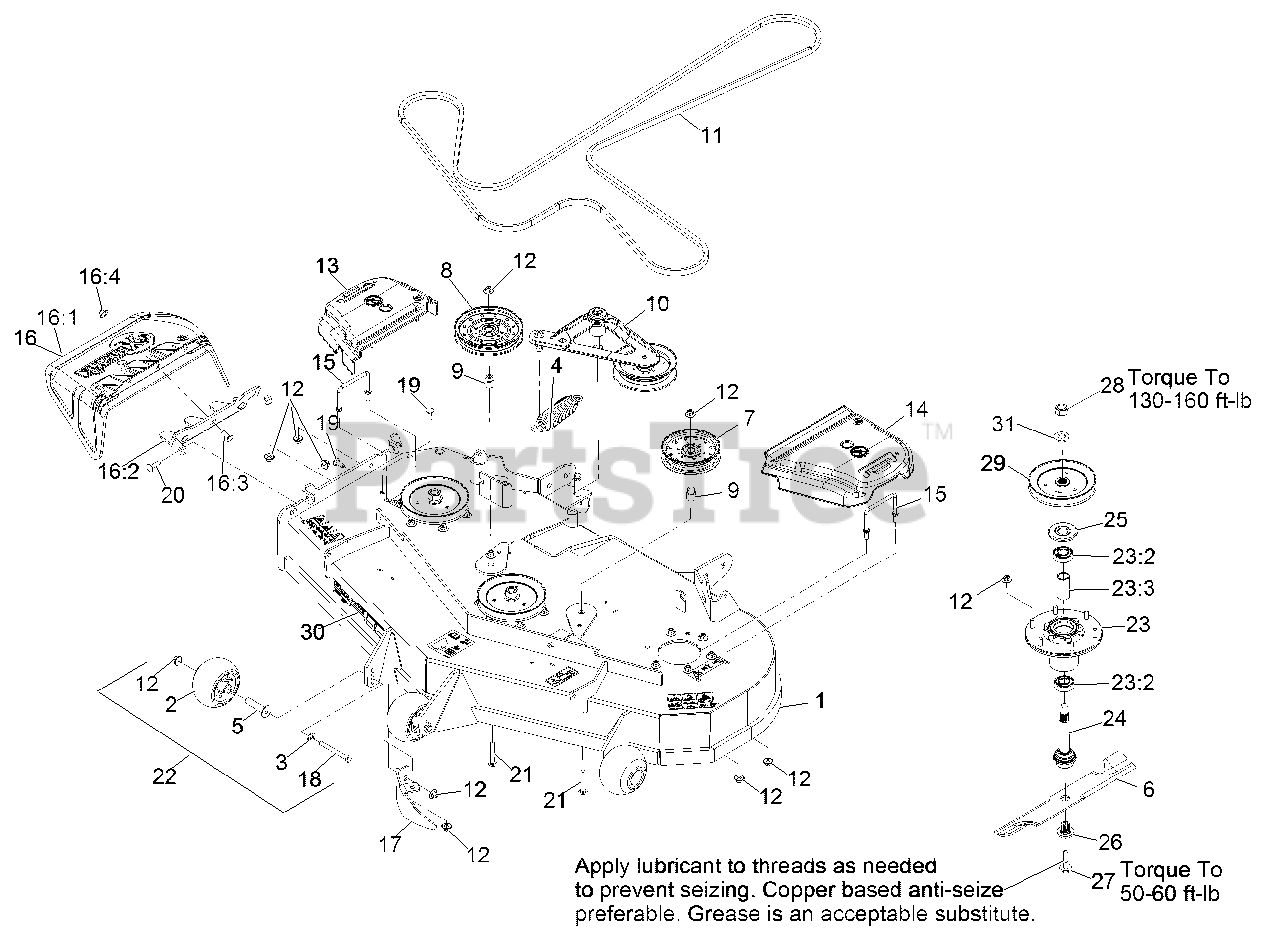
The drive belt diagram for your Exmark Lazer Z isn't just a piece of paper; it's the roadmap to understanding and maintaining the heart of your mower's power transmission system. Whether you're tackling a snapped belt, diagnosing a sluggish drive, or simply performing preventative maintenance, having a clear understanding of this diagram is crucial. This guide will walk you through the intricacies of the Exmark Lazer Z drive belt diagram, empowering you to confidently diagnose and address belt-related issues.
Why This Diagram Matters
Think of the drive belt diagram as the circulatory system chart for your Exmark Lazer Z. It illustrates how power is transferred from the engine to the various components responsible for propelling the mower. Without it, you're essentially working blind. The diagram helps with:
- Repairs: Identifying the correct routing for a new belt after a failure is paramount. An improperly routed belt can lead to premature wear, reduced performance, and even damage to other components.
- Maintenance: Inspecting the belt's condition and tension is a regular part of mower maintenance. The diagram helps you locate the belt, tensioning idlers, and other relevant components.
- Troubleshooting: When you experience a loss of power, unusual noises, or uneven cutting, the diagram can guide you through diagnosing potential belt-related causes.
- Part Identification: The diagram often includes part numbers for belts, pulleys, idlers, and other associated components, making ordering replacements a breeze.
- Learning: Understanding the diagram allows you to grasp the overall power transmission system of your mower, leading to a better understanding of its operation and potential issues.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The specific specs will vary slightly depending on the exact model year and deck size of your Exmark Lazer Z, but some common key components and characteristics are generally consistent. The drive belt is typically a heavy-duty V-belt, designed to withstand significant tension and heat. It's crucial to use the correct belt specified for your model; using a belt that is too short or too long will negatively affect performance and longevity.
Here's a breakdown of the main components you'll typically find in the diagram:
- Engine Pulley: The starting point of the power transmission. The engine's rotation drives this pulley.
- Pump Drive Belt: Transfers the rotational energy from the engine pulley to the hydraulic pump, enabling the motion of the mower.
- Hydraulic Pump(s): These pumps are the heart of the hydrostatic drive system, providing fluid power to the wheel motors. Usually two pumps, one for each wheel.
- Idler Pulleys (Tensioning and Guide): These pulleys maintain proper belt tension and guide the belt along its intended path. Tensioning idlers are often spring-loaded or adjustable to accommodate belt wear and stretching. Incorrect tension is a major cause of premature belt failure.
- Wheel Motors: Hydraulic motors that use hydraulic pressure to turn the wheels to provide the drive of the mower.
- Belt Guides/Keepers: These small metal pieces prevent the belt from jumping off the pulleys, especially during sudden changes in speed or direction.
- Hydrostatic Transmission: The entire system that uses hydraulic fluid to transfer power from the engine to the wheels.
- PTO Clutch: Connects and disconnects the engine to the drive belt.
Understanding the Symbols
Like any technical diagram, the Exmark Lazer Z drive belt diagram uses specific symbols and conventions to convey information efficiently. Understanding these symbols is critical to correctly interpreting the diagram.
- Solid Lines: Typically represent the drive belt itself. A thicker solid line may indicate the primary drive belt, while thinner lines could represent secondary belts or connecting linkages.
- Dashed Lines: Often indicate the centerline of a pulley or the path of motion of a component.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of belt rotation. Pay close attention to these, as incorrect routing can reverse the direction of rotation for certain components.
- Circles: Represent pulleys. The diameter of the circle may or may not be proportional to the actual pulley size.
- Spring Symbols: Indicate spring-loaded tensioning idlers. These maintain constant tension on the belt.
- Part Numbers: Usually located adjacent to each component, allowing for easy identification and ordering.
- Torque Specifications: May be included near mounting bolts for critical components like pulleys and idlers. Always adhere to these torque specs to prevent loosening or damage.
Colors can also be used, though this is less common in older diagrams. If colors are present, they may be used to differentiate between different belt systems or to highlight specific components.
How It Works
The drive belt system on the Exmark Lazer Z is a relatively straightforward power transmission mechanism. The engine's rotational energy is transferred to the main drive belt via the engine pulley. This belt then snakes its way through a series of pulleys, including tensioning idlers, and ultimately connects to the hydraulic pump. The hydraulic pump(s) then convert the mechanical energy into hydraulic pressure, which is then used to power hydraulic wheel motors. These motors then turn the wheels, propelling the mower.
The tensioning idlers play a crucial role in maintaining proper belt tension. Proper tension is essential for efficient power transfer and preventing slippage. If the belt is too loose, it will slip, resulting in reduced power and increased wear. If it's too tight, it can overload the bearings in the pulleys and the hydraulic pump, leading to premature failure.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are a few common problems and how the drive belt diagram can help you diagnose them:
- Slipping Belt: A squealing noise, especially when engaging the blades or climbing hills, often indicates a slipping belt. Check the diagram to ensure the belt is correctly routed and that the tensioning idler is functioning properly.
- Belt Coming Off: If the belt repeatedly comes off the pulleys, check for worn pulleys, damaged belt guides, or a misaligned tensioning idler. The diagram will help you identify the correct placement of the belt guides.
- Loss of Power: A sudden loss of power could be due to a broken belt, but it could also be caused by a slipping belt or a malfunctioning tensioning idler. Use the diagram to visually inspect the belt and idler for damage.
- Uneven Cutting: Uneven cutting can sometimes be attributed to unequal belt tension. The diagram can help you compare the belt routing and tensioning mechanisms on both sides of the mower.
When troubleshooting, always start by visually inspecting the belt for cracks, fraying, or other signs of wear. Also, check the pulleys for damage and ensure they are properly aligned. Remember to consult your Exmark Lazer Z service manual for specific troubleshooting procedures and recommended maintenance intervals.
Safety Considerations
Working on the drive belt system can be hazardous if proper precautions are not taken. Always disengage the blades, turn off the engine, and remove the key before working on the mower.
- Hot Components: Be aware that the engine and exhaust system can remain hot for some time after the engine is shut off. Allow these components to cool before working near them.
- Moving Parts: Keep your hands and clothing away from moving parts, such as pulleys and belts, when the engine is running.
- Tensioning Springs: Tensioning idlers are often spring-loaded and can snap back with considerable force if not handled carefully. Use appropriate tools to relieve tension on the spring before removing the belt.
- Hydraulic Fluid: Hydraulic fluid is under high pressure and can cause serious injury if it comes into contact with your skin. If you suspect a leak, do not attempt to stop it with your bare hands. Seek professional assistance.
Remember that safety is paramount. If you are not comfortable performing a particular repair, it is best to consult a qualified mechanic.
We have access to a comprehensive collection of Exmark Lazer Z drive belt diagrams. To get the specific diagram for your model and year, please contact us with your mower's model number. We can then provide you with a downloadable PDF file.
Disclaimer: This information is for general guidance only. Always refer to your Exmark Lazer Z service manual for specific instructions and safety precautions. We are not responsible for any injury or damage resulting from the use of this information.
